Abstract
Purpose: To develop inhouse made (IHM) embryo culture medium with a Multipurpose Isolator and compare the embryo development in a prospective randomized study with commercial media.
Methods: Fertilization by intracytoplasmic single sperm injection (ICSI) of Metaphase II oocytes obtained after 96 controlled ovarian hyperstimulation cycles in patients not older than 37 years. Transfer of zygotes to IHM or commercial Cook Sydney IVF Cleavage medium (SIC) immediately after pronucleus observation. Evaluation of embryo cleavage and score, pregnancy, and implantation rate.
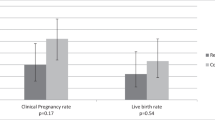
Results: From 100 zygotes cultured in SIC, 61% were at the 4 cell stage 45 h after ICSI compared to 77% (78/101) in the IHM, P<0.05. The mean embryo score with IHM was 3.9±0.9 compared to 3.5±1.2 with SIC, P<0.05. The clinical pregnancy rate per transfer was 38.9% (37/95), the implantation rate was 23% (46/200), and no differences were observed between the groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steptoe PC, Edwards RG: Birth after reimplantation of a human embryo. Lancet 1978 Aug. 12; 2(8085):366
Staessens C, Janssenswillems C, De Clerck E, Van Steirtheghem A: Controlled comparison of commercial media for human in-vitro fertilization: Menezo B2 medium versus Medi-Cult universal and BM1 medium. Hum Reprod 1998; 13(9):2548–2554
Staessens C, Van den Abeel E, Janssenswillen C, Devroey P, Van Steirteghem AC: Controlled comparison of Earle’s balanced salt solution with Menezo B2 medium for human in-vitro fertilization performance. Hum Reprod 1994;9(10):1915–1919
Van Langendonckt A, Demylle D, Wyns C, Nisolle M, Donnez J: Comparison of G1.2/G2.2 and Sydney IVF cleavage/blastocyst sequential media for the culture of human embryos: A prospective, randomized, comparative study. Fertil Steril 2001;76(5):1023–1031
Macklon NS, Piters MH, Hassan MA, Jeucken PH, Eijkemans MJ, Fauser BC: A prospective randomized comparison of sequential versus monoculture systems for in-vitro human blastocyst development. Hum Reprod 2002;17(10):2700–2705
Mitidieri A: Intallation/Operation Protocol for the MPI Isolator. Document VA MPI 01, Sintetica SA. Via Penate 5, 6850 Mendrisio, Switzerland, 2001.
Puissant F, Van Rysselberge M, Barlow P, Deweze J, Jeroy F: Embryo scoring as a prognostic tool in IVF treatment. Hum Reprod 1987;2:705–708
Staessens C, Camus M, Bollen N, Devroey P, Van Steirteghem AC: The relationship between embryo quality and the occurrence of multiple pregnancies. Fertil Steril 1992;47:626–630
Leese HJ, Hooper MA, Edwards RG, Ashwood-Smith MJ: Uptake of pyruvate by early human embryos determined by a non invasive technique. Hum Reprod 1986;1:181–182
Hardy K, Hooper MA, Handysude AH, Rutherford AJ, Winston RM, Leese HJ: Non-invasive measurement of glucose and pyruvate uptake by individual human oocytes and preimplantation embryos. Hum Reprod 1989;4:188–191
Gott AL, Hardy K, Winston RM, Leese HJ: Non-invasive measurement of pyruvate and glucose uptake and lactate production by single human preimplantation embryos. Hum Reprod 1990;5:104–108
Gardner DK, Lane M, Calderon I, Leeton J: Environment of the preimplantation embryo in vivo: Metabolite analyse of the oviduct and uterine fluids during the menstrual cycle and metabolism of cumulus cells. Fertil Steril 1996;65:349–353
Ménézo YJ, Guerin JF, Czyba JC: Improvement of human embryo development in vitro by co-culture on mono layers of vero-cells Biol Reprod 1990;42:301–306
