Abstract
Active electrocatalytic electrode designs are needed for the sensitive and selective detection of a single or multi-active biomolecule among biological components. We report the design of hierarchical NiO catalyst (HNC) for one-step monitoring of bioactive molecules such as ascorbic acid (AA), dopamine (DA), and uric acid (UA). The novel mesostructured geometries, active surface sites, and multi-diffused spaces for easy electron movement through gaps provide highly active electrocatalytic electrode designing surface. Controlled HNC architecture along electrode-design surface domains having double-head branches spread out along both sides of the dipole-like rod may lead to the vital electron transfer and fast response signaling of multi-bioactive molecules in one-shot triggering individually or simultaneously. Electrochemical analyses showed evidence that the proposed electrode design can detect each component up to 0.02 µM. Sensitive detection up to 1.127, 0.02, and 0.978 µM and wide-range responses of 25–800, 2–60, and 10–000 µM for AA, DA, and UA, respectively, were observed. The simultaneous monitoring and selective signaling of AA, DA, and UA in real urine samples in one step under different potentials were realized. Thus, the HNC-modified electrode can monitor and evaluate the coexistence of biomolecules simultaneously in multi-components.
Graphical Abstract
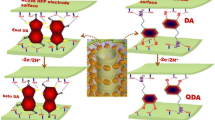
The electrochemical oxidation of AA, DA, and UA at the HNC-modified electrode and the corresponding DPV peaks with losing of 2e−/2H+.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen A, Chatterjee S (2013) Nanomaterials based electrochemical sensors for biomedical applications. Chem Soc Rev 42(12):5425–5438
Li B-R, Hsieh Y-J, Chen Y-X, Chung Y-T, Pan C-Y, Chen Y-T (2013) An ultrasensitive nanowire-transistor biosensor for detecting dopamine release from living PC12 cells under hypoxic stimulation. J Am Chem Soc 135(43):6034–16037
Zhang X, Chen X, Kai S, Wang H-Y, Yang J, Wu F-G, Chen Z (2015) Highly sensitive and selective detection of dopamine using one-pot synthesized highly photoluminescent silicon nanoparticles. Anal Chem 87(6):3360–3365
Farjami E, Campos R, Nielsen JS, Gothelf KV, Kjems J, Ferapontova EE (2013) RNA aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for selective and label-free analysis of dopamine. Anal Chem 85:121–128
Huang J, Liu Y, Hou H, You T (2008) Simultaneous electrochemical determination of dopamine, uric acid and ascorbic acid using palladium nanoparticle-loaded carbon nanofibers modified electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 24:632–637
Jiang J, Du X (2014) Sensitive electrochemical sensors for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid based on Au@Pd-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites. Nanoscale 6:11303–11309
Wachman ES, Poage RE, Stiles JR, Farkas DL, Meriney SD (2004) Spatial distribution of calcium entry evoked by single action potentials within the presynaptic active zone. J Neurosci 24(12):2877–2885
Cheng F-C, Kuo J-S, Huang H-M, Yang D-Y, Wu T-F, Tsai T-H (2000) Determination of catecholamines in pheochromocytoma cell (PC-12) culture medium by microdialysis–microbore liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 870:405–441
Zheng W, Shen B, Zhai W, Gong LR (eds) (2013) New progress on graphene research, InTech Publishing Co., Rijeka
Lapainis T, Scanlan C, Rubakhin SS, Sweedler JV (2007) A multichannel native fluorescence detection system for capillary electrophoretic analysis of neurotransmitters in single neurons. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:97–105
Xu T-Q, Zhang Q-L, Zheng J-N, Lv Z-Y, Wei J, Wang A-J, Feng J-J (2014) Simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid in the presence of ascorbic acid using Pt nanoparticles supported on reduced graphene oxide. Electrochim Acta 115:109–115
