Abstract
Background
Human leukocyte antigen G (HLA-G) is thought to play a key role in implantation by modulating cytokine secretion to control trophopblastic cell invasion and to maintain a local immunotolerance.
Method of study
The literature is reviewed to provide a description of the genetic background, properties of the protein, and the function of HLA-G. Data are presented on potential clinical applications of HLA-G including the use of evaluation of HLA-G gene polymorphisms in the diagnosis of patients experiencing recurrent pregnancy loss and evaluation and testing of soluble HLA-G (sHLA-G) in embryo culture media for the selection of embryos for transfer after in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Results
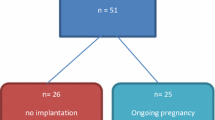
The literature supports a central role of HLA-G for successful implantation. Of couples experiencing recurrent pregnancy loss, 32% demonstrated the -1725G HLA-G polymorphism. Our data showed that when embryos were selected for transfer after IVF based on culture media concentrations of sHLA-G ≥ 2 U/ml and good morphologic grade, a 65% pregnancy rate compared with a 0% pregnancy rate in those with <2 U/ml sHLA-G.
Conclusions
HLA-G is important for successful implantation in human beings. The HLA-G -725 promoter polymorphism is a risk factor for recurrent miscarriage. Measurement of sHLA-G in embryo culture media can help select embryos for transfer after IVF allowing fewer embryos to be transferred in an attempt to lower multiple gestation rates.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hunt JS. HLA and maternal–fetal relationship. Austin: RG Landes Co.; 1996.
Puppo F, Ghio M, Contini P, Brenci S, Bignardi D, Filaci G, et al. Immunoregulatory role of soluble HLA molecules: a new skin for an old subject? Arch Immunol Ther Exp 1998;46:157–60.
Chu W, Fant ME, Geraghty DE, Hunt JS. Soluble HLA-G in human placentas: synthesis in trophoblasts and in interferon-gamma-activated macrophages but not placental fibroblasts. Hum Immunol 1998;59:435–42.
Ellis SA, Sargent IL, Redman CW, McMichael AJ. Evidence for a novel HLA antigen found on human extravillous trophoblast and a choriocarcinoma cell line. Immunology 1986;59:595–601.
Ishitani A, Geraghty DE. Alternative splicing of HLA-G transcripts yields proteins with primary structures resembling both class I and class II antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992;89:3947–51.
Kirszenbaum M, Moreau P, Gluckman E, Dausset J, Carosella E. An alternatively spliced form of HLA-G mRNA in human trophoblasts and evidence for the presence of HLA-G transcript in adult lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994;91:4209–13.
Fujii T, Ishitani A, Geraghty DE. A soluble form of the HLA-G antigen is encoded by a messenger ribonucleic acid containing intron 4. J Immunol 1994;153:5516–24.
Paul P, Cabestre FA, Ibrahim EC, Lefebvre S, Khalil-Daher I, Vazeux G, et al. Identification of HLA-G7 as a new splice variant of the HLA-G mRNA and expression of soluble HLA-G5, -G6, and -G7 transcripts in human transfected cells. Hum Immunol 2000;61:1138–49.
Loke YW, King A. Human implantation: cell biology and immunlogy. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1995.
Hunt SJ, Petroff MG, McIntyre RH, Ober C. HLA-G and immune tolerance in pregnancy. FASEB J 2005;5:681–93.
Blaschitz A, Lenfant F, Mallet V, Hartmann M, Bansusan A, Geraghty DE, et al. Endothelial cells in chorionic fetal vessels of first trimester placenta express HLA-G. Eur J Immunol 1997;27:3380–8.
McMaster M, Zhou Y, Shorter S, Kapasi K, Geraghty D, Lim K, et al. HLA-G isoforms produced by placental cytotrophoblast and found in amniotic fluid are due to unusual glycosylation. J Immunol 1998;160:5922–8.
Crisa L, McMaster M, Ishii JK, Fisher S, Salomon DR. Identification of a thymic epithelial cell subset sharing expression of the class Ib HLA-G molecule with fetal trophoblasts. J Exp Med 1997;186:289–98.
Yang Y, Chu W, Geraghty DE, Hunt S. Expression of HLA-G in human mononuclear phagocytes and selective induction by IFN-gamma. J Immunol 1996;156:4224–31.
Parham P, Lomen CE, Lawlor DA, Ways JP, Holmes N, Coppin HL, et al. Nature of polymorphism in HLA-A, -B, and -C molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1988;85:4005–9.
Shimizu Y, Geraghty DE, Koller BH, Orr HT, DeMars R. Transfer and expression of three cloned human non-HLA-A,B,C class I major histocompatibility complex genes in mutant lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1988;85:227–31.
Dobbe LM, Stam NJ, Neefjes JJ, Giphart MJ. Biochemical complexity of serum HLA class I molecules. Immunogenetics 1988;27:203–10.
Van Rood JJ, Van Leeuwan A, Van Santen MCT. Anti-HLA-A2 inhibitor in normal human sera. Nature 1970;226:336–67.
