Abstract
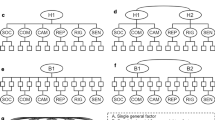
It is common to administer measures of autistic traits to those without autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) with, for example, the aim of understanding autistic personality characteristics in non-autistic individuals. Little research has examined the extent to which measures of autistic traits actually measure the same traits in the same way across those with and without an ASD. We addressed this question using a multi-group confirmatory factor invariance analysis of the Autism Quotient Short Form (AQ-S: Hoekstra et al. in J Autism Dev Disord 41(5):589–596, 2011) across those with (n = 148) and without (n = 168) ASD. Metric variance (equality of factor loadings), but not scalar invariance (equality of thresholds), held suggesting that the AQ-S measures the same latent traits in both groups, but with a bias in the manner in which trait levels are estimated. We, therefore, argue that the AQ-S can be used to investigate possible causes and consequences of autistic traits in both groups separately, but caution is due when combining or comparing levels of autistic traits across the two groups.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison, C., Auyeung, B., & Baron-Cohen, S. (2011). Toward brief “red flags” for autism screening: The short autism spectrum quotient and the short quantitative checklist in 1,000 cases and 3,000 controls. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 51(2), 202–212.e7.
American Psychiatric Association (APA). (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed., p. 75). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
Austin, E. J. (2005). Personality correlates of the broader autism phenotype as assessed by the autism spectrum quotient (AQ). Personality and Individual Differences, 38(2), 451–460.
Baron-Cohen, S., Hoekstra, R. A., Knickmeyer, R., & Wheelwright, S. (2006). The autism-spectrum quotient (AQ)—adolescent version. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 36(3), 343–350.
Baron-Cohen, S., & Wheelwright, S. (2004). The empathy quotient: An investigation of adults with Asperger syndrome or high functioning autism, and normal sex differences. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 34(2), 163–175.
Baron-Cohen, S., Wheelwright, S., Skinner, R., Martin, J., & Clubley, E. (2001). The autism-spectrum quotient (AQ): Evidence from Asperger syndrome/high-functioning autism, males and females, scientists and mathematicians. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 31(1), 5–17.
Borsboom, D. (2006). When does measurement invariance matter? Medical Care, 44(11), S176–S181.
Chen, F. F. (2007). Sensitivity of goodness of fit indices to lack of measurement invariance. Structural Equation Modeling, 14(3), 464–504.
Chen, F. F., Sousa, K. H., & West, S. G. (2005). Teacher’s corner: Testing measurement invariance of second-order factor models. Structural Equation Modeling, 12(3), 471–492.
Constantino, J. N., & Todd, R. D. (2003). Autistic traits in the general population: A twin study. Archives of General Psychiatry, 60(5), 524.
Frazier, T. W., Youngstrom, E. A., Sinclair, L., Kubu, C. S., Law, P., Rezai, A., et al. (2010). Autism spectrum disorders as a qualitatively distinct category from typical behavior in a large, clinically ascertained sample. Assessment, 17(3), 308–320.
Frazier, T. W., Youngstrom, E. A., Speer, L., Embacher, R., Law, P., Constantino, J., et al. (2012). Validation of proposed DSM-5 criteria for autism spectrum disorder. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 51(1), 28–40.e3.
Hoekstra, R. A., Vinkhuyzen, A. A., Wheelwright, S., Bartels, M., Boomsma, D. I., Baron-Cohen, S., et al. (2011). The construction and validation of an abridged version of the autism-spectrum quotient (AQ-short). Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 41(5), 589–596.
Hu, L. T., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 6(1), 1–55.
Johnson, S. A., Filliter, J. H., & Murphy, R. R. (2009). Discrepancies between self-and parent-perceptions of autistic traits and empathy in high functioning children and adolescents on the autism spectrum. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39(12), 1706–1714.
Kim, E. S., & Yoon, M. (2011). Testing measurement invariance: A comparison of multiple-group categorical CFA and IRT. Structural Equation Modeling, 18(2), 212–228.
