Abstract
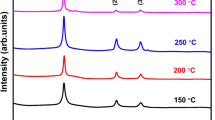
As-prepared electrodeposited CuInSe2 film is amorphous and rough. After CuInSe2 films growth, cadmium sulfide layers are deposited by chemical bath. The interface between the CuInSe2 layer and the CdS layer is a p–n junction for high-efficiency solar cells. The CuInSe2 layer must be defect-free and smooth to make a junction. In this work, CuInSe2 films with a smooth surface are obtained by heating the substrate and solution, and the solar cell of open circuit voltage is improved from 69 to 371 mV, the fill factor from 26.3 to 52 % and the conversion efficiency from 0.49 to 6.46 %. The structural properties of these selenized films are investigated using X-ray diffraction (XRD). Field-emission scanning electron microscopy images indicate that the ordered copper indium diselenide thin films are entirely filled. XRD results show that the copper indium diselenide thin films are crystalline with highly preferential orientation. Energy-dispersive spectroscopy analysis was used to determine the composition of the films.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luque A, Hegedus S (eds) (2006) Handbook of photovoltaic science and engineering. Wiley, New York
Rega N, Siebentritt S, Beckers I, Beckmann J, Alberts J, Lux-Steiner M (2003) Thin Solid Films 431–432:186
Tseng BH, Lin SB, Hsieh KC, Hwang HL (1995) J Cryst Growth 1206–1210:150
Akl AAS, Ashour A, Ramadan AA, Abd El-Hady K (2001) Vacuum 61:75
Hsiao YJ, Hsueh TJ, Shieh JM, Yeh YM, Wang CC, Dai BT (2011) IEEE 978-1-4577-0505
Hanna G, Mattheis J, Laptev V, Yamamoto Y, Rau U, Schock HW (2003) Thin Solid Films 431–432:31
Hu SY, Lee WH, Chang SC, Cheng YL, Wang YL (2011) J Electrochem Soc 158(5):B557–B561
Minemoto T, Wakisaka Y, Takakura H (2011) Jpn J Appl Phys 031203:50
Benaicha M, Benouattas N, Benazzouz C, Ouahab L (2009) Solar Energy Mater Solar Cells 93:262–266
Oliveira MCF, Azevedo M, Cunha A (2002) Thin Solid Films 405:129
Chassaing E, Ramdani O, Grand PP, Guillemoles JF, Lincot D (2008) Phys Stat Solid (c) 5:3445
Zaretskaya EP et al (2003) Raman spectroscopy of CuInSe2 thin films prepared by selenization. J Phys Chem Solids 64(9–10):1989–1993
Dejene FB (2010) Curr Appl Phys 36:10
Tanino H, Maeda T, Fujikake H, Nakanishi H, Endo S, Irie T (1992) Am Phys Soc 13323–13330:45
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiang, CS., Lee, W.H., Chang, T.W. et al. Improving conversion efficiency of co-electrodeposited CuInSe2 thin film solar cells with substrate and solution heating. J Appl Electrochem 45, 549–556 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-015-0799-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-015-0799-y