Abstract
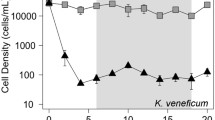
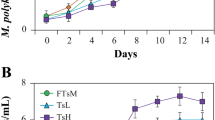
Naturally occurring allelopathic compounds, specific to some phytoplankton, may be a good source of bio-control agents against microalgae responsible for harmful algal blooms (HABs). Global expansion of HABs has invigorated research into different approaches to control these algae, including the search for naturally derived algicidal compounds. Here, we investigated the effects of a filtrate from the algicidal marine bacterium Shewanella sp. IRI-160 on photochemical function of four cultured dinoflagellates, Karlodinium veneficum, Gyrodinium instriatum, Prorocentrum minimum, and Alexandrium tamarense. The filtrate (designated IRI-160AA) contains bioactive compound(s), which were recently shown to inhibit growth of several dinoflagellate species. Results of this study show that all dinoflagellates but P. minimum exhibited photosystem II (PSII) inhibition, loss of photosynthetic electron transport, and varying degrees of cellular mortality. Exposure assays over 24 h showed that PSII inhibition and loss of cell membrane integrity occurred simultaneously in G. instriatum, but not in K. veneficum, where PSII activity declined prior to losing outer-membrane integrity. In addition, PSII inhibition and population growth inhibition were dose-dependent in K. veneficum, with an average EC-50 of 7.9 % (v/v) IRI-160AA. Application of IRI-160AA induced significantly higher PSII inhibition and cell mortality in K. veneficum subjected to continuous darkness as compared to cells maintained with 12:12 h light/dark cycles, while no such dark effect was noted for G. instriatum. The marked differences in the rate and impact of this algicide suggest that multiple cellular targets and different cascades of cellular dysfunction occur across these dinoflagellates.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DM, Glibert PM, Burkholder JM (2002) Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuaries 25:562–584
Anderson DM, Burkholder JM, Cochlan W, Glibert PM, Gobler CJ, Heil CA, Kudela RM, Parsons ML, Rensel JEJ, Townsend DW, Trainer VL, Vargo GA (2008) Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: examining linkages from selected coastal regions of the United States. Harmful Algae 8:39–53
Bachmann RW, Hoyer MV, Fernandez C, Canfield DE Jr (2003) An alternative to proposed phosphorus TMDLs for the management of Lake Okeechobee. Lake Reserv Manage 19:251–264
Bergo E, Segalla A, Giacometti GM, Tarantino D, Soave C, Andreucci F, Barbato R (2003) Role of visible light in the recovery of photosystem II structure and function from ultraviolet-B stress in higher plants. J Exp Bot 54:1665–1673
Bolch CJS, de Salas MF (2007) A review of the molecular evidence for ballast water introduction of the toxic dinoflagellates Gymnodinium catenatum and the Alexandrium “tamarensis complex” to Australasia. Harmful Algae 6:465–485
Boylan JD, Morris JE (2003) Limited effects of barley straw on algae and zooplankton in a midwestern pond. Lake Reserv Manage 19:265–271
Cosgrove J, Borowitzka MA (2010) Chlorophyll fluorescence terminology: an introduction. In: Suggett DJ, Prasil OJ, Borowitzka MA (eds) Chlorophyll a fluorescence in aquatic sciences: methods and applications. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 1–18
Daugbjerg N, Hansen G, Larsen J, Moestrup Ø (2000) Phylogeny of some of the major genera of dinoflagellates based on ultrastructure and partial LSU rDNA sequence data, including the erection of three new genera of unarmoured dinoflagellates. Phycologia 39:302–317