Haga JA, She JX, Kao KJ. Biochemical characterization of 39 kDa class I histocompatibility antigen plasma. A secretable membrane protein derived from transmembrane domain deletion. J Biol Chem 1991;266:3695–701.
LeMaoult J, Zafaranloo K, Le Danff C, Carosella ED. HLA-G up-regulates ILT2, ILT3, ILT4, and KIR2DL4 in antigen-presenting cells, NK cells, and T cells. FASEB J 2005;19:662–4.
Fournel S, Aguerre-Girr M, Huc X, Lenfant F, Alam A, Toubert A, et al. Cutting edge: soluble HLA-G1 triggers CD95/CD95 ligand-mediated apoptosis in activated CD8+ cells by interacting with CD8. J Immunol 2000;164:6100–4.
Morales PJ, Pace JL, Platt JS, Phillips TA, Morgan K, Fazleabas AT, et al. Placental cell expression of HLA-G2 isoforms is limited to the invasive trophoblast phenotype. J Immunol 2003;171:6215–24.
Rajagopalan S, Long EO. A human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen (HLA)-G-specific receptor expressed on all natural killer cells. J Exp Med 1999;189:1093–100.
van der Meer A, Lukassen HG, van Cranenbroek B, Weiss EH, Braat DD, van Lierop MJ, et al. Soluble HLA-G promotes Th1-type cytokine production by cytokine-activated uterine and peripheral natural killer cells. Mol Hum Reprod 2007;13:123–33.
McIntire RH, Morales PJ, Petroff MG, Colonna M, Hunt JS. Recombinant HLA-G5 and -G6 drive U937 myelomonocytic cell production of TGF-beta-1. J Leukoc Biol 2004;76:1220–8.
Kanai T, Fujii T, Kozuma S, Yamashita T, Miki A, Kikuchi A, et al. Soluble HLA-G influences the release of cytokines from allogeneic peripheral blood mononuclear cells in culture. Mol Hum Reprod 2001;7:195–200.
Kapasi K, Albert SE, Yie S, Zavazava N, Librach CL. HLA-G has concentration-dependent effect on the generation of an allo-CTL response. Immunology 2000;101:191–200.
Roussev RG, Ng SC, Coulam CB. Natural killer cell functional activity suppression by intravenous immunoglobulin, intralipid and soluble human leucocyte antigen-G. Am J Reprod Immunol 2007;57:262–9.
Marchal-Bras-Goncalves R, Rouas-Freiss N, Connan F, Choppin J, Dausset J, Carosella ED, et al. A soluble HLA-G protein that inhibits natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Transplant Proc 2001;33:2355–9.
Hackmon R, Hallak M, Krup M, Weitzman D, Sheiner E, Kaplan B, et al. HLA-G antigen and parturition: maternal serum, fetal serum and amniotic fluid levels during pregnancy. Fetal Diagn Ther 2004;19:404–9.
Ober C, Aldrich C, Rosinsky B, Robertson A, Walker MA, Willadsen S, et al. HLA-G1 protein expression is not essential for fetal survival. Placenta 1998;19:127–32.
Aldrich CL, Stephenson MD, Karrison T, Odem RR, Branch DW, Scott JR, et al. HLA-G genotypes and pregnancy outcome in couples with unexplained recurrent miscarriage. Mol Hum Reprod 2001;7:1167–72.
Pfeiffer KA, Fimmers R, Engels G, van der Ven H, van der Ven K. The HLA-G genotype is potentially associated with idiopathic recurrent spontaneous abortion. Mol Hum Reprod 2001;7:373–8.
Hviid TV, Sorensen S, Morling N. Polymorphism in the regulatory region located more than 1.1 kilobases 5′ to the start site of transcription, the promoter region, and exon 1 of the HLA-G gene. Hum Immunol 1999;60:1237–44.
Ober C, Aldrich CL, Chervoneva I, Billstrend C, Rahimov F, Gray HL, et al. Variation in the HLA-G promoter region influences miscarriage rates. Am J Hum Genet 2003;72:1425–35.
Jurisicova A, Casper RF, MacLusky NJ, Mills GB, Librach CL. HLA-G expression during pre-implantation human embryo development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996;93:161–5.
Menicucci A, Noci I, Fuzzi B, Criscuoli L, Scarselli G, Baricordi O, et al. Non-classic sHLA class I in human oocyte culture medium. Hum Immunol 1999;60:1054–7.
McElhinny AS, Exley GE, Warner CM. Painting Qa-2 onto Ped slow preimplantation embryos increases the rate of cleavage. Am J Reprod Immunol 2000;44:52–8.
Fuzzi B, Rizzo R, Criscuoli L, Noci I, Melchiorri L, Scarselli B, et al. HLA-G expression in early embryos is a fundamental prerequisite for the obtainment of pregnancy. Eur J Immunol 2002;32:311–5.
Roussev RG, Keskintepe L, Coulam CB, Sher G, Maasarani G. Soluble HLA-G (sHLA-G) in human embryo culture media: a useful marker for assessing embryo quality and implantation potential for IVF. Fertil Steril 2003;80(Suppl 3):S12.
