Abstract
Purpose
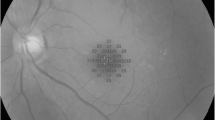
To explore a measuring method for retinal sensitivity in macular hole area by Microperimeter-3 (MP-3) and evaluate its predictive value on visual prognosis.
Methods
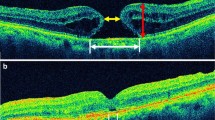
This was a case series study including 44 eyes of 44 patients with idiopathic macular hole. Retinal sensitivity inside and 0.5 degree outside the macular hole margin was measured, and its mean value was defined as macular hole sensitivity (MHS). Best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), minimum diameter of macular hole (MD), IS/OS defect diameter, retinal sensitivity in 8 degrees and 2 degrees were also recorded preoperatively and 4 months after operation.
Results
All macular holes were closed after surgery. BCVA was significantly improved from 1.06 ± 0.39 at baseline to 0.31 ± 0.24 at 4 months postoperatively (P < 0.001). Meanwhile, MHS was also significantly improved from 12.02 ± 3.74 dB at baseline to 20.72 ± 4.00 dB at 4 months postoperatively (P < 0.001). MD, preoperative IS/OS defect diameter, preoperative BCVA, preoperative retinal sensitivity in 8 degrees and 2 degrees, and preoperative MHS were all correlated with postoperative BCVA at 4 months, but only preoperative MHS showed liner relationships to postoperative BCVA at 4 months by multivariate stepwise linear analysis.
Conclusions
Macular hole sensitivity by MP-3 could reflect the change of central retinal function after successful macular hole surgery. Compared to preoperative retinal sensitivity in 8 degrees and 2 degrees, preoperative macular hole sensitivity is a better predictor for visual prognosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mcdonnell PJ, Fine SL, Hillis AI (1982) Clinical features of idiopathic macular cysts and holes. Am J Ophthalmol 93(6):777–786
Polk TD, Smiddy WE Jr, Flynn HW (1996) Bilateral visual function after macular hole surgery. Ophthalmology 103(3):422–426
Kelly NE, Wendel RT (1991) Vitreous surgery for idiopathic macular holes. Results of a pilot study. Arch Ophthalmol 109(5):654
Shinoda H, Shinoda K, Satofuka S, Imamura Y, Ozawa Y, Ishida S, Inoue M (2010) Visual recovery after vitrectomy for macular hole using 25-gauge instruments. Acta Ophthalmol 86(2):151–155
Richter-Mueksch S, Sacu S, Osarovsky-Sasin E, Stifter E, Kiss C, Velikay-Parel M (2009) Visual performance 3 years after successful macular hole surgery. Br J Ophthalmol 93(5):660–663
Meng Q, Zhang S, Ling Y, Cui D, Jin Y (2011) Long-term anatomic and visual outcomes of initially closed macular holes. Am J Ophthalmol 151(5):896–900
Sun Z, Gan D, Jiang C, Wang M, Sprecher A, Jiang AC, Xu G (2012) Effect of preoperative retinal sensitivity and fixation on long-term prognosis for idiopathic macular holes. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 250(11):1587–1596
Chen WC, Wang Y, Li XX (2012) Morphologic and functional evaluation before and after successful macular hole surgery using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography combined with microperimetry. Retina 32(9):1733–1742
Scupola A, Mastrocola A, Sasso P, Fasciani R, Montrone L, Falsini B, Abed E (2013) Assessment of retinal function before and after idiopathic macular hole surgery. Am J Ophthalmol 156(1):132–139
Imai H, Ohta K (2010) Microperimetric determination of retinal sensitivity in areas of dissociated optic nerve fiber layer following internal limiting membrane peeling. Jpn J Ophthalmol 54(5):435
Pilli S, Zawadzki RJ, Werner JS et al (2012) Visual outcome correlates with inner macular volume in eyes with surgically closed macular hole. Retina 32(10):2085
Shpak AA, Shkvorchenko DO, Sharafetdinov IK, Yukhanova OA (2016) Predicting anatomical results of surgical treatment of idiopathic macular hole. Int J Ophthalmol 9(2):253
Nizawa T, Baba T, Kitahashi M, Oshitari T, Yamamoto S (2017) Different fixation targets affect retinal sensitivity obtained by microperimetry in normal individuals. Clin Ophthalmol 11:2011–2015