Sun JY, Gan T, Deng YP, Shi ZX, Lv Z (2015) Pt nanoparticles-functionalized hierarchically porous γ-Al2O3 hollow spheres based electrochemical sensor for ultrasensitive guaiacol detection. Sens Actuators B 211:339–345
Zhang YY, Gan T, Wan CD, Wu KB (2013) Morphology-controlled electrochemical sensing amaranth at nanomolar levels using alumina. Anal Chim Acta 764:53–58
Wu C, Tang Y, Wan CD, Liu HY, Wu KB (2015) Enhanced-oxidation and highly-sensitive detection of acetaminophen, guanine, and adenine using NMP-exfoliated graphene nanosheets-modified electrode. Electrochim Acta 166:285–292
Qu Y, Ma M, Wang Z, Zhan G, Li B, Wang X, Fang H, Zhang H, Li C (2013) Sensitive amperometric biosensor for phenolic compounds based on graphene–silk peptide/tyrosinase composite nanointerface. Biosens Bioelectron 44:85–88
Yang YJ, Li W (2014) CTAB functionalized graphene oxide/multiwalled carbon nanotube composite modified electrode for the simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and nitrite. Biosens Bioelectron 56:300–306
Fernandes DM, Costa M, Pereira C, Bachiller-Baeza B, Rodríguez-Ramos I, Guerrero-Ruiz A, Freire C (2014) Novel electrochemical sensor based on N-doped carbon nanotubes and Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Simultaneous voltammetric determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. J Colloidal Interfaces Sci 432:207–213
Abdelwahab AA, Shim Y-B (2015) Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and folic acid based on activated graphene/MWCNT nanocomposite loaded Au nanoclusters. Sens Actuators B 221:659–665
Cai W, Lai J, Lai T, Xie H, Ye J (2016) Controlled functionalization of flexible graphene fibers for the simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Sens Actuators B 224:225–232
Zhang X, Zhang Y-C, Ma L-X (2016) One-pot facile fabrication of graphene-zinc oxide composite and its enhanced sensitivity for simultaneous electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Sens Actuators B 227:488–496
Palanisamy S, Thirumalraj B, Chen S-M, Ali MA, Al-Hemaid FMA (2015) Palladium nanoparticles decorated on activated fullerene modified screen printed carbon electrode for enhanced electrochemical sensing of dopamine. J Colloidal Interfaces Sci 448:251–256
Wang Y, Huang Y, Wang B, Fang T, Chen J, Liang C (2016) Three-dimensional porous graphene for simultaneous detection of dopamine and uric acid in the presence of ascorbic acid. J Electroanal Chem 782:76–83
Wang C, Li J, Shi K, Wang Q, Zhao X, Xiong Z, Zou X, Wang Y (2016) Graphene coated by polydopamine/multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified electrode for highly selective detection of dopamine and uric acid in the presence of ascorbic acid. J Electroanal Chem 770:56–61
Ojani R, Raoof JB, Maleki AA, Safshekan S (2014) Simultaneous and sensitive detection of dopamine and uric acid using a poly(L-methionine)/gold nanoparticle-modified glassy carbon electrode. Chin J Catal 35:423–442
Hu H, Song Y, Feng M, Zhan (2016) Carbon nanomaterials for simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid in the presence of ascorbic acid: from one-dimensional to the quasi one-dimensional. Electrochim Acta 190:40–48
Ghanbari Kh, Moludi M (2016) Flower-like ZnO decorated polyaniline/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid. Anal Biochem 512:91–102
Sun CL, Lee HH, Yang JM, Wu CC (2011) The simultaneous electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid using graphene/size-selected Pt nanocomposites. Biosens Bioelectron 26(8):3450–3455
Zhang X, Yan W, Zhang J, Li Y, Tang W, Xu Q (2015) NiCo-embedded in hierarchically structured N-doped carbon nanoplates for the efficient electrochemical determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid. RSC Adv 5:65532–65539
El-Safty SA, Kiyozumi Y, Hanaoka T, Mizukami F (2008) Nanosized NiO particles wrapped into uniformly mesocaged silica frameworks as effective catalysts of organic amines. Appl CatalA 337(2):121–129