Sher G, Keskintepe L, Nouriani M, Roussev R, Batzofin J. Expression of sHLA-G in supernatants of individually cultured 46-h embryos: a potentially valuable indicator of ‘embryo competency’ and IVF outcome. Reprod Biomed Online 2004;9:74–8.
Roussev RG, Coulam CB. Detection of soluble HLA-G levels in embryo culture media is predictive for embryo quality and successful pregnancy in IVF. Am J Reprod Immunol 2004;51:471–2.
Sergent IL. Does ‘soluble’ HLA-G really exist? Another twist to the tale. Mol Hum Reprod 2005;11:695–8.
Menezo Y, Elder K, Viville S. Soluble HLA-G release by the human embryo: an interesting artefact? Reprod Biomed Online 2006;13:763–4.
Yie SM, Li LH, Li YM, Librach C. HLA-G protein concentrations in maternal serum and placental tissue are decreased in preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;191:525–9.
Emmer PM, Steegers EA, van Lierop MJ, Steegers-Theunissen RP, Loke YW, Joosten I. Amniotic fluid soluble human leukocyte antigen G is markedly decreased in offspring with neural tube defects. Early Hum Dev 2002;66:101–5.
Fuzzi B, Rizzo R, Criscuoli L, Noci I, Melchiorri L, Scarselli B, et al. HLA-G expression in early embryos is a fundamental prerequisite for the obtainment of pregnancy. Eur J Immunol 2002;32:311–5.
Rebmann V, Pfeiffer K, Passler M, Ferrone S, Maier S, Weiss E, et al. Detection of soluble HLA-G molecules in plasma and amniotic fluid. Tissue Antigens 1999;53:14–22.
Sebti Y, Le Friec G, Pangault C, Gros F, Drenou B, Guilloux V, et al. Soluble HLA-G molecules are increased in lymphoproliferative disorders. Hum Immunol 2003;64:1093–101.
Hunt JS, Jadhav L, Chu W, Geraghty DE, Ober C. Soluble HLA-G circulates in maternal blood during pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;183:682–8.
Rebmann V, Lamaoult J, Rouas-Freiss N, Carosella ED, Grosse-Wilde H. Report of the wet workshop for quantification of soluble HLA-G in Essen, 2004. Hum Immunol 2005;66:853–63.
Pfeiffer KA, Rebman V, Passier M, van der Ven K, van der Ven H, Krebs D, et al. Soluble HLA levels in early pregnancy after in vitro fertilization. Hum Immunol 2000;61:559–64.
Van Lierop MJ, Wijnands F, Loke YW, Emmer PM, Lukassen HG, Braat DD, et al. Detection of HLA-G by a specific sandwich ELISA using monoclonal antibodies 6233 and 56B. Mol Hum Reprod 2002;8:776–84.
Lim KH, Zhou Y, Janatpour M, McMaster M, Bass K, Chun SH, et al. Human cytotrophoblast differentiation/invasion is abnormal in pre-eclampsia. Am J Pathol 1997;151:1809–18.
Pijnenborg R, Dixon G, Robertson WB, Brosens I. Trophoblastic invasion of human decidua from 8 to 18 weeks of pregnancy. Placenta 1980;1:3–19.
Redman CW. Immunology of preeclampsia. Semin Perinatol 1991;15:257–62.
Hara N, Fujii T, Yamashita T, Kozuma S, Okai T, Taketani Y. Altered expression of human leukocyte antigen G (HLA-G) on extravillous trophoblasts in preeclampsia: immunohistological demonstration with anti-HLA-G specific antibody “87G” and anti-cytokeratin antibody “CAM5.2”. Am J Reprod Immunol 1996;36:349–58.
Singer G, Rebmann V, Chen YC, Liu HT, Ali SZ, Reinsberg J, et al. HLA-G is a potential tumor marker in malignant ascites. Clin Cancer Res 2000;9:4460–4.
Ugurel S, Rebmann V, Ferrone S, Tilgen W, Grosse-Wilde H, Reinhold U. Soluble human leukocyte antigen-G serum level is elevated in melanoma patients and is further increased by interferon-alpha immunotherapy. Cancer 2001;92:369–76.
Nuckel H, Rebmann V, Durig J, Duhrsen U, Grosse-Wilde H. HLA-G expression is associated with an unfavorable outcome and immunodeficiency in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2005;105:1694–8.
Creput C, Durrbach A, Menier C, Guettier C, Samuel D, Dausset J, et al. Human leukocyte antigen-G (HLA-G) expression in biliary epithelial cells is associated with allograft acceptance in liver-kidney transplantation. J Hepatol 2003;39:587–94.
Lila N, Carpentier A, Amrein C, Khalil-Daher I, Dausset J, Carosella ED. Implication of HLA-G molecule in heart-graft acceptance. Lancet 2000;355:2138–42.
Lila N, Amrein C, Guillemain R, Chevalier P, Latremouille C, Fabiani JN, et al. Human leukocyte antigen-G expression after heart transplantation is associated with a reduced incidence of rejection. Circulation 2002;105:1949–54.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roussev, R.G., Coulam, C.B. HLA-G and its role in implantation (review). J Assist Reprod Genet 24, 288–295 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-007-9148-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-007-9148-3