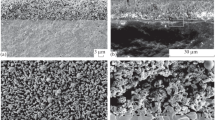
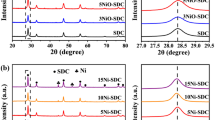
Abstract
Ni-based alloys were prepared by using the oxalate method and subsequent in-situ reduction. The crystallographic phase and microstructure of the catalysts were investigated. These bimetallic alloys were mixed with gadolinium-doped ceria in order to obtain a composite material with mixed electronic-ionic conductivity. Catalytic and electrocatalytic properties of the composite materials for the conversion of ethanol were investigated. Electrochemical tests were carried out by utilizing the Ni-based alloy/CGO cermet as a barrier layer in a conventional anode-supported solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC). A comparative study between the modified cells and a conventional anode-supported SOFC without the protective layer was made. The aim was to efficiently convert the fuel directly into electricity or syngas (H2 and CO) just before the conventional anode support. In accordance with the ex-situ catalytic tests, the SOFC anode modified with Ni–Co/CGO showed superior performance towards the direct utilization of dry ethanol than the bare anode and that modified with Ni–Cu/CGO. A peak power of 550 mW cm−2 was achieved with the dry ethanol-fed Ni–Co/CGO pre-layer modified-cell at 800 °C. A total low frequency resistance of <0.5 Ω cm2 at 0.8 V of cell voltage was recorded in the presence of ethanol directly fed to the SOFC.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xuan J, Leung MKH, Leung DYC, Ni M (2009) A review of biomass-derived fuel processors for fuel cell systems. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 13(6–7):1301–1313. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2008.09.027
Vasileiadis S, Ziaka-Vasileiadou Z (2004) Biomass reforming process for integrated solid oxide-fuel cell power generation. Chem Eng Sci 59(22–23):4853–4859. doi:10.1016/j.ces.2004.07.071
Lo Faro M, Minutoli M, Monforte G, Antonucci V, Aricò AS (2011) Glycerol oxidation in solid oxide fuel cells based on a Ni-perovskite electrocatalyst. Biomass Bioenergy 35(3):1075–1084. doi:10.1016/j.biombioe.2010.11.018
Lo Faro M, La Rosa D, Antonucci V, Aricò AS (2009) Intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cell electrolytes. J Indian Inst Sci 89(4):363–381. doi:10.1002/chin.201137207
Cowin PI, Petit CTG, Lan R, Irvine JTS, Tao S (2011) Recent progress in the development of anode materials for solid oxide fuel cells. Adv Energy Mater 1(3):314–332. doi:10.1002/aenm.201100108
Barbucci A, Viviani M, Carpanese P, Vladikova D, Stoynov Z (2006) Impedance analysis of oxygen reduction in SOFC composite electrodes. Electrochim Acta 51(8–9):1641–1650. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2005.02.106
Steele BCH, Bae J-M (1998) Properties of La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3−x (LSCF) double layer cathodes on gadolinium-doped cerium oxide (CGO) electrolytes: II. Role of oxygen exchange and diffusion. Solid State Ion 106(3–4):255–261. doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(97)00430-X
Lo Faro M, Vita A, Pino L, Aricò AS (2013) Performance evaluation of a solid oxide fuel cell coupled to an external biogas tri-reforming process. Fuel Process Technol 115:238–245. doi:10.1016/j.fuproc.2013.06.008
Schlapbach L, Zuttel A (2001) Hydrogen-storage materials for mobile applications. Nature 414(6861):353–358. doi:10.1038/35104634
Zignani SC, Baglio V, Linares JJ, Monforte G, Gonzalez ER, Aricò AS (2012) Performance and selectivity of PtxSn/C electro-catalysts for ethanol oxidation prepared by reduction with different formic acid concentrations. Electrochim Acta 70:255–265. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2012.03.055
Aricò AS, Cretì P, Antonucci P, Antonucci V (1998) Comparison of ethanol and methanol oxidation in a liquid-feed solid polymer electrolyte fuel cell at high temperature. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 1(2):66–68. doi:10.1149/1.1390638
de Carvalho Macedo I (1998) Greenhouse gas emissions and energy balances in bio-ethanol production and utilization in Brazil (1996). Biomass Bioenergy 14(1):77–81. doi:10.1016/S0961-9534(97)00038-X
Hernández L, Kafarov V (2009) Use of bioethanol for sustainable electrical energy production. Int J Hydrog Energy 34(16):7041–7050. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.07.089
Tsiakaras P, Demin A (2001) Thermodynamic analysis of a solid oxide fuel cell system fuelled by ethanol. J Power Sour 102(1–2):210–217. doi:10.1016/S0378-7753(01)00803-5
