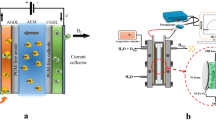
Abstract
Investigations on configurations and properties of the electrode in the membrane electrode assembly (MEA) of an electrolyzer using an anion exchange membrane (AEM) were performed based on an experimental study using a small single electrolysis cell. First, two different configurations of the catalyst layer (CL) for the MEA were prepared using commercially available materials: a catalyst-coated membrane (CCM) and a catalyst-coated substrate (CCS). Experimental electrolysis results revealed that the electrode configuration appropriate for the MEA of AEM electrolyzers is CCM-cathode and CCS-anode. Then, the effect of electrode properties (catalyst loading and binder content in CLs) on electrolysis performance was examined experimentally, revealing an optimal range of catalyst loading and binder content.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(i\) :
-
Current density, A cm− 2
- \({R_{{\text{cell}}}}\) :
-
Ohmic resistance of cell, Ω cm2
- \({T_{{\text{cell}}}}\) :
-
Cell temperature, K (°C)
- t :
-
Time, sec (min)
- \({V_{{\text{cell}}}}\) :
-
Cell voltage, V
- \({w_{{\text{cat\_A}}}}\) :
-
Catalyst loading in anode catalyst layer, mg cm− 2
- \({w_{{\text{cat\_C}}}}\) :
-
Catalyst loading in cathode catalyst layer, mg cm− 2
- \({\omega _{\text{i}}}\) :
-
Ionomer (binder) content in catalyst layer formed by catalyst-coated membrane, wt%
- \({\omega _{\text{P}}}\) :
-
Polytetrafluoroethylene (binder) content in catalyst layer formed by catalyst-coated substrate, wt%
- AEM:
-
Anion exchange membrane
- AFC:
-
Alkaline fuel cell
- CCM:
-
Catalyst-coated membrane
- CCS:
-
Catalyst-coated substrate
- CL:
-
Catalyst layer
- GDL:
-
Gas diffusion layer
- HER:
-
Hydrogen evolution reaction
- IEC:
-
Ion exchange capacity
- IPA:
-
Isopropyl alcohol
- MEA:
-
Membrane electrode assembly
- NHE:
-
Normal hydrogen electrode
- OER:
-
Oxygen evolution reaction
- OPE:
-
Octylphenol ethoxylate
- PEM:
-
Proton exchange membrane
- PEMFC:
-
Proton exchange membrane fuel cell
- PFA:
-
Perfluoroalkoxy alkane
- PGM:
-
Platinum-group metals
- PTFE:
-
Polytetrafluoroethylene
- RES:
-
Renewable energy sources
References
Mazloomi K, Gimes C (2012) Hydrogen as an energy carrier: prospects and challenges. Renew Sust Energy Rev 16:3024–3033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.02.028
Gahleitner G (2013) Hydrogen from renewable electricity: an international review of power-togas pilot plants for stationary application. Int J Hydrog Energy 38:2039–2061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.12.010
Zoulias E, Varkaraki E, Lymberopoulos N (2004) A review on water electrolysis. TCJST 4:41–71
Carmo M, Fritz DL, Mergel J, Stolten D (2013) A comprehensive review on PEM water electrolysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 38:4901–4934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.01.151
Moçoteguy P, Brisse A (2013) A review and comprehensive analysis of degradation mechanisms of solid oxide electrolysis cells. Int J Hydrog Energy 38:15887–15902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.09.045
Ito H, Maeda T, Nakano A, Kato A, Yoshida T (2013) Influence of pore structural properties of current collectors on the performance of proton exchange membrane electrolyzer. Electrochim Acta 100:242–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.05.068
Ito H (2015) Membranes. In: Bessarabov D, Wang H, Li H, Zhao N (eds) PEM electrolysis for hydrogen production. CRC Press, New York, Ch 6
Wang C (2015) Bipolar plates and plate materials. In: Bessarabov D, Wang H, Li H, Zhao N (eds) PEM electrolysis for hydrogen production. CRC Press, New York, Ch 7
Ayers KE, Anderson EB, Capuano CB, Carter BD, Dalton LT, Hanlon G, Manco J, Niedzwiecki M (2010) Research advances towards low cost, high efficiency PEM electrolysis. ECS Trans 33:3–15. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.3484496
Merle G, Wessling M, Nijmeijer K (2011) Anion exchange membranes for alkaline fuel cells: a review. J Mem Sci 377:1–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2011.04.043
Yanagi H, Fukuta K (2008) Anion exchange membrane and ionomer for alkaline membrane fuel cells (AMFCs). ECS Trans 16:257–262. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2981860
Fukuta K, Inoue H, Watanabe S, Yanagi H (2009) In-situ observation of CO2 through the self-purging in alkaline membrane fuel cell (AMFC). ECS Trans 19:23–37. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.3271358
Cao YC, Wu X, Scott K (2012) A quaternary ammonium grafted poly vinyl benzyl chloride membrane for alkaline anion exchange membrane water electrolysers with no-noble-metal catalysts. Int J Hydrog Energy 37:9524–9528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.03.116
Faraj M, Boccia M, Miller H, Martini F, Borsacchi S, Geppi M, Pucci A (2012) New LDPE based anion-exchange membranes for alkaline solid polymeric electrolyte water electrolysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 37:14992–15002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.08.012