Shenashen MA, Hassen D, El-Safty SA, Isago H, Elmarakbi A, Yamaguchi H (2017) Axially oriented tubercle vein and X-crossed sheet of N-Co3O4@C hierarchical mesoarchitectures as potential heterogeneous catalysts for methanol oxidation reaction. Chem Eng J 313:83–98
Shenashen MA, Hassen D, El-Safty SA, Selim MM, Akhtar N, Chatterjee A, Elmarakbi A (2016) Mesoscopic fabric sheet racks and blocks as catalysts with efficiently exposed surfaces for methanol and ethanol electrooxidation. Adv Mater Interfaces 3(24):1600743
Gomaa H, Khalifa H, Selim MM, Shenashen MA, Kawada S, Alamoudi AS, Azzam AM, Alhamid AA, El-Safty SA (2017) Selective, photo-enhanced trapping/detrapping of arsenate anions using mesoporous blobfish head TiO2 monoliths. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(11):10826–10839
Azzam AM, Shenashen MA, Selim MM, Yamaguchi H, El-Sewify IM, Kawada S, Alhamid AA, El-Safty SA (2017) Nanospherical inorganic α-Fe core-organic shell necklaces for the removal of arsenic (V) and chromium (VI) from aqueous solution. J Phys Chem Solids 109:78–88
Selim MS, Elmarakbi A, Azzam AM, Shenashen MA, EL-Saeed AM, El-Safty SA (2018) Eco-friendly design of superhydrophobic nano-magnetite/silicone composites for marine foul-release paints. Prog Org Coat 116:21–34
Selim MS, Shenashen MA, Elmarakbi A, El-Saeed AM, Selim MM, El-Safty SA (2017) Sunflower oil-based hyperbranched alkyd/spherical ZnO nanocomposite modeling for mechanical and anticorrosive applications. RSC Adv 7:21796–21808
Selim MS, Shenashen MA, Elmarakbi A, Fatthallah NA, Hasegawa S-i, El-Safty SA (2017) Synthesis of ultrahydrophobic and thermally stable inorganic–organic nanocomposites for self-cleaning foul release coatings. Chem Eng J 320:653–666
El-Safty SA, Sakai M, Selim MM, Hendi AA (2015) Mesosponge optical sinks for multifunctional mercury ion assessment and recovery from water sources. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(24):13217–13231
Khairy M, El-Safty SA (2013) Mesoporous NiO nanoarchitectures for electrochemical energy storage: influence of size, porosity, and morphology. RSC Adv 3(45):23801–23809
Khairy M, El-Safty SA, Ismael M, Kawarada H (2012) Mesoporous NiO nanomagnets as catalysts and separators of chemical agents. Appl Catal B 127:1–10
Akhtar N, El-Safty SA, Abdelsalam ME, Kawarada H (2015) One-pot fabrication of dendritic NiO@carbon–nitrogen dot electrodes for screening blood glucose level in diabetes. Adv Healthc Mater 4(14):2110–2119
Akhtar N, El-Safty SA, Abdelsalam ME, Shenashen MA, Kawarada H (2016) Radially oriented nanostrand electrodes to boost glucose sensing in mammalian blood. Biosens Bioelectron 77:656–665
Akhtar N, Emran MY, Shenashen MA, Khalifa H, Osaka T, Faheem A, Homma T, Kawarada H, El-Safty SA (2017) Fabrication of Photo-electrochemical biosensor for ultrasensitive screening of mono-bioactive molecules: effect of geometrical structures and crystal surfaces. J Mater Chem B 5:7985–7996
Zhang X, Shi W, Zhu J, Zhao W, Ma J, Mhaisalkar S, Maria T, Yang Y, Zhang H, Hng H, Yan Q (2010) Synthesis of porous NiO nanocrystals with controllable surface area and their application as supercapacitor electrodes. Nano Res 3:643–652
Hassan D, El-Safty SA, Khalil KA, Dewidar M, Abu El-Maged G (2016) Mesoporous carbon/Co3O4 hybrid as efficient electrode for methanol electrooxidation in alkaline conditions. Int J Electrochem Sci 11:8374–8390
Khairy M, El-Safty SA (2014) Nanosized rambutan-like nickel oxides as electrochemical sensor and pseudocapacitor. Sens Actuators B 193:644–652
El-Sewify IM, Shenashen MA, Shahat A, Yamaguchi H, Selim MM, Khalil MM, El-Safty SA (2017) Ratiometric fluorescent chemosensor for Zn2+ ions in environmental samples using supermicroporous organic–inorganic structures as potential platforms. ChemistrySelect 2:11083–11090
Shenashen MA, El-Safty SA, Khairy M (2013) Trapping of biological macromolecules in the three-dimensional mesocage pore cavities of monolith adsorbents. J Porous Mater 20:679–692
Shenashen MA, Elshehy EA, El-Safty SA, Khairy M (2013) Visual monitoring and removal of divalent copper, cadmium, and mercury ions from water by using mesoporous cubic Ia3d aluminosilica sensors. Sep Pur Techn 116:73–86
