Abstract
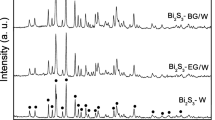
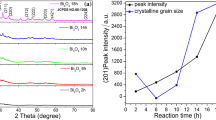
This paper reports a systematic study of the synthesis of rod-like Bi2O3 via a facile one-step precipitation method with the addition of different surfactants. The formation mechanisms for the surfactants assisted chemical precipitation method of rod-like Bi2O3 have been briefly discussed. The electrochemical measurement shows the Bi2O3 prepared by using P123 as surfactant exhibits the largest specific capacitance of 1,350 F g−1 at current density of 0.1 A g−1 as well as superior rate capability and excellent cycle stability. The scalable syntheses and prominent capacitive properties of this material suggest its potential applications in energy storage.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gujar TP, Shinde VR, Lokhande CD, Mane RS, Han SH (2005) Bismuth oxide thin films prepared by chemical bath deposition (CBD) method: annealing effect. Appl Surf Sci 250:161–167
Takeyama T, Takahashi N, Nakamura T, Itoh S (2005) Microstructure characterization of δ-Bi2O3 thin film under atmospheric pressure by means of halide CVD on c-sapphire. J Cryst Growth 275:460–466
Sammes NM, Tompsett GA, Nafë H, Aldinger F (1999) Bismuth based oxide electrolytes- structure and ionic conductivity. J Eur Ceram Soc 19:1801–1826
Fan HT, Teng XM, Pan SS, Ye C, Li GH, Zhang LD (2005) Optical properties ofδ-Bi2O3 thin films grown by reactive sputtering. Appl Phys Lett 87:231916
He WD, Qin W, Wu XH, Ding XB, Chen L, Jiang ZH (2007) The photocatalytic properties of bismuth oxide films prepared through the sol-gel method. Thin Solid Films 515:5362–5365
Ng SN, Tan YP, Taufiq-Yap YH (2009) Mechanochemical synthesis and characterisation of bismuth-niobium oxide ion conductors. J Phys Sci 20(1):75–86
Oprea II, Hesse H, Betzler K (2004) Optical properties of bismuth borate glasses. Opt Mater 26:235–237
Hanna TA (2004) The role of bismuth in the SOHIO process. Coord Chem Rev 248:429–440
Azad AM, Larose S, Akbar SA (1994) Bismuth oxide-based solid electrolytes for fuel cells. J Mater Sci 29:4135–4151
Adamian ZN, Abovian HV, Aroutiounian VM (1996) Smoke sensor on the base of Bi2O3 sesquioxide. Sens Actuators B 35:241–243
Gujar TP, Shinde VR, Lokhande CD, Han SH (2006) Electrosynthesis of Bi2O3 thin films and their use in electrochemical supercapacitors. J Power Sources 161:1479–1485
Zheng FL, Li GR, Ou YN, Wang ZL, Su CY, Tong YX (2010) Synthesis of hierarchical rippled Bi2O3 nanobelts for supercapacitor applications. Chem Commun 46:5021–5023
Wang HW, Hu ZA, Chang YQ, Chen YL, Lei ZQ, Zhang ZY, Yang YY (2010) Facile solvothermal synthesis of a graphene nanosheet-bismuth oxide composite and its electrochemical characteristics. Electrochim Acta 55:8974–8980
Yuan DS, Zeng JH, Kristian N, Wang Y, Wang X (2009) Bi2O3 deposited on highly ordered mesoporous carbon for supercapacitors. Electrochem Commun 11:313–317
Xia NN, Yuan DS, Zhou TX, Chen JX, Mo SS, Liu YL (2011) Microwave synthesis and electrochemical characterization of mesoporous carbon@Bi2O3 composites. Mater Res Bull 46:687–691
Shen XP, Wu SK, Zhao H, Liu Q (2007) Synthesis of single-crystalline Bi2O3 nanowires by atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition approach. Phys E 39:133–136
Shen YD, Li YW, Li WM, Zhang JZ, Hu ZG, Chu JH (2012) Growth of Bi2O3 ultrathin films by atomic layer deposition. J Phys Chem C 116:3449–3456
Li W (2006) Facile synthesis of monodisperse Bi2O3 nanoparticles. Mater Chem Phys 99:174–180
Bodé M, Cachet C, Bach S, Pereira-Ramos JP, Ginoux JC, Yu LT (1997) Rechargeability of MnO2 in KOH media produced by decomposition of dissolved KMnO4 and Bi(NO3)3 mixtures, Mn-Bi complexes. J Electrochem Soc 144:792–801
Li JT, Zhao W, Huang FQ, Manivannan A, Wu NQ (2011) Single-crystalline Ni(OH)2 and NiO nanoplatelet arrays as supercapacitor electrodes. Nanoscale 3:5103–5109
Zang JF, Li XD (2011) In situ synthesis of ultrafine β-MnO2/polypyrrole nanorod composites for high-performance supercapacitors. J Mater Chem 21:10965–10969
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21031001 and 21376105) and 44th Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, H., Cao, S., Xia, N. et al. Controllable growth of Bi2O3 with rod-like structures via the surfactants and its electrochemical properties. J Appl Electrochem 44, 735–740 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-014-0681-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-014-0681-3