Macklon NS, Pieters HHEC, Hassan MA, Jeucken PHM, Eijkemans MJC, Fauser BCJM: A prospective randomized comparison of sequential versus monoculture system for in-vitro human blastocyst development. Hum Reprod 2002;17:2700–2705
Lane M, Gardner D: Lactate regulates pyruvate uptake and metabolism in the preimplantation mouse embryo. Biol Reprod 2000
Van den Bergh M, Devreker F, Emiliani S, Englert Y: Online 3, Suppl 1,8 Glycolytic activity: A possible tool for human blastocyst selection. Reprod Biomed 2001
Devreker F, Van den Bergh M, Biramane J, Winston RL, Englert Y, Hardy K: Effects of taurine on human embryo development in vitro. Hum Reprod 1999;14(9):2350–2356
Devreker F, Hardy K, Van den Bergh M, Vannin AS, Emiliani S, Englert Y: Amino acids promote human blastocyst development in vitro. Hum Reprod 2001;16(4):749–756
Devreker F, Winston RM, Hardy K: Glutamine improves human preimplantation development in vitro. Fertil Steril 1998;69(2):293–299
Lane M, Gardner DJ: Nonessential Amino Acids and glutamine decrease the time of the first three cleavage divisions and increase compaction of mouse zygotes in vitro. Assist Reprod Genet 1997;14:398–403
Quin P, Mainipanah R, Steinberg J, Weathersbee P: Successful human in vitro fertilization using modified human tubal medium lacking glucose and phosphate ions. Fertil Steril 1995;63:922–924
Hammamah S, Ménézo Y: Ed. Ellipses. In Ovocyte et embryon: De la physiologie è la pathologie, Paris 1999, p 204
Coates A, Rutherford AJ, Hunter H, Leese HJ: Glucose-free medium in human in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer: A large-scale, prospective, randomized clinical trial. Fertil Steril 1999;72(2):229–232
Weathersbee PS, Pool TB, Ord TJ: Synthetic serum substitute (SSS): A globulin-enriched protein supplement for human embryo culture. Assist Reprod Genet 1995;12(6):354–356
Graham MC, Partridge AB, Lewis V, Phipps WR: A prospective comparison of Synthetic Serum Substitute and human serum albumin in culture for in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer. Fertil Steril 1995;64(5):1036–1038
Desai NN, Sheean LA, Martin D, Gindlesperger V, Austin CM, Lisbonna H, Peskin B, Godfard J: Clinical experience with synthetic serum substitute as a protein supplement in IVF culture media: A retrospective study. J Assist Reprod Genet 1996;13(1):23–31
Ben-Yosef D, Yovel I, Schwartz T, Azem F, Lessing JB, Amit A: Increasing synthetic serum substitute concentrations in P1 glucose/phosphate-free medium improves implantation rate: A comparative study. J Assist Reprod Genet 2001;18(1):588–592
Heckert RR, Best M, Jordan LT, Dulac GC, Eddington DL, Sterrit WG: Efficacy of vaporized hydrogen peroxide against exotic animal virusses. Appl Environ Microbiol 1997;63(10):3916–3918
Hall J, Gilligan A, Schimmel T, Cecchi M, Cohen J: The origin, effects and control of air pollution in laboratories used for human embryo culture. Hum Reprod 1998;13(Suppl 4):146–155
Cohen J, Gilligan A, Esposito W, Schimmel T, Dale B: Ambient air and its potential effects on conception in vitro. Hum Reprod 1997;12(8):1742–1749
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van den Bergh, M.J.G., Siragusa, A., Dubied, A. et al. The Use of an Hydrogen Peroxide Multipurpose Isolator for Inhouse Preparation of Human Embryo Culture Media: A Unique Successful Swiss Randomized Prospective Study. J Assist Reprod Genet 21, 381–386 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-004-7525-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-004-7525-8