Abstract
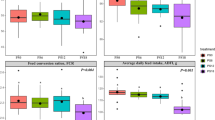
This study evaluated the nutritional potential of three seaweed extracts (Ulva lactuca, Eisenia sp. and Porphyra sp.) as possible ingredients in shrimp feed to improve growth and main digestive enzyme activities. Seaweed extracts were included in replacement of wheat and soybean meal in isoproteic diets (35 ± 0.5%) at three levels of inclusion (5, 10, and 15%) and tested during 28 days in a feeding trial on Litopenaeus vannamei (initial weight 1.15 ± 0.08 g). Growth performance and feed utilisation parameters, in addition to trypsin, chymotrypsin, lipase and amylase activities, were evaluated. An increase of ash content in experimental diets was observed as seaweed extract inclusion level increased (from 7 up to 13.4%). All shrimps fed with seaweed diets significantly improved (p < 0.01) final weight (FW), weight gain (WG), specific growth rate (SGR) and feed intake (FI) in contrast to control diet. In general, Ulva diets presented the best shrimp growth performance, among which inclusion of 15% Ulva extract resulted in significantly higher FW, WG and SGR (p < 0.01) compared to control, Porphyra and Eisenia diets. In the case of chymotrypsin, lipase and amylase enzyme activity, a significant interaction between seaweed type and inclusion level was found (p < 0.01), where in most cases, inclusion level of 5% of all type of seaweed resulted in an increase of the enzyme activities. The use of any of the three proposed seaweed extracts in balanced feed, especially Ulva, is suggested to promote shrimp growth productivity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramo D (1989) Lipid requirements of shrimp. In: Advances in Tropical Aquaculture, Workshop at Tahiti, French Polynesia
Amaya EA, Davis DA, Rouse DB (2007) Replacement of fish meal in practical diets for the Pacific white shrimp (L. vannamei) reared under pond conditions. Aquaculture 262:393–401
Anand PS, Kohli MPS, Roy SD, Sundaray JK, Kumar S, Sinha A, Pailan GH, Kumar Sukham M (2013) Effect of dietary supplementation of periphyton on growth performance and digestive enzyme activities in Penaeus monodon. Aquaculture 392:59–68
Anderson JL (2016) Global shrimp survey: GOAL 2016. Retrieved from https://www.aquaculture alliance.org/advocate/global-shrimp-survey-goal-2016/
Azmir J, Zaidul ISM, Rahman MM, Sharif KM, Mohamed A, Sahena F, Jahurul MHA, Ghafoor K, Narulaini NAN, Omar AKM (2013) Techniques for extraction of bioactive compounds from plant materials: a review. J Food Eng 117:426–436
Balasubramaniam V, Mustar S, Khalid NM, Rashed AA, Noh MFM, Wilcox MD, Chater PI, Brownlee IA, Pearson JP (2013) Inhibitory activities of three Malaysian edible seaweeds on lipase and α-amylase. J Appl Phycol 25:1405–1412
Bitou N, Ninomiya M, Tsujita T, Okuda H (1999) Screening of lipase inhibitors from marine algae. Lipids 34:441–445
Briggs MRP, Funge-Smith SJ (1996) The potential use of Gracilaria sp. meal in diets for juvenile Penaeus monodon Fabricius. Aquac Res 27:345–354
Brito R, Rosas C, Chimal ME, Gaxiola G (2001) Effect of different diets on growth and digestive enzyme activity in Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone 1931) early post-larvae. Aquac Res 32:257–266
Brito LO, Arantes R, Magnotti C, Derner R, Pchara F, Olivera A, Vinatea L (2014) Water quality and growth of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) in co-culture with green seaweed Ulva lactuca (Linaeus) in intensive system. Aquac Int 22:497–508
Cárdenas JV, Gálvez AO, Brito LO, Galarza EV, Pitta DC, Rubin VV (2015) Assessment of different levels of green and brown seaweed meal in experimental diets for whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei, Boone) in recirculating aquaculture system. Aquac Int 23:1491–1504
Chojnacka K, Saeid A, Witkowska Z, Tuhy L (2012) Biologically active compounds in seaweed extracts—the prospects for the application. Open Conf Proc J 3:20–28
Cruz-Suárez LE, Ricque-Marie D, Tapia-Salazar M, Guajardo-Barbosa C (2000) Uso de harina de kelp (Macrocystis pyrifera) en alimentos para camarón. In LE Cruz Suárez, D. Ricque Marie, M. Tapia Salazar, MG Nieto López (eds.). Avances en Nutrición Acuícola V. Memorias del V Simposium Internacional de Nutrición Acuícola. Yucatán, Mexico. Pp 227–266