Shenashen MA, El-Safty SA, Elshehy EA (2014) Monolithic scaffolds for highly selective ion sensing/removal of Co(II), Cu(II), and Cd(II) ions in water. Analyst 139:6393–6405
Shenashen MA, El-Safty SA, Elshehy EA (2014) Synthesis, morphological control, and properties of silver nanoparticles in potential applications. Part Part Syst Charact 31:293–316
Zhuo K, Jeong M-G, Chung C-H (2013) dendritic nanoporous nickel oxides for a supercapacitor prepared by a galvanic displacement reaction with chlorine ions as an accelerator. RSC Adv 3:12611–12615
Hassen D, El-Safty SA, Tsuchiya K, Chatterjee A, Elmarakbi A, Shenashen MA, Sakai M (2016) Longitudinal hierarchy Co3O4 mesocrystals with high-dense exposure facets and anisotropic interfaces for direct-ethanol fuel cells. Sci Rep 6:24330
El-Safty SA, Kiyozumi Y, Hanaoka T, Muzukami F (2014) Heterogeneous catalytic activity of NiO-silica composites designated with cubic Pm3n cage nanostructures. Appl Catal B 82:169–179
Shenashen MA, Akhtar N, Selim MM, Morsy WM, Yamaguchi H, Kawada S, Alhamid AA, Ohashi N, Ichinose I, Alamoudi AS, El-Safty SA (2017) Effective, low-cost recovery of toxic arsenate anions from water by using hollow-sphere geode traps. Chem Asian J 12(15):1952–1964
Shenashen MA, Kawada S, Selim MM, Morsy WM, Yamaguchi H, Alhamid AA, Ohashi N, Ichinose I, El-Safty SA (2017) Bushy sphere dendrites with husk-shaped branches axially spreading out from the core for photo-catalytic oxidation/remediation of toxins. Nanoscale 9:7947–7959
Emran MY, Shenashen MA, Mekawy M, Azzam AM, Akhtar N, Gomaa H, Selim MM, Faheem A, El-Safty SA (2018) Ultrasensitive in-vitro monitoring of monoamine neurotransmitters from dopaminergic cells. Sens Actuators B 259:114–124
Emran MY, Mekawy M, Akhtar N, Shenashen MA, EL-Sewify IM, Faheem A, El-Safty SA (2018) Broccoli-shaped biosensor hierarchy for electrochemical screening of noradrenaline in living cells. Biosens Bioelectron 100:122–131
Emran MY, Khalifa H, Gomaa H, Shenashen MA, Akhtar N, Mekawy M, Faheem A, El-Safty SA (2017) Hierarchical CN doped NiO with dual-head echinop flowers for ultrasensitive monitoring of epinephrine in human blood serum. Microchim Acta 184(11):4553–4562
Laviron E (1979) General expression of the linear potential sweep voltammogram in the case of diffusionless electrochemical systems. J Electroanal Chem Interfacial Electrochem 101:19–28
Chen L, Feng M, Zhan H (2014) Fundamental electrochemistry of three-dimensional graphene aerogels. RSC Adv 4:30689–30696
Kim SJ, Kim YL, Yu A, Lee J, Lee SC, Lee C, Kim MH, Lee Y (2014) Electrospun iridium oxide nanofibers for direct selective electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid. Sens Actuators B 196:480–488
Pisoschi AM, Pop A, Serban AI, Fafaneata C (2014) Electrochemical methods for ascorbic acid determination. ElectrochimActa 121:443–460
Zhao DY, Fan DW, Wang JP, Xu CX (2015) Hierarchical nanoporous platinum-copper alloy for simultaneous electrochemical determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid. MicrochimActa 182:1345–1352
Granero AM, Pierini GD, Robledo SN, Di Nezio MSD, Fernández H, Zon MA (2016) Simultaneous determination of ascorbic and uric acids and dopamine in human serum samples using three-way calibration with data from square wave voltammetry. Microchem J 129:205–212
Wang W, Xu G, Cui XT, Sheng G, Luo X (2014) Enhanced catalytic and dopamine sensing properties of electrochemically reduced conducting polymer nanocomposite doped with pure graphene oxide. Biosens Bioelectron 58:153–156
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emran, M.Y., Shenashen, M.A., Abdelwahab, A.A. et al. Design of hierarchical electrocatalytic mediator for one step, selective screening of biomolecules in biological fluid samples. J Appl Electrochem 48, 529–542 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-018-1175-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-018-1175-5