Abstract
Purpose
To develop a reliable preimplantation genetic diagnosis protocol for couples who both carry a mutant PKHD1 gene wishing to conceive children unaffected with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD).
Methods
Development of a unique protocol for preimplantation genetic testing using whole genome amplification of single blastomeres by multiple displacement amplification (MDA), and haplotype analysis with novel short tandem repeat (STR) markers from the PKHD1 gene and flanking sequences, and a case report of successful utilization of the protocol followed by successful IVF resulting in the birth of an infant unaffected with ARPKD.
Results
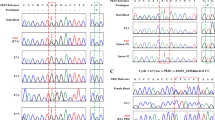
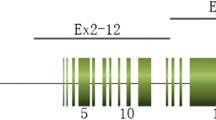
We have developed 20 polymorphic STR markers suitable for linkage analysis of ARPKD. These linked STR markers have enabled unambiguous identification of the PKHD1 haplotypes of embryos produced by at-risk couples.
Conclusions
We have developed a reliable protocol for preimplantation genetic diagnosis of ARPKD using single-cell MDA products for PKHD1 haplotyping.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harris PC, Torres VE. Polycystic kidney disease. Annu Rev Med. 2009;60:321–37.
Dell KM, Sweeney WE, Avner ED. Polycystic kidney disease. In: Avner ED, Harmon WE, Niaudet P, Yoshikawa N, editors. Pediatric nephrology. 6th ed. Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag; 2009. p. 849–88.
Sweeney WE, Avner ED. Molecular and cellular pathophysiology of Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Cell Tissue Res. 2006;326:671–85.
Dell KM, Avner ED (July 2008) Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. In: GeneClinics: Online Clinical Genetic Information Resource; www.geneclinics.org
Sweeney WE, Avner ED. Renal cystic disease: new insights for the clinician. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2006;53:889–909.
European Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium. The polycystic kidney disease 1 gene encodes a 14kb transcript and lies within a duplicated region on chromosome 16. Cell. 1994;77:881–94.
Mochizuki T, Wu G, Hayashi T, Xenophontos SL, Veldhuisen B, Saris JJ, et al. PKD2, a gene for polycystic kidney disease that encodes an integral membrane protein. Science. 1996;272:1339–42.
Hughes J, Ward CJ, Peral B, Aspinwall R, Clark K, San Millán JL, et al. The polycystic kidney disease (PKD1) gene encodes a novel protein with multiple cell recognition domains. Nat Genet. 1995;10:151–60.
Ward CJ, Hogan MC, Rossetti S, Walker D, Sneddon T, Wang X, et al. The gene mutated in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease encodes a large, receptor-like protein. Nat Genet. 2002;30:259–69.
Onuchic LF, Furu L, Nagasawa Y, Hou X, Eggermann T, Ren Z, et al. PKHD1, the polycystic kidney and hepatic disease 1 gene, encodes a novel large protein containing multiple immunoglobulin-like plexin-transcription-factor domains and parallel ß-helix 1 repeats. Am J Hum Genet. 2002;70:1305–17.
Bick DP, Lau EC. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2006;53(4):559–77.
Swanson A, Strawn E, Lau E, Bick D. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis: technology and clinical applications. WMJ. 2007;106(3):145–51.
Spits C, Sermon K. PGD for monogenic disorders: aspects of molecular biology. Prenat Diagn. 2008;29(1):50–6.
Fallon L, Harton GL, Sisson ME, Rodriguez E, Field LK, Fugger EF, et al. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis for spinal muscular atrophy type I. Neurology. 1999;53(5):1087–90.
Xu K, Shi ZM, Veeck LL, Hughes MR, Rosenwaks Z. First unaffected pregnancy using preimplantation genetic diagnosis for sickle cell anemia. JAMA. 1999;281:1701–6.
Consugar MB, Anderson SA, Rossetti S, Pankratz S, Ward CJ, Torra R, et al. Haplotype analysis improves molecular diagnostics of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005;45(1):77–87.