Cruz-Suárez LE, Tapia Salazar M, Nieto López MG, Ricque Marie D (2008) A review of the effects of macroalgae in shrimp feeds and in co-culture. In: Cruz Suárez LE, Ricque Marie D, Tapia Salazar M, Nieto López MG (eds) Avances en Nutrición Acuícola IX. Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León, Mexico, pp 304–333
Cruz-Suárez LE, León A, Peña-Rodríguez A, Rodríguez-Peña G, Moll B, Ricque-Marie D (2010) Shrimp/Ulva co-culture: a sustainable alternative to diminish the need for artificial feed and improve shrimp quality. Aquaculture 301:64–68
Elizondo-González R, Quiroz-Guzmán E, Escobedo-Fregoso C, Magallón-Servín P, Peña-Rodríguez A (2018) Use of seaweed Ulva lactuca for water bioremediation and as feed additive for white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Peer J 6:e4459
Erlanger BF, Kokowsky N, Cohen W (1961) The preparation and properties of two new chromogenic substrates of trypsin. Arch Biochem Biophys 95:271–278
Ezquerra J, García-Carreño FL, Haard NF (1997) Effects of feed diets on digestive proteases from the hepatopancreas of white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei). J Food Biochem 21:401–419
FAO, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2016) The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2016. Contributing to food security and nutrition for all. Rome. 200 pp
Felix NR, Brindo A (2006) Fermented feed ingredients as fish meal replacer in Aquafeed production. Aquaculture Asia 13:33–34
Flegel TW, Lightner DV, Lo CF, Owens L (2008) Shrimp disease control: past, present and future. In: Bondad-Reantaso MG, Mohan CV, Crumlish M, Subasinghe RP (eds) Diseases in Asian aquaculture VI. Fish Health Section. Asian Fisheries Society, Philippines, pp 355–378
Francis G, Makkar HP, Becker K (2001) Antinutritional factors present in plant-derived alternate fish feed ingredients and their effects in fish. Aquaculture 199:197–227
Galgani ML, Benyamin Y, Ceccaldi HJ (1984) Identification of digestive proteinases of Penaeus kerathurus (Forskal): a comparison with Penaeus japonicus. Comp Biochem Physiol B 78:355–361
Galgani ML, Benyamin Y, Van Wormhoudt A (1985) Purification, properties and immunoassays of trypsin from the shrimp Penaeus japonicus. Comp Biochem Physiol B, 81, 447–452
Gamboa-Delgado J, Molina-Poveda C, Cahu C (2003) Digestive enzyme activity and food ingesta in juvenile shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone 1931) as a function of body weight. Aquac Res 34:1403–1411
González-Félix ML, Gatlin Iii DM, Lawrence AL, Perez-Velazquez M (2003) Nutritional evaluation of fatty acids for the open thelycum shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei: II. Effect of dietary n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated and highly unsaturated fatty acids on juvenile shrimp growth, survival, and fatty acid composition. Aquac Nutr 9:115–122
Guillard RRL (1975) Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In: Smith WL, Chanley MH (eds) Culture of marine invertebrate animals. Plenum Press, New York, USA, pp 26–60
Jimenez-Escrig A, Sanchez-Muniz FJ (2000) Dietary fibre from edible seaweeds: chemical structure, physicochemical properties and effects on cholesterol metabolism. Nutr Res 20:585–598
Kadam SU, Álvarez C, Tiwari BK, O'Donnell CP (2016) Extraction and characterization of protein from Irish brown seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum. Food Res Int 99:1021–1027
Kumar KS, Ganesan K, Selvaraj K, Rao PS (2014) Studies on the functional properties of protein concentrate of Kappaphycus alvarezii (Doty) Doty–an edible seaweed. Food Chem 153:353–360
Le Moullac G, Klein B, Sellos D, Van Wormhoudt A (1997) Adaptation of trypsin, chymotrypsin and α-amylase to casein level and protein source in Penaeus vannamei (Crustacea Decapoda). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 208:107–125
Lim C, Dominy W (1990) Evaluation of soybean meal as a replacement for marine animal protein in diets for shrimp (Penaeus vannamei). Aquaculture 87:53–63
Mabeau S, Fleurence J (1993) Seaweed in food products: biochemical and nutritional aspects. Trends Food Sci Technol 4:103–107
MacArtain P, Gill CIR, Brooks M, Campbell R, Rowland IR (2007) Nutritional value of edible seaweeds. Nutr Rev 65:535–543