Einhellig FA (1999) An integrated view of allelochemcials amid multiple stresses. In: Inderjit, Dakshini KMM, Foy CL (eds) Principles and practices in plant ecology: allelochemical interactions. CRC, Boca Raton, pp 479–494
Faust MA, Larsen J, Moestrup Ø (1999) Potentially toxic phytoplankton. 3. Genus Prorocentrum (Dinophyceae). In: Lindley JA (ed) ICES identification leaflets for plankton. Leaflet no. 184. Copenhagen, pp 1–24
Fukuyo Y (1985) Morphology of Protogonyaulax tamarensis (Lebour) Taylor and Protogonyaulax catenella (Whedon and Kofoid) Taylor from Japanese coastal waters. Bull Mar Sci 37:529–537
Furusato E, Asaeda T, Manatunge J (2004) Tolerance for prolonged darkness of three phytoplankton species, Microcystis aeruginosa (Cyanophyceae), Scenedesmus quadricauda (Chlorophyceae), and Melosira ambigua (Bacillariophyceae). Hydrobiologia 527:153–162
Gleason FK, Case DE (1986) Activity of the natural algicide, cyanobacterin, on angiosperms. Plant Physiol 80:834–837
Guillard RRL, Ryther JH (1962) Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt and Detonula confervacea Cleve. Can J Microbiol 8:229–239
Gustafsson S, Hultberg M, Figueroa RI, Rengefors K (2009) On the control of HAB species using low biosurfactant concentrations. Harmful Algae 8:857–863
HAB RDDTT (2008) In: Dortch Q, Anderson DM, Ayres DL, Glibert PM (eds) Harmful algal bloom research, development, demonstration, and technology transfer national workshop report. Woods Hole, Massachusetts, USA
Hallegraeff GM (1993) A review of harmful algal blooms and their apparent global increase. Phycologia 32:79–99
Hallegraeff GM (2010) Ocean climate change, phytoplankton community responses, and harmful algal blooms: a formidable predictive challenge. J Phycol 46:220–235
Hare CE, Demir ED, Coyne KJ, Cary SC, Kirchman DL, Hutchins D (2005) A bacterium that inhibits the growth of Pfiesteria piscicida and other dinoflagellates. Harmful Algae 4:221–234
Heisler J, Glibert P, Burkholder J, Anderson D, Cochlan W, Dennison W, Dortch Q, Gobler C, Heil C, Humphries E, Lewitus A, Magnien R, Marshall HG, Sellner K, Stockwell D, Stoecker DK, Suddleson M (2008) Eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: a scientific consensus. Harmful Algae 8:3–13
Hoagland P, Scatasta S (2006) The economic effects of harmful algal blooms. In: Granéli E, Turner JT (eds) Ecology of harmful algae. Springer, Berlin, pp 391–402
Jauzein C, Collos Y, Laabir M, Vaquer A (2011) Dark metabolism and carbon-nitrogen uncoupling in the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 11:73–80
Jeong H, Yim JH, Lee C, Choi SH, Park YK, Yoon SH, Hur CG, Kang HY, Kim D, Lee HH, Park KH, Park SH, Park HS, Lee HK, Oh TK, Kim JF (2005) Genomic blueprint of Hahella chejuensis, a marine microbe producing an algicidal agent. Nucleic Acids Res 33:7066–7073
Jeong HJ, Kim JS, Yoo YD, Kim ST, Song JY, Kim TH, Seong KA, Kang NS, Kim MS, Kim JH, Kim S, Ryu J, Lee HM, Yih WH (2008) Control of the harmful alga Cochlodinium polykrikoides by the naked ciliate Strombidinopsis jeokjo in mesocosm enclosures. Harmful Algae 7:368–377
Jungo E, Visser PM, Stroom J, Mur LR (2001) Artificial mixing to reduce growth of the blue-green alga Microcystis in Lake Nieuwe Meer, Amsterdam: an evaluation of 7 years of experience. Water Sci Technol Water Supply 1:17–23
Kang Y-H, Jung SW, Jo S-H, Han M-S (2011) Field assessment of the potential of algicidal bacteria against diatom blooms. Biocontrol Sci Techn 21:969–984