Leng Y, Chen G, Mendoza AJ, Tighe TB, Hickner MA, Wang CY (2012) Solid-state water electrolysis with an alkaline membrane. J Am Chem Soc 134:9054–9057. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja302439z
Wu X, Scott K (2013) A Li-doped Co3O4 oxygen evolution catalyst for non-precious metal alkaline anion exchange membrane water electrolysers. Int J Hydrog Energy 38:3123–3129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.12.087
Xiao L, Zhang S, Pan J, Yang C, He M, Zhuamg L, Lu J (2012) First implementation of alkaline polymer electrolyte water electrolysis working only with pure water. Energy Environ Sci 5:7869–7871. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2EE22146B
Pavel CC, Cecconi F, Emiliani C, Santiccioli S, Scaffidi A, Catanorchi S, Comotti M (2014) High efficient platinum group metal free based membrane-electrode assembly for anion exchange membrane water electrolysis. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:1378–1381. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201308099
Vincent I, Kruger A, Bessarabov D (2017) Development of efficient membrane electrode assembly for low cost hydrogen production by anion exchange membrane electrolysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 42:10752–10761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.03.069
Kocha SS (2010) Principle of MEA preparation. In: Vielstich W, Lamm A, Gasteiger HA (eds.) Handbook of fuel cells, vol 3. Wiley, Chichester, Ch 43. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470974001.f303047
Ito H, Maeda T, Nakano A, Hasegawa Y, Yokoi M, Hwang CM, Ishida M, Kato A, Yoshida T (2010) Effect of flow regime of circulating water on a proton exchange membrane electrolyzer. Int J Hydrog Energy 35:9550–9560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.06.103
Hwang CM, Ishida M, Ito H, Maeda T, Nakano A, Hasegawa Y, Yokoi N, Kato A, Yoshida T (2011) Influence of properties of gas diffusion layers on the performance of polymer electrolyte-based unitized reversible fuel cells. Int J Hydrog Energy 36:1740–1753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.10.091
Yanagi H, Fukuta K (2010) Electrolyte materials for alkaline fuel cells and their cell performance. J Hydrog Energy Syst Soc Japan 35–2:9–14 (in Japanese).
Hibbs MR, Fujimoto CH, Cornelius CJ (2009) Synthesis and characterization of poly (phenylene)-based anion exchange membranes for alkaline fuel cells. Macromolecules 42:8316–8321. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma901538c
Switzer EE, Olson TS, Datye AK, Atanassov P, Hibbs MR, Fujimoto C, Cornelius CJ (2010) Novel KOH-free anion-exchange membrane fuel cell: performance comparison of alternative anion-exchange ionomers in catalyst ink. Electrochim Acta 55:3404–3408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2009.12.073
Wu X, Scott K (2012) A polymethacrylate-based quaternary ammonium OH– ionomer binder for non-precious metal alkaline anion exchange membrane water electrolysers. J Power Sources 214:124–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.03.069
Leng Y, Wang L, Hickner MA, Wang CY (2015) Alkaline membrane fuel cells with in-situ cross-linked ionomers. Electrochim Acta 152:93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.11.055
Piana M, Boccia M, Filpi A, Flammia E, Miller HA, Orsini M, Salusti F, Santiccioli S, Ciardelli F, Pucci A (2010) H2/air alkaline membrane fuel cell performance and durability, using novel ionomer and non-platinum group metal cathode catalyst. J Power Sources 195:5875–5881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.12.085
Wilson MS, Gottesfeld S (1992) Thin-film catalyst layers for polymer electrolyte fuel cell electrodes. J Appl Electrochem 22:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01093004
Xie J, More KL, Zawodzinski TA, Smith WH (2004) Porosimetry of MEAs made by “Thin Film Decal” method and its effect on performance of PEFCs. J Electrochem Soc 151:A1841–A1846. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1796991
Xie J, Xu F, Wood DL III, More KL, Zawodzinski TA, Smith WH (2010) Influence of ionomer content on the structure and performance of PEFC membrane electrode assembles. Electrochim Acta 55:7404–7412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2010.06.067
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) through the Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI)—Grant Number JP17K05970. The authors wish to express their gratitude to Tokuyama Corporation for their helpful advice. The authors also thank Mr. Akira Takatsuki (AIST) for his SEM expertise.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, H., Miyazaki, N., Sugiyama, S. et al. Investigations on electrode configurations for anion exchange membrane electrolysis. J Appl Electrochem 48, 305–316 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-018-1159-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-018-1159-5