Abstract
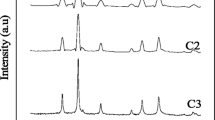
This paper shows how magnetic nanoparticles are produced by electrochemical synthesis using a low carbon steel bar as an anode and 100 mA cm−2 electric perturbations at room temperature. Two different kinds of salts, (CH3)4NCl and NaCl, were used to prepare the supporting electrolyte solutions. This allowed a comparison to be made between a surfactant and common salt, and allowed their influence on particle size to be analyzed. Additionally, mixtures of water and ethanol were added to the electrolyte solution in order to improve particle size distribution. The nanoparticle samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction, TEM, magnetization measurements, and Raman and Mössbauer spectroscopy. The results showed that after an optimized time of 10 min, the nanoparticles obtained in all the evaluated electrolytes were mainly magnetite (Fe3O4). The particles were between 8 and 10 nm in size. Depending on the nature of the electrolyte, the magnetite nanoparticles exhibited high purity and stoichiometry. The presence of ethanol in the electrolyte avoided particle agglomeration during the formation of magnetite. When the magnetic nanoparticles were exposed to an external magnetic field they showed superparamagnetic behavior and negligible coercivity. Such qualities are extremely useful for applications like ferrofluid precursors.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salas G, Costo R, Morales MP (2012) Chapter 2—Synthesis of inorganic nanoparticles. In: Frontiers of nanoscience. Elsevier, New York, pp 35–79
Fajaroh F, Setyawan H, Widiyastuti W, Winardi S (2012) Synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles by surfactant-free electrochemical method in an aqueous system. Adv Powder Technol 23:328–333
Cabrera L, Gutierrez S, Menendez N, Morales MP, Herrasti P (2008) Magnetite nanoparticles: electrochemical synthesis and characterization. Electrochim Acta 53:3436–3441
Figuerola A, Corato R di, Manna L, Pellegrino T (2010) From iron oxide nanoparticles towards advanced iron-based inorganic materials designed for biomedical applications. Pharmacol Res 62:126–143
Ningthoujam RS, Vatsa RK, Kumar A, Pandey BN, Banerjee S, Tyagi AK (2012) Functionalized magnetic nanoparticles: concepts, synthesis and application in cancer hyperthermia. Functional materials. Elsevier, New York, pp 229–260
Petcharoen K, Sirivat A (2012) Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles via the chemical co-precipitation method. Mat Sci Eng B 177:421–427
Chin AB, Yaacob II (2007) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles via w/o micro emulsion and Massart’s procedure. J Mater Process Technol 191:235–237
Marques RFC, Garcia C, Lecante P, Ribeiro SJL, Noé L, Silva NJO, Amaral VTS, Millán A, Verelst M (2008) Electro-precipitation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles in ethanol. J Magn Magn Mater 320:2311–2315
Ibrahim M, Serrano KG, Noe L, Garcia C, Verelst M (2009) Electro-precipitation of magnetite nanoparticles: an electrochemical study. Electrochim Acta 55:155–158
Dang F, Enomoto N, Hojo J, Enpuku K (2009) Sonochemical synthesis of monodispersed magnetite nanoparticles by using an ethanol–water mixed solvent. Ultrason Sonochem 16:649–654
Hajdú A, Tombácz E, Illés E, Bica D, Vékás L (2008) Magnetite nanoparticles stabilized under physiological conditions for biomedical application. Progr Colloid Polym Sci 135:29–37
Tombácz E (2006) Magnetite in aqueous medium: coating its surface coated with it. Romanian Rep Phys 58(3):281–286
Li G, Li X, Peng W, Fan X, Zhang G, Zhang F (2009) Synthesis of nearly monodisperse nanoparticles in alcohol: a pressure and solvent-induced low-temperature strategy. Appl Surf Sci 255:7021–7027
Levy L, Sahoo Y, Kim KS, Bergey EJ, Prasad PN (2002) Nanochemistry: synthesis and characterization of multifunctional nanoclinics for biological applications. Chem Mat 14:3715–3721
Guo C, Hu Y, Qian H, Ning J, Xu S (2011) Magnetite (Fe3O4) tetrakaidecahedral microcrystals: synthesis, characterization, and micro-Raman study. Mater Charact 62:148–151
Roychowdhury A, Pati SP, Kumar S, Das D (2014) Effects of magnetite nanoparticles on optical properties of zinc sulfide in fluorescent-magnetic Fe3O4/ZnS nanocomposites. Powder Technol 254:583–590
Legodi M, De Waal D (2007) The preparation of magnetite, goethite, hematite and maghemite of pigment quality from mill scale iron waste. Dye Pigment 74:161–168
Urquijo JP, Casanova H, Morales AL, Zysler RD (2014) Engineering iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedicine and bioengineering applications. Rev Fac de Ing 71:230–243
Stevens JG, Khasanov A, Miller JW, Pollak H, Li Z (1998) Mössbauer mineral handbook. Mössbauer Effect Data Center, Asheville
Murad E, Cashion J (2004) Mössbauer spectroscopy of environmental materials and their industrial utilization. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Norwell, p 417
Barrero CA, Morales AL, Mazo-Zuluaga J, Jaramillo F, Pérez G, Escobar DM, Arroyave C, Tobón J, Montoya PM, Osorio L, Vandenberghe RE, Greneche JM (2003) Synthesis and Mössbauer characterization of Cu and Cr doped magnetites. ReV de Metal (Madrid) 39:62–67
Araújo-Neto RP, Silva-Freitas EL, Carvalho JF, Pontes TRF, Silva KL, Damasceno IHM, Egito EST, Dantas AL, Morales MA, Carriço AS (2014) Monodisperse sodium oleate coated magnetite high susceptibility nanoparticles for hyperthermia applications. J Magn Magn Mater 364:72–79
López-López MT, Durán JDG, Delgado AV, González-Caballero F (2005) Stability and magnetic characterization of oleate-covered magnetite ferrofluids in different nonpolar carriers. J Colloid Interface Sci 291:144–151
Knobel M, Nunes WC, Socolovsky LM, De Biasi E, Vargas JM, Denardin JC (2008) Superparamagnetism and other magnetic features in granular materials: a review on ideal and real systems. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 8:2836–2857
Acknowledgments
The authors are pleased to acknowledge the financial assistance of the “Departamento Administrativo de Ciencia, Tecnología e Innovación—COLCIENCIAS”, and the Universidad de Antioquia through the project 111556934616 and “Estrategia de Sostenibilidad 2013–2014 de la Universidad de Antioquia”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marín, T., Ortega, D., Montoya, P. et al. A new contribution to the study of the electrosynthesis of magnetic nanoparticles: the influence of the supporting electrolyte. J Appl Electrochem 44, 1401–1410 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-014-0766-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-014-0766-z