Abstract
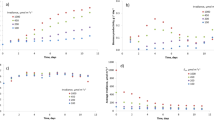
Cyanobacteria exhibit a variety of adaptive strategies that allow them to thrive in ever-changing aquatic environments. Here, successive steady states of continuous cultures were used to investigate the effects of quantified turbulence on the biochemical compounds and physiological processes of Anabaena flos-aquae in a photobioreactor under different dilution rates. A rapid increase in cell density was clearly observed following an increase in the turbulent dissipation rate at all growth rates of A. flos-aquae. The photosynthetic response to irradiance curves showed that the turbulence-treated strains exhibited lower photosynthetic oxygen evolution and saturating irradiance as well as higher respiration in rapidly growing young cells, indicating that they might not be very adaptable to high turbulent dissipation rates. Additionally, there was an increase in the protein levels of A. flos-aquae with increasing turbulence at all growth rates, whereas carbohydrate formation and lipid accumulation demonstrated the opposite trends. At a high growth rate, the level of carbohydrates decreased whereas that of lipids increased, which was interpreted as reflecting an adaptation to the turbulent environment. These findings suggest that turbulence sensitivity is shear regimen- and growth rate-dependent in A. flos-aquae. The high respiration capacity, low saturating irradiance, and conversion of carbohydrates to lipids represent effective measures for revealing the adaptive strategies of rapidly growing young cells under hydrodynamic regimes. The results regarding optimum lipid accumulation with specific growth traits have important implications for the design of cultivation methods of cyanobacteria resource utilization with respect to regulating turbulence.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Carey CC, Ibelings BW, Hoffmann EP, Hamilton DP, Brookes JD (2012) Eco-physiological adaptations that favour freshwater cyanobacteria in a changing climate. Water Res 46:1394–1407
Çelekli A, Arslanargun H, Soysal Ç, Gültekin E, Bozkurt H (2016) Biochemical responses of filamentous algae in different aquatic ecosystems in South East Turkey and associated water quality parameters. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 133:403–412
Chen D, Yan X, Xu J, Su X, Li L (2013) Lipidomic profiling and discovery of lipid biomarkers in Stephanodiscus sp. under cold stress. Metabolomics 9:949–959
Chengala A, Hondzo M, Mashek DG (2013) Fluid motion mediates biochemical composition and physiological aspects in the green alga Dunaliella primolecta Butcher. Limnol Oceanogr Fluids Environ 3:74–88
Chisti Y (2010) Shear sensitivity. In: Flickinger MC (ed) Encyclopedia of industrial biotechnology: bioprocess, bioseparation, and cell technology. Wiley, New York, pp 4360–4398
Czitrom V (1999) One-factor-at-a-time versus designed experiments. Am Stat 53:126–131
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Grobbelaar JU (1994) Turbulence in algal mass cultures and the role of light/dark fluctuations. J Appl Phycol 6:331–335
Grondahl F (2009) Removal of surface blooms of the cyanobacteria Nodularia spumigena: a pilot project conducted in the Baltic Sea. Ambio 38:79–84
Guasto JS, Rusconi R, Stocker R (2012) Fluid mechanics of planktonic microorganisms. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 44:373–400
Guedes AC, Katkam NG, Varela J, Malcata FX (2014) Photobioreactors for cyanobacterial culturing. In: Sharma NK, Rai AK, Stal LJ (eds) Cyanobacteria: an economic perspective. Wiley, New York, pp 270–292
Han F, Pei H, Hu W, Song MM, Ma GX, Pei RT (2015) Optimization and lipid production enhancement of microalgae culture by efficiently changing the conditions along with the growth-state. Energy Convers Manag 90:315–322
Hansen TJ, Hondzo M, Mashek MT, Mashek DG, Lefebvre PA (2013) Algal swimming velocities signal fatty acid accumulation. Biotechnol Bioeng 110:143–152
Hondzo M, Wüest A (2009) Do microscopic organisms feel turbulent flows? Environ Sci Technol 43:764–768