Kuenssberg, R., Murray, A. L., Booth, T., & McKenzie, K. (2012). Structural validation of the abridged autism spectrum quotient—short form in a clinical sample of people with autism spectrum disorders. Autism. doi:10.1177/1362361312467708.
Kunihira, Y., Senju, A., Dairoku, H., Wakabayashi, A., & Hasegawa, T. (2006). Autistic traits in non-autistic Japanese populations: Relationships with personality traits and cognitive ability. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 36, 553–566.
Lundström, S., Chang, Z., Rastam, M., Gillberg, C., Larsson, H., Anckarsater, H., et al. (2012). Autism spectrum disorders and autisticlike traits: Similar etiology in the extreme end and the normal variation. Archives of General Psychiatry, 69(1), 46.
Matson, M. L., Matson, J. L., & Beighley, J. S. (2011). Comorbidity of physical and motor problems in children with autism. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 32(6), 2304–2308.
Matson, J. L., & Shoemaker, M. (2009). Intellectual disability and its relationship to autism spectrum disorders. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 30(6), 1107–1114.
McDonald, R. P., & Ho, M.-H. R. (2002). Principles and practice in reporting structural equation analyses. Psychological Methods, 7, 64–82.
Meredith, W., & Teresi, J. A. (2006). An essay on measurement and factorial invariance. Medical Care, 44(11), S69–S77.
Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. (2010). Mplus user’s guide (6th ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Muthen & Muthen.
Rajendran, G., & Mitchell, P. (2007). Cognitive theories of autism. Developmental Review, 27(2), 224–260.
Rhemtulla, M., Brosseau-Liard, P. É., & Savalei, V. (2012). When can categorical variables be treated as continuous? A comparison of robust continuous and categorical SEM estimation methods under suboptimal conditions. Psychological Methods, 17(3), 354.
Rivet, T. T., & Matson, J. L. (2011). Review of gender differences in core symptomatology in autism spectrum disorders. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 5(3), 957–976.
Rogers, S. J., Hepburn, S., & Wehner, E. (2003). Parent reports of sensory symptoms in toddlers with autism and those with other developmental disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 33(6), 631–642.
Schermelleh-Engel, K., Moosbrugger, H., & Müller, H. (2003). Evaluating the fit of structural equation models: Tests of significance and descriptive goodness-of-fit measures. Methods of psychological research online, 8(2), 23–74.
Stark, S., Chernyshenko, O. S., & Drasgow, F. (2006). Detecting differential item functioning with confirmatory factor analysis and item response theory: Toward a unified strategy. Journal of Applied Psychology, 91(6), 1292.
Sung, Y. J., Dawson, G., Munson, J., Estes, A., Schellenberg, G. D., & Wijsman, E. M. (2005). Genetic investigation of quantitative traits related to autism: Use of multivariate polygenic models with ascertainment adjustment. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 76(1), 68–81.
Tabachnick, B. G., & Fidell, L. S. (2007). Using multivariate statistics (p. 63). Boston, MA: Pearson Education Inc.
Vandenberg, R. J., & Lance, C. E. (2000). A review and synthesis of the measurement invariance literature: Suggestions, practices, and recommendations for organizational research. Organizational Research Methods, 3(1), 4–70.
Wheelwright, S., Auyeung, B., Allison, C., & Baron-Cohen, S. (2010). Defining the broader, medium and narrow autism phenotype among parents using the autism spectrum quotient (AQ). Molecular Autism, 1, 1–10.
Yu, C. Y. (2002). Evaluating cut-off criteria of model fit indices for latent variable models with binary and continuous outcomes. Unpublished Doctoral Dissertation, University of California, Los Angeles, CA. Accessed January 5, 2011 from http://www.statmodel.com/download/Yudissertation.pdf.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murray, A.L., Booth, T., McKenzie, K. et al. Are Autistic Traits Measured Equivalently in Individuals With and Without An Autism Spectrum Disorder? An Invariance Analysis of the Autism Spectrum Quotient Short Form. J Autism Dev Disord 44, 55–64 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-013-1851-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-013-1851-6