Kim HG (2006) Mitigation and controls of HABs. In: Granéli E, Turner JT (eds) Ecology of harmful algae. Springer, Berlin, pp 327–338
Kim B-H, Sang M, Hwang S-J, Han M-S (2008) In situ bacterial mitigation of the toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa: implications for biological bloom control. Limnol Oceanog-Meth 6:513–522
Kim Y-M, Wu Y, Duong TU, Ghodake GS, Kim SW, Jin ES, Cho H (2010) Thiazolidinediones as a novel class of algicides against red tide harmful algal species. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 162:2273–2283
Kolber ZS, Prasil O, Falkowski PG (1998) Measurements of variable chlorophyll fluorescence using fast repetition rate techniques: defining methodology and experimental protocols. Biochim Biophys Acta 1367:88–106
Legrande C, Rengefors K, Fistarol GO, Granéli E (2003) Allelopathy in phytoplankton—biochemical, ecological and evolutionary aspects. Phycologia 42:406–419
Leu E, Krieger-Liszkay A, Goussias C, Gross EM (2002) Polyphenolic allelochemicals from the aquatic angiosperm Myriophyllum spicatum inhibit photosystem II. Plant Physiol 130:2011–2018
Lu Y, Wang J, Yu Y, Su W, Kong F (2013) Inhibition of Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze on Microcystis aeruginosa and isolation of the inhibition factors. Biotechnol Lett. doi:10.1007/s10529-013-1188-4
Matthijs HCP, Visser PM, Reeze B, Meeuse J, Slot PC, Wijn G, Talens R, Huisman J (2012) Selective suppression of harmful cyanobacteria in an entire lake with hydrogen peroxide. Water Res 46:1460–1472
Mayali X, Franks PJS, Azam F (2007) Bacterial induction of temporary cyst formation by the dinoflagellate Lingulodinium polyedrum. Aquat Microb Ecol 50:51–62
Mcleod DJ, Hallegraeff GM, Hosie GW, Richardson AJ (2012) Climate-driven range expansion of the red-tide dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans into the Southern Ocean. J Plankton Res 34:332–337
Moore SK, Trainer VL, Mantua NJ, Parker MS, Laws EA, Backer LC, Fleming LE (2008) Impacts of climate variability and future climate change on harmful algal blooms and human health. Environ Health. doi:10.1186/1476-069X-7-S2-S4
Mu R, He Y, Liu S, Wang X, Fan Z (2009) The algicidal characteristics of one algae-lysing FDT5 bacterium on Microcystis aeruginosa. Geomicrobiol J 26:516–521
Park SC, Lee JK, Kim SW, Park Y (2011) Selective algicidal action of peptides against harmful algal bloom species. PLoS ONE 6(10):e26733
Patron NJ, Waller RF, Keeling PJ (2006) A tertiary plastid uses genes from two endosymbionts. J Mol Biol 357:1373–1382
Paul C, Pohnert G (2012) Interactions of the algicidal bacterium Kordia algicida with diatoms: regulated protease excretion for specific algal lysis. PLoS ONE 6(6):e21032
Peters E, Thomas DN (1996) Prolonged darkness and diatom mortality: I. Marine Antarctic species. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 207:25–41
Pokrzywinski KL, Place AR, Warner ME, Coyne KJ (2012) Investigation of the algicidal exudate produced by Shewanella sp. IRI-160 and its effect on dinoflagellates. Harmful Algae 19:23–29
Popels LC, MacIntyre HL, Warner ME, Zhang YH, Hutchins DA (2007) Physiological responses during dark survival and recovery in Aureococcus anophagefferens (Pelagophyceae). J Phycol 43:32–42
Rensel JE, Whyte JNC (2003) Finfish mariculture and harmful algal blooms. In: Hallegraeff, GM, Anderson DM, Cembella AD (eds) Manual on harmful marine algae, revised edn. IOC UNESCO, pp 693–722