Karp-Boss L, Boss E, Jumars PA (1996) Nutrients fluxes to planktonic osmotrophs in the presence of fluid motion. Oceanogr Mar Biol 34:71–107
Klok AJ, Lamers PP, Martens DE, Draaisma RB, Wijffels RH (2014) Edible oils from microalgae: insights in TAG accumulation. Trends Biotechnol 32:521–582
Kumar R, Biswas K, Singh PK, Singh PK, Elumalai S, Shukla P, Pabbi S (2017) Lipid production and molecular dynamics simulation for regulation of accD gene in cyanobacteria under different N and P regimes. Biotechnol Biofuels 10:94
Leupold M, Hindersin S, Gust G, Kerner M, Hanelt D (2013) Influence of mixing and shear stress on Chlorella vulgaris, Scenedesmus obliquus, and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Appl Phycol 25:485–495
Li YT, Han DX, Hu GR, Sommerfeld M, Hu Q (2010) Inhibition of starch synthesis results in overproduction of lipids in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biotechnol Bioeng 107:258–268
Li YT, Han DX, Sommerfeld M, Hu Q (2011) Photosynthetic carbon partitioning and lipid production in the oleaginous microalga Pseudochlorococcum sp. (Chlorophyceae) under nitrogen-limited conditions. Bioresour Technol 102:123–129
Litchman E, de Tezanos Pinto P, Klausmeier CA, Thomas MK, Yoshiyama K (2010) Linking traits to species diversity and community structure in phytoplankton. Hydrobiologia 653:15–28
MacIntyre HL, Kana TM, Geider RJ (2000) The effect of water motion on short-term rates of photosynthesis by marine phytoplankton. Trends Plant Sci 5:12–17
Markou G, Nerantzis E (2013) Microalgae for high-value compounds and biofuels production: a review with focus on cultivation under stress conditions. Biotechnol Adv 31:1532–1542
Merel S, Walker D, Chicana R, Snyder S, Baurès E, Thomas O (2013) State of knowledge and concerns on cyanobacterial blooms and cyanotoxins. Environ Int 59:303–327
Michel G, Tonon T, Scornet D, Cock JM, Kloareg B (2010) Central and storage carbon metabolism of the brown alga Ectocarpus siliculosus: insights into the origin and evolution of storage carbohydrates in eukaryotes. New Phytol 188:67–81
Michels MHA, van der Goot AJ, Vermuë MH, Wijffels RH (2016) Cultivation of shear stress sensitive and tolerant microalgal species in a tubular photobioreactor equipped with a centrifugal pump. J Appl Phycol 28:53–62
Mirón AS, Cerón García MC, Contreras Gómez A, Camacho FG, Grima EM, Chisti Y (2003) Shear stress tolerance and biochemical characterization of Phaeodactylum tricornutum in quasi steady-state continuous culture in outdoor photobioreactors. Biochem Eng J 16:287–297
Moisander PH, Hench JL, Kononen K, Paerl HW (2002) Small-scale shear effects on heterocystous cyanobacteria. Limnol Oceanogr 47:108–119
Nusch EA (1980) Comparison of different methods for chlorophyll and phaeopigment determination. Arch Hydrobiol Beih Ergebn Limnol 14:14–36
Olesen TD, Ganf GG (1986) Photosynthate partitioning: a labile, adaptive phenomenon in Microcystis aeruginosa. Arch Hydrobiol 108:55–76
Oliver RL, Hamilton DP, Brookes JD, Ganf GG (2012) Physiology, blooms and prediction of planktonic cyanobacteria. In: Whitton BA (ed) Ecology of cyanobacteria II. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 155–194
Paerl H, Otten T (2013) Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: causes, consequences, and controls. Microb Ecol 65:995–1010
Pandit PR, Fulekar MH, Karuna MS (2017) Effect of salinity stress on growth, lipid productivity, fatty acid composition, and biodiesel properties in Acutodesmus obliquus and Chlorella vulgaris. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:13437–13451
Peters F, Marrasé C (2000) Effects of turbulence on plankton: an overview of experimental evidence and some theoretical considerations. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 205:291–306
Prairie JC, Sutherland KR, Nickols KJ, Kaltenberg AM (2012) Biophysical interactions in the plankton: a cross-scale review. Limnol Oceanogr Fluids Environ 2:121–145
Quintana N, Van der Kooy F, Van de Rhee MD, Voshol GP, Verpoorte R (2011) Renewable energy from Cyanobacteria: energy production optimization by metabolic pathway engineering. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:471–490