Bonnabel A, Bron AM, Isaico R, Dugas B, Nicot F, Creuzot-Garcher C (2013) Long-term anatomical and functional outcomes of idiopathic macular hole surgery. The yield of spectral-domain OCT combined with microperimetry. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 251(11):2505–2511
Itoh Y, Inoue M, Rii T, Hiraoka T, Hirakata A (2012) Significant correlation between visual acuity and recovery of foveal cone microstructures after macular hole surgery. Am J Ophthalmol 153(1):111–119
Yanagita T, Shimizu K, Fujimura F, Takano M (2009) Fixation point after successful macular hole surgery with internal limiting membrane peeling. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging 40(2):109
Dal VM, Lavia C, Nassisi M, Grignolo FM, Fea AM (2016) Microperimetric assessment after epiretinal membrane surgery: 4-year follow-up. J Ophthalmol 1:1–5
Ozdemir H, Karacorlu SA, Senturk F, Karacorlu M, Uysal O (2008) Assessment of macular function by microperimetry in unilateral resolved central serous chorioretinopathy. Eye 22(2):204
Midena E, Vujosevic S (2011) Microperimetry in diabetic retinopathy. Saudi J Ophthalmol 25(2):131
Sugawara T, Sato E, Baba T, Hagiwara A, Tawada A, Yamamoto S (2011) Relationship between vision-related quality of life and microperimetry-determined macular sensitivity in patients with retinitis pigmentosa. Jpn J Ophthalmol 55(6):643–646
Sjaarda RN, Frank DA, Glaser BM, Thompson JT, Murphy RP (1993) Assessment of vision in idiopathic macular holes with macular microperimetry using the scanning laser ophthalmoscope. Ophthalmology 100(10):1513–1518
Chung H, Shin CJ, Kim JG, Yoon YH, Kim HC (2011) Correlation of microperimetry with fundus autofluorescence and spectral-domain optical coherence tomography in repaired macular holes. Am J Ophthalmol 151(1):128–136
Sjaarda RN, Frank DA, Glaser BM, Thompson JT, Murphy RP (1993) Assessment of vision in idiopathic macular holes with macular microperimetry using the scanning laser ophthalmoscope. Ophthalmology 100(10):1513
Ozdemir H, Karacorlu M, Senturk F, Karacorlu SA, Uysal O (2010) Retinal sensitivity and fixation changes 1 year after triamcinolone acetonide assisted internal limiting membrane peeling for macular hole surgery–a MP-1 microperimetric study. Acta Ophthalmol 88(6):e222–e227
Ooto S, Hangai M, Takayama K, Uedaarakawa N, Hanebuchi M, Yoshimura N (2012) Photoreceptor damage and foveal sensitivity in surgically closed macular holes: an adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscopy study. Am J Ophthalmol 154(1):174–186
Nakabayashi M, Fujikado T, Ohji M, Saito Y, Tano Y (2000) Fixation patterns of idiopathic macular holes after vitreous surgery. Retina 20(2):170
Tarita-Nistor L, González EG, Mandelcorn MS, Lillakas L, Steinbach MJ (2009) Fixation stability, fixation location, and visual acuity after successful macular hole surgery. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 50(1):84
Chalam KV, Murthy RK, Gupta SK, Brar VS, Grover S (2010) Foveal structure defined by spectral domain optical coherence tomography correlates with visual function after macular hole surgery. Eur J Ophthalmol 20(3):572–577
Kadonosono K, Yabuki K, Nishide T, Uchio E, Marron JA (2003) Measured visual acuity of fellow eyes as a prognostic factor in macular hole surgery. Am J Ophthalmol 135(4):493–498
Tsuiki E, Fujikawa A, Miyamura N, Yamada K, Mishima K, Kitaoka T (2007) Visual field defects after macular hole surgery with indocyanine green-assisted internal limiting membrane peeling. Am J Ophthalmol 143(4):704–705
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge, or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Qi, Y., Liang, X. et al. MP-3 measurement of retinal sensitivity in macular hole area and its predictive value on visual prognosis. Int Ophthalmol 39, 1987–1994 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-018-1032-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-018-1032-x