Marinho-Soriano E, Camara MR, Cabral TDM, Carneiro MADA (2007) Preliminary evaluation of the seaweed Gracilaria cervicornis (Rhodophyta) as a partial substitute for the industrial feeds used in shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) farming. Aquac Res 38:182–187
Men-Qing L, Qing C, Aksnes A (2001) Identification of feeding stimulants for shrimp. Mar Fish Res 22:71–74
Nachlas MM, Blackburn R (1958) The colorimetric determination of urinary lipase. J Biol Chem 230:1051–1061
Nakagawa H (1997) Effect of dietary algae on improvement of lipid metabolism in fish. BiomedPharmacother 51:345–348
Naylor RL, Goldburg RJ, Primavera JH, Kautsky N, Beveridge MC, Clay J, Folke C, Lubchanco J, Mooney TM (2000) Effect of aquaculture on world fish supplies. Nature 405:1017–1024
Neori A, Chopin T, Troell M, Buschmann AH, Kraemer GP, Halling C, Shpigel M, Yarish C (2004) Integrated aquaculture: rationale, evolution and state of the art emphasizing seaweed biofiltration in modern mariculture. Aquaculture 231:361–391
Ortiz J, Romero N, Robert P, Araya J, Lopez-Hernández J, Bozzo C, Navarrete E, Osorio A, Rios A (2006) Dietary fiber, amino acid, fatty acid and tocopherol contents of the edible seaweeds Ulva lactuca and Durvillaea antarctica. Food Chem 99:98–104
Peixoto MJ, Salas-Leitón E, Pereira LF, Queiroz A, Magalhães F, Pereira R, Abreu H, Reis PA, Magalhães Gonçalves JF, de Almeida Ozório RO (2016) Role of dietary seaweed supplementation on growth performance, digestive capacity and immune and stress responsiveness in European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquacult Rep 3, 189–197
Peñaflorida VD, Golez NV (1996) Use of seaweed meals from Kappaphycus alvarezii and Gracilaria heteroclada as binders in diets for juvenile shrimp Penaeus monodon. Aquaculture 143:393–401
Peña-Rodríguez A, Mawhinney TP, Ricque-Marie D, Cruz-Suárez LE (2011) Chemical composition of cultivated seaweed Ulva clathrata (Roth) C. Food Chem 129:491–498
Peña-Rodríguez A, Elizondo-González R, Nieto-López MG, Ricque-Marie D, Cruz-Suárez LE (2017) Practical diets for the sustainable production of brown shrimp, Farfantepenaeus californiensis, juveniles in presence of the green macroalga Ulva clathrata as natural food. J Appl Phycol 29:413–421
Pereira H, Barreira L, Figueiredo F, Custódio L, Vizetto-Duarte C, Polo C, Rešek E, Engelen A, Varela J (2012) Polyunsaturated fatty acids of marine macroalgae: potential for nutritional and pharmaceutical applications. Mar Drugs 10:1920–1935
Perera E, Moyano FJ, Rodríguez-Viera L, Cervantes A, Martínez-Rodríguez G, Mancera JM (2010) In vitro digestion of protein sources by crude enzyme extracts of the spiny lobster Panulirus argus (Latreille, 1804) hepatopancreas with different trypsin isoenzyme patterns. Aquaculture 310:178–185
Portillo-Clark G, Casillas-Hernández R, Servín-Villegas R, Magallón-Barajas FJ (2012) Growth and survival of the juvenile yellowleg shrimp Farfantepenaeus californiensis cohabiting with the green feather alga Caulerpa sertularioides at different temperatures. Aquac Res 44:22–30
Reilly P, O’Doherty JV, Pierce KM, Callan JJ, O’sullivan JT, Sweeney T (2008) The effects of seaweed extract inclusion on gut morphology, selected intestinal microbiota, nutrient digestibility, volatile fatty acid concentrations and the immune status of the weaned pig. Animal 2:1465–1473
Rodríguez-González H, Orduña-Rojas J, Villalobos-Medina JP, García-Ulloa M, Polanco-Torres A, López-Álvarez ES, Montoya-Mejía M, Hernández-Llamas A (2014) Partial inclusion of Ulva lactuca and Gracilaria parvispora meal in balanced diets for white leg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). J Appl Phycol 26:2453–2459
Santizo RB, Serrano AE Jr, Corre VL (2014) Proximate composition and dry matter digestibility of Ulva lactuca in the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Animal Biol Animal Husbandry 6:75–83
Sathivel A, Raghavendran HRB, Srinivasan P, Devaki T (2008) Anti-peroxidative and anti-hyperlipidemic nature of Ulva lactuca crude polysaccharide on D-Galactosamine induced hepatitis in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 46:3262–3267