Reis A, Gouveia L, Veloso V, Fernández HL, Empis JA, Novais JM (1996) Eicosapentaenoic acid-rich biomass production by the microalga Phaeodactylum tricornutum in a continuous-flow reactor. Bioresour Technol 55:83–88
Reynolds CS (2006) The ecology of phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, New York
Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury JB, Herdman M, Stanier RY (1979) Generic assignments, strains histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 111:1–61
Rubio FC, Camacho FG, Fernández Sevilla JM, Chisti Y, Grima EM (2003) A mechanistic model of photosynthesis in microalgae. Biotechnol Bioeng 81:459–473
Sengupta A, Carrara F, Stocker R (2017) Phytoplankton can actively diversify their migration strategy in response to turbulent cues. Nature 543:555–558
Singh S, Verma E, Tiwari B, Niveshika, Mishra AK (2017) Modulation of fatty acids and hydrocarbons in Anabaena 7120 and its ntcA mutant under calcium. J Basic Microbiol 57:171–183
Sobczuk T, Camacho F, Grima E, Chisti Y (2006) Effects of agitation on the microalgae Phaeodactylum tricornutum and Porphyridium cruentum. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 28:243–250
Steinhoff FS, Karlberg M, Graeve M, Wulff A (2014) Cyanobacteria in Scandinavian coastal waters—a potential source for biofuels and fatty acids? Algal Res 5:42–51
Suali E, Sarbatly R (2012) Conversion of microalgae to biofuel. Renew Sust Energ Rev 16(6):4316–4342
Sullivan JM, Swift E, Donaghay PL, Rines JE (2003) Small-scale turbulence affects the division rate and morphology of two red-tide dinoflagellates. Harmful Algae 2:183–199
Tang JW, Wu QY, Hao HW, Chen Y, Wu M (2004) Effect of 1.7 MHz ultrasound on a gas-vacuolate cyanobacterium and a gas-vacuole negative cyanobacterium. Colloids Surf B 36:115–121
Tang HY, Chen M, Ng KYS, Salley SO (2012) Continuous microalgae cultivation in a photobioreactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 109:2468–2474
Tedesco MA, Duerr EO (1989) Light, temperature and nitrogen starvation effects on the total lipid and fatty acid content and composition of Spirulina platensis UTEX 1928. J Appl Phycol 1:201–209
Thomas WH, Vernet M, Gibson CH (1995) Effects of small-scale turbulence on photosynthesis, pigmentation, cell division, and cell size in the marine dinoflagellate Gomaulax polyedra (Dinophyceae). J Phycol 31:50–59
Walsby AE (1997) Numerical integration of phytoplankton photosynthesis through time and depth in a water column. New Phytol 136:189–209
Wang PL, Shen H, Xie P (2012) Can hydrodynamics change phosphorus strategies of diatoms?—nutrient levels and diatom blooms in lotic and lentic ecosystems. Microb Ecol 63:369–382
Wilbur KM, Anderson NG (1948) Electrometric and colorimetric determination of carbonic anhydrase. J Biol Chem 1715:147–154
Wilhelm C, Jakob T (2011) From photons to biomass and biofuels: evaluation of different strategies for the improvement of algal biotechnology based on comparative energy balances. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:909–919
Xiao Y, Li Z, Li C, Zhang Z, Guo JS (2016) Effect of small-scale turbulence on the physiology and morphology of two bloom-forming cyanobacteria. PLoS One 11(12):e0168925
Yu Z, Song MM, Pei HY, Jiang LQ, Hou QJ, Nie CL, Zhang LJ (2017) The effects of combined agricultural phytohormones on the growth, carbon partitioning and cell morphology of two screened algae. Bioresour Technol 239:87–96
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation (No. 51779240, 51679226, 51509233), the Chongqing Natural Science Program (cstc2015jcyjBX0006), and Open Foundation by Key Laboratory of Sediments in Yellow River, Ministry of Water Resources. Dr. Yan Xiao is supported by the “Youth Innovation Promotion Association” Program funded by the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Y., Zhang, S., Li, Z. et al. Turbulent mixing mediates the photosynthetic activities and biochemical composition of Anabaena: implications for bioengineering. J Appl Phycol 30, 2227–2236 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1465-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1465-7