Rounsefell GA, Evans JE (1958) Large-scale experimental test of copper sulfate as a control for the Florida red tide. US Fish Wld S Spec Sci Rep 270
Saradadevi K, Raghavendra S (1992) Dark respiration protects photosynthesis against photoinhibition in mesophyll protoplasts of pea (Pisum sativum). Plant Physiol 99:1232–1237
Segovia M, Berges JA (2005) Effect of inhibitors of protein synthesis and DNA replication on the induction of proteolytic activities, caspase-like activities and cell death in the unicellular chlorophyte Dunaliella tertiolecta. Eur J Phycol 40:21–30
Sengco MR (2009) Prevention and control of Karenia brevis blooms. Harmful Algae 8:623–628
Sengco MR, Anderson DM (2004) Controlling harmful algal blooms through clay flocculation. J Eukaryot Microbiol 51:169–172
Shi S, Tang D, Liu Y (2009) Effects of an algicidal bacterium Pseudomonas mendocina on the growth and antioxidant system of Aphanizomenon flos-aquae. Curr Microbiol 59:107–112
Smayda TJ (2007) Reflections on the ballast water dispersal—harmful algal bloom paradigm. Harmful Algae 6:601–622
Smayda TJ, Mitchell-Innes B (1974) Dark survival of autotrophic, planktonic marine diatoms. Mar Biol 25:195–202
Smith GD, Doan NT (1999) Cyanobacterial metabolites with bioactivity against photosynthesis in cyanobacteria, algae and higher plants. J Appl Phycol 11:337–344
Smith VH, Schindler DW (2009) Eutrophication science: where do we go from here? Trends Ecol Evol 24:201–207
Sotirova AV, Spasova DI, Galabova DN, Karpenko E, Shulga A (2008) Rhamnolipid-biosurfactant permeabilizing effects on gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial strains. Curr Microbiol 56:639–647
Takamura Y, Yamada T, Kimoto A, Kanehama N, Tanaka T, Nakadaira S, Yagi O (2004) Growth inhibition of Microcystis cyanobacteria by l-lysine and disappearance of natural Microcystis blooms with spraying. Microbes Environ 19:31–39
Terlizzi DE, Ferrier MD, Armbrester EA, Anlauf KA (2002) Inhibition of dinoflagellate growth by extracts of barley straw (Hordeum vulgare). J Appl Phycol 14:275–280
Trainer VM, Suddleson M (2005) Monitoring approaches for early warning of domoic acid events in Washington State. Oceanography 18:228–237
Van Dolah FV (2000) Marine algal toxins: origins, health effects, and their increased occurrence. Environ Health Persp 108:133–141
Wang X, Gong L, Liang S, Han X, Zhu C, Li Y (2005) Algicidal activity of rhamnolipid biosurfactants produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Harmful Algae 4:433–443
Wisecaver JH, Hackett JD (2011) Dinoflagellate genome evolution. Annu Rev Microbiol 65:369–387
Wu J-T, Chiang Y-R, Huang W-Y, Jane W-N (2006) Cytotoxic effects of free fatty acids on phytoplankton algae and cyanobacteria. Aquat Toxicol 80:338–345
Yoon HS, Hackett JD, Van Dolah FM, Nosenko T, Lidie KL, Bhattacharya D (2005) Tertiary endosymbiosis driven genome evolution in dinoflagellate algae. Mol Biol Evol 22:1299–1308
Zingone A, Enevoldsen HO (2000) The diversity of harmful algal blooms: a challenge for science and management. Ocean Coast Manage 43:725–748
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Association (NOAA) Prevention, Control and Mitigation of HABs (PCM HAB) program (Grant #NA10NOS4780136 to KJC and MEW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tilney, C.L., Pokrzywinski, K.L., Coyne, K.J. et al. Growth, death, and photobiology of dinoflagellates (Dinophyceae) under bacterial-algicide control. J Appl Phycol 26, 2117–2127 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-014-0248-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-014-0248-z