Bick SL, Bick BP, Wells BE, Roesler MR, Strawn EY, Lau EC. Preimplantation HLA haplotyping using tri-, tetra-, and pentanucleotide short tandem repeats for HLA matching. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2008;25:323–31.
Verlinsky Y, Rechitsky S, Verlinsky O, Chistokhina A, Sharapova T, Masciangelo C, et al. Preimplantation diagnosis for neurofibromatosis. Reprod Biomed Online. 2002;4(3):218–22.
Michaelides K, Tuddenham EGD, Turner C, Lavender B, Lavery SA. Live birth following the first mutation specific pre-implantation genetic diagnosis for haemophilia A. Thromb Haemost. 2006;95:373–9.
Sanchez-Garcia JF, Fallardo D, Ramirez L, Vidal F. Multiple fluorescent analysis of four short tandem repeats for rapid haemophilia A molecular diagnosis. Thromb Haemost. 2005;94(5):1099–103.
Spits C, De Rycke M, Verpoest W, Lissens W, Van Steirteghem A, Liebaers I, et al. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis for Marfan syndrome. Fertil Steril. 2006;86(2):310–20.
Christofidou C, Sofocleous C, Vrettou C, Destouni A, Traeger-Synodinos J, Kekou K, et al. PGD for X-linked and gender-dependent disorders using a robust, flexible single-tube PCR protocol. Reprod Biomed Online. 2009;19(3):418–25.
Spits C, De Rycke M, Van Ranst N, Joris H, Verpoest W, Lissens W, et al. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis for neurofibromatosis type 1. Mol Hum Reprod. 2005;11(5):381–7.
Malcov M, Ben-Yosef D, Schwartz T, Mey-Raz N, Azem F, Lessing JB, et al. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) by triplex-nested PCR. Prenat Diagn. 2005;25:1200–5.
Gigarel N, Frydman N, Burlet P, Kerbrat V, Tachdjian G, Fanchin R, et al. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis for autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Reprod Biomed Online. 2008;16(1):152–8.
Handyside AH, Robinson MD, Simpson RJ, Omar MB, Shaw M-A, Grudzinskas JG, et al. Isothermal whole genome amplification from single and small numbers of cells: a new era for preimplantation genetic diagnosis of inherited disease. Mol Hum Reprod. 2004;10(10):676–72.
Hellani A, Coskun S, Benkhalifa M, Thakhi A, Sakati N, Al-Odaib A, et al. Multiple displacement amplification on single cell and possible PGD applications. Mol Hum Reprod. 2004;10(11):847–52.
Spits C, Le Caignec C, De Rycke M, Van Haute L, Van Steirteghem A, Liebaers I, et al. Optimization and evaluation of single-cell whole-genome multiple displacement amplification. Hum Mutat. 2006;27(5):496–503.
Spits C, Le Caignec C, De Rycke M, Van Haute L, Van Steirteghem A, Liebaers I, et al. Whole-genome multiple displacement amplification from single cells. Nat Protoc. 2006;1(4):1965–70.
Renwick PJ, Lewis CM, Abbs S, Ogilvie CM. Determination of the genetic status of cleavage-stage human embryos by microsatellite marker analysis following multiple displacement amplification. Prenat Diagn. 2007;27:206–15.
Ren Z, Zhou C, Xu Y, Deng J, Zeng H, Zeng Y. Mutation and haplotype analysis for Duchenne muscular dystrophy by single cell multiple displacement amplification. Mol Hum Reprod. 2007;13(6):431–6.
Ren Z, Zeng H-T, Xu Y-W, Zhuang G-L, Deng J, Zhang C, et al. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis for Duchenne muscular dystrophy by multiple displacement amplification. Fertil Steril. 2009;91(2):359–64.
Glentis S, SenGupta S, Thornhill A, Wang R, Craft I, Harper JC. Molecular comparison of single cell MDA products derived from different cell types. Reprod BioMed Online. 2009;19:89–98.