Cimenti M, Hill JM (2009) Thermodynamic analysis of solid oxide fuel cells operated with methanol and ethanol under direct utilization, steam reforming, dry reforming or partial oxidation conditions. J Power Sour 186(2):377–384. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.10.043
Saunders GJ, Preece J, Kendall K (2004) Formulating liquid hydrocarbon fuels for SOFCs. J Power Sour 131(1–2):23–26. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2004.01.040
Murray EP, Tsai T, Barnett SA (1999) A direct-methane fuel cell with a ceria-based anode. Nature 400(6745):649–651. doi:10.1038/23220
Tippawan P, Arpornwichanop A (2014) Energy and exergy analysis of an ethanol reforming process for solid oxide fuel cell applications. Bioresour Technol 157:231–239. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.113
La Rosa D, Sin A, Lo Faro M, Monforte G, Antonucci V, Aricò AS (2009) Mitigation of carbon deposits formation in intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells fed with dry methane by anode doping with barium. J Power Sour 193(1):160–164. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.01.096
La Rosa D, Lo Faro M, Monforte G, Antonucci V, Aricò AS (2009) Comparison of the electrochemical properties of intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells based on protonic and anionic electrolytes. J Appl Electrochem 39(4):477–483. doi:10.1007/s10800-008-9668-2
Sin A, Kopnin E, Dubitsky Y, Zaopo A, Aricò AS, La Rosa D, Gullo LR, Antonucci V (2007) Performance and life-time behaviour of NiCu–CGO anodes for the direct electro-oxidation of methane in IT-SOFCs. J Power Sour 164(1):300–305. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.10.078
Lo Faro M, La Rosa D, Nicotera I, Antonucci V, Aricò AS (2009) Electrochemical behaviour of propane-fed solid oxide fuel cells based on low Ni content anode catalysts. Electrochim Acta 54(22):5280–5285. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2009.03.077
Sin A, Kopnin E, Dubitsky Y, Zaopo A, Aricò AS, Gullo LR, La Rosa D, Antonucci V (2006) Influence of operating conditions on the direct electrochemical oxidation of methane on cermet based anodes. Fuel Cells 6(2):137–140. doi:10.1002/fuce.200500107
Lo Faro M, Frontera P, Antonucci P, Aricò AS (2015) Ni–Cu based catalysts prepared by two different methods and their catalytic activity toward the ATR of methane. Chem Eng Res Des 93:269–277. doi:10.1016/j.cherd.2014.05.014
Lo Faro M, Reis R, Saglietti G, Sato A, Ticianelli E, Zignani S, Aricò AS (2014) Ni–Cu/CGO composite electrocatalyst as protective layer for a solid oxide fuel cell anode fed with ethanol. ChemElectroChem. doi:10.1002/celc.201402017
Montinaro D, Sglavo V, Bertoldi M, Zandonella T, Aricò AS, Lo Faro M, Antonucci V (2006) Tape casting fabrication and co-sintering of solid oxide “half cells” with a cathode–electrolyte porous interface. Solid State Ion 177(19):2093–2097. doi:10.1016/j.ssi.2006.01.016
Lo Faro M, La Rosa D, Frontera P, Antonucci P, Antonucci V, Aricò AS (2010) Propane-fed solid oxide fuel cell based on a composite Ni-La-CGO anode catalyst. Catal Lett 136(1–2):57–64. doi:10.1007/s10562-010-0295-2
Lo Faro M, Modafferi V, Frontera P, Antonucci P, Aricò AS (2013) Catalytic behavior of Ni-modified perovskite and doped ceria composite catalyst for the conversion of odorized propane to syngas. Fuel Process Technol 113:28–33. doi:10.1016/j.fuproc.2013.03.010
Lo Faro M, Antonucci V, Antonucci P, Aricò AS (2012) Fuel flexibility: a key challenge for SOFC technology. Fuel 102:554–559. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2012.07.031
Acknowledgments
The present work was in part carried out in the framework of the Research Program promoted by the Brazialian “Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico“entitled “Ciência sem Fronteiras” processo no 402180/2012-7. S. C. Zignani wants to thank CNPq for post-doctoral fellowship awarded under the reference number (CNPq Proc. 238319/2012-1). R. M. Reis wants to thank FAPESP agency for post-doctoral fellowship (FAPESP Proc. 2014/04100-2). The authors acknowledge the Italian Ministry of Research and Education for the financial support of the BIOITSOFC project within the program “PROGRAMMI DI RICERCA SCIENTIFICA DI RILEVANTE INTERESSE NAZIONALE- PRIN PROGRAMMA DI RICERCA - Anno 2010–2011 - prot. 2010KHLKFC”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lo Faro, M., Reis, R.M., Saglietti, G.G.A. et al. Investigation of Ni-based alloy/CGO electro-catalysts as protective layer for a solid oxide fuel cell anode fed with ethanol. J Appl Electrochem 45, 647–656 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-015-0849-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-015-0849-5