Serrano AE Jr, Santizo RB (2014) Dietary substitution of protein concentrate of Ulva lactuca for soybean meal in the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon fry. Animal Biol Animal Husbandry 6(2):140–147
Serrano AE Jr, Santizo RB, Tumbokon BLM (2015) Potential use of the sea lettuce Ulva lactuca replacing soybean meal in the diet of the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon juvenile. Aquacult Aquar Conservat Legislat 8:245–252
Subasinghe RP, Curry D, McGladdery SE, Bartley D (2003) Recent technological innovations in aquaculture. FAO Fisheries Circular, pp. 59–74
Tabarsa M, Rezaei M, Ramezanpour Z, Waaland JR (2012) Chemical compositions of the marine algae Gracilaria salicornia (Rhodophyta) and Ulva lactuca (Chlorophyta) as a potential food source. J Sci Food Agric 92:2500–2506
Tacon AG, Metian M (2008) Global overview on the use of fish meal and fish oil in industrially compounded aquafeeds: trends and future prospects. Aquaculture 285(1):146–158
Tan SH, Mailer RJ, Blanchard CL, Agboola SO (2011) Canola proteins for human consumption: extraction, profile, and functional properties. J Food Sci 76:16–28
Tincy V, Mishal P, Akhtar MS, Pal AK (2014) Aquaculture nutrition: turning challenges into opportunities. World Aquacult 45:67–69
Tsai IH, Lu PJ, Chuang JL (1991) The midgut chymotrypsins of shrimps (Penaeus monodon, Penaeus japonicus and Penaeus penicillatus). Biochim Biophys Acta-Protein Struct Molec Enzymol 1080:59–67
Tsuge K, Okabe M, Yoshimura T, Sumi T, Tachibana H, Yamada K (2004) Dietary effects of porphyran from Porphyra yezoensis on growth and lipid metabolism of Sprague-Dawley rats. Food Sci Technol Res 10(2):147–151
Van Alstyne KL, Wolfe GV, Freidenburg TL, Neill A, Hicken C (2001) Activated defense systems in marine macroalgae: evidence for an ecological role for DMSP cleavage. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 213:53–65
Vega-Villasante F, Nolasco H, Civera R (1993) The digestive enzymes of the pacific brown shrimp Penaeus californiensis.: I—properties of amylase activity in the digestive tract. Comp Biochem Physiol B 106(3):547–550
Wahbeh MI (1997) Amino acid and fatty acid profiles of four species of macroalgae from Aqaba and their suitability for use in fish diets. Aquaculture 159(1–2):101–109
Yang Q, Zhou X, Zhou Q, Tan B, Chi S, Dong X (2009) Apparent digestibility of selected feed ingredients for white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei, Boone. Aquac Res 41:78–86
Yildirim O, Ergun S, Yaman S, Turker A (2009) Effects of two seaweeds (Ulva lactuca and Enteromorpha linza) as a feed additive in diets on growth performance, feed utilization, and body composition of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Kafkas Universitesi Veteriner Fakultesi Dergisi 15(3):455–460
Yu YY, Chen WD, Liu YJ, Niu J, Chen M, Tian LX (2016) Effect of different dietary levels of Gracilaria lemaneiformis dry powder on growth performance, hematological parameters and intestinal structure of juvenile Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquaculture 450:356–362
Acknowledgements
We thank Ignacio Beamonte from Baja Kelp Talasoterapia S.A. de C.V. and Gustavo Pineda from Acuacultura Mahr, S.A. de C.V. for kindly donating the seaweed meals and the juvenile shrimp, respectively. We also thank to Patricia Hinojosa-Baltazar from the Laboratory of Compared Physiology at CIBNOR for the technical support.
Funding
This work was funded by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACYT) Mexico (Project PDCPN 2015-887). This work was realised within the framework of a UBO/CIBNOR agreement to receive Master’s degree students from UBO in order to complete their master thesis project and was supported by a grant to Alexia Omont by the “Laboratoire d’Excellence” LabexMER (ANR-10-LABX-19) and co-funded by a grant from the French government under the program “Investissements d’Avenir”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Omont, A., Quiroz-Guzman, E., Tovar-Ramirez, D. et al. Effect of diets supplemented with different seaweed extracts on growth performance and digestive enzyme activities of juvenile white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. J Appl Phycol 31, 1433–1442 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1628-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1628-6