Qubbaj W, Al-Aqeel AI, Al-Hassnan Z, Al-Duraihim A, Awartani K, Al-Rejjal R, et al. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis of Morquio disease. Prenat Diagn. 2008;28(10):900–3.
Burlet P, Frydman N, Gigarel N, Kerbrat V, Tachdjian G, Feyereisen E, et al. Multiple displacement amplification improves PGD for fragile X syndrome. Mol Hum Reprod. 2006;12(10):647–52.
Obradors A, Fernández E, Rius M, Oliver-Bonet M, Martínez-Fresno M, Benet J et al (2009) Outcome of twin babies free of Von Hippel-Lindau disease after a double-factor preimplantation genetic diagnosis: monogenetic mutation analysis and comprehensive aneuploidy screening. Fertil Steril 91(3):933.e1–7. [Epub 2009 Jan 10]
Dean FB, Hosono S, Fang L, Wu X, Faruqi AF, Bray-Ward P, et al. Comprehensive human genome amplification using multiple displacement amplification. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:5261–6.
Hellani A, Sammour A, Johansson L, El-Sheikh A. Delivery of a normal baby after preimplantation genetic diagnosis for non-ketotic hyperglycinaemia. Reprod BioMed Online. 2008;16(6):893–7.
Lledo B, Ten J, Rodriguez-Arnedo D, Llacer J, Bernabeu R. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis of X-linked retinoschisis. Reprod BioMed Online. 2008;16(6):886–92.
Hellani A, Abu-Amero K, Azouri J, Al-Sharif H, Barblet H, El-Akoum S. Pregnancy after preimplantation genetic diagnosis for brachydactyly type B. Reprod Biomed Online. 2009;18(1):127–31.
Benson G. Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999;27(2):573–80.
Brownstein MJ, Carpten JD, Smith JR. Modulation of non-templated nucleotide addition by Taq DNA polymerase: primer modifications that facilitate genotyping. BioTechniques. 1996;20:1004–10.
Altarescu G, Geva TE, Brooks B, Margalioth E, Levy-Lahad E, Renbaum P. PGD on a recombinant allele: crossover between the TSC2 gene and ‘linked’ markers impairs accurate diagnosis. Prenat Diagn. 2008;28(10):929–33.
Li Y, Kim H-J, Zheng C, Chow WHA, Lim J, Keenan B, et al. Primase-based whole genome amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36(13):e79. Epub 2008 Jun 17.
Hellani A, Abu-Amero K, Azouri J, El-Akoum S. Successful pregnancies after application of array-comparative genomic hybridization in PGS-aneuploidy screening. Reprod BioMed Online. 2008;17(6):841–7.
Handyside AH, Harton GL, Mariani B, Thornhill AR, Affara N, Shaw M-A et al (2009 Oct. 25) Karyomapping: a universal method for genome wide analysis of genetic disease based on mapping crossovers between parental haplotypes. J Med Genet. [Epub ahead of print]
Kumar G, Garnova E, Reagin M, Vidali A. Improved multiple displacement amplification with phi29 DNA polymerase for genotyping of single human cells. BioTechniques. 2008;44(7):879–90.
Chow JF, Yeung WS, Lau EY, Lam ST, Tong T, Ng EH, Ho PC (2009) Singleton birth after preimplantation genetic diagnosis for Huntington disease using whole genome amplification. Fertil Steril 92(2):828.e7–10. [Epub 2009 Jun 9].
Acknowledgments
The excellent support of our colleagues Barbara Szlendakova, Amy Granlund, Dr. Peter vanTuinen, Brent Wells, Sarah Bick and Bridget Lawler are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Capsule Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis of Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease using Multiple Displacement Amplification and Haplotype Analysis of PKHD1 Gene with Linked Short Tandem Repeat Markers
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lau, E.C., Janson, M.M., Roesler, M.R. et al. Birth of a healthy infant following preimplantation PKHD1 haplotyping for autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease using multiple displacement amplification. J Assist Reprod Genet 27, 397–407 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-010-9432-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-010-9432-5