Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the effect of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection on choroidal thickness (CT) and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness (RNFLT).
Methods
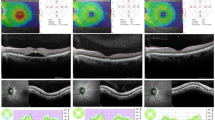
The study included 25 patients with H. pylori infection and 25 healthy individuals as the control group. Helicobacter pylori patients were classified as the pre-treatment (Group 1; n: 25) and the post-treatment (Group 2; n: 25). RNFLT and CT were measured before and after treatment of H. pylori infection, using enhanced depth imaging (EDI) spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (Spectralis, Heidelberg Engineering, Heidelberg, Germany). The axial length and intraocular pressure were also measured.
Results
The mean subfoveal CT was 320.96 ± 29.15 μm in Group 1 and 287.48 ± 49.17 in the control group (p = 0.007), while the mean subfoveal CT did not show any difference between Group 2 and the control group (p > 0.05). No statistically significant difference was determined between the H. pylori patients and the control group in respect of RNFLT values (p > 0.05).
Conclusions
CT increases during H. pylori infection and returns to the normal range within 6 weeks of treatment. RNFLT does not show any change during H. pylori infection. The data related to the subfoveal CT may be useful in understanding the pathogenesis of central serous chorioretinopathy developing in H. pylori patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suerbaum S, Michetti P (2002) Helicobacter pylori infection. N Engl J Med 347:1175–1186
Parsonnet J, Shmuely H, Haggerty T (1999) Fecal and oral shedding of Helicobacter pylori from healthy infected adults. JAMA 282:2240–2245
Malaty HM (2007) Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 21:205–214
Cardenas VM, Mulla ZD, Ortiz M, Graham DY (2006) Iron deficiency and Helicobacter pylori infection in the United States. Am J Epidemiol 163:127–134
Franceschi F, Gasbarrini A (2007) Helicobacter pylori and extragastric diseases. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 21:325–334
Realdi G, Dore MP, Fastame L (1999) Extradigestive manifestations of Helicobacter pylori infection: fact and fiction. Dig Dis Sci 44:229–236
Arslan E, Atilgan H, Yavaşoğlu I (2009) The prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in obese subjects. Eur J Intern Med 20:695–697
Ersoy O, Ersoy R, Yayar O et al (2007) H pylori infection in patients with Behcet’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 13:2983–2985
Mindel JS, Rosenberg EW (1997) Is Helicobacter pylori of interest to ophthalmologists? Ophthalmology 104:1729–1730
Cotticelli L, Borrelli M, D’Alessio AC et al (2006) Central serous chorioretinopathy and Helicobacter pylori. Eur J Ophthalmol 16:274–278
Saccà SC, Pascotto A, Venturino GM et al (2006) Prevalence and treatment of Helicobacter pylori in patients with blepharitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:501–508
Kim JM, Kim SH, Park KH et al (2011) Investigation of the association between Helicobacter pylori infection and normal tension glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:665–668
Chey WD, Wong BCY, Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology (2007) American College of Gastroenterology guideline on the management of Helicobacter pylori infection. Am J Gastroenterol 102:1808–1825
Garza-González E, Perez-Perez GI, Maldonado-Garza HJ, Bosques-Padilla FJ (2014) A review of Helicobacter pylori diagnosis, treatment, and methods to detect eradication. World J Gastroenterol 20:1438–1449
Spaide RF, Koizumi H, Pozzoni MC, Pozonni MC (2008) Enhanced depth imaging spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol 146:496–500
Mateo-Montoya A, Mauget-Faÿse M (2014) Helicobacter pylori as a risk factor for central serous chorioretinopathy: literature review. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 5:355–358
Testerman TL, Morris J (2014) Beyond the stomach: an updated view of Helicobacter pylori pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. World J Gastroenterol 20:12781–12808
Chmiela M, Gajewski A, Rudnicka K (2015) Helicobacter pylori vs coronary heart disease - searching for connections. World J Cardiol 7:187–203
Aragona P, Magazzù G, Macchia G et al (1999) Presence of antibodies against Helicobacter pylori and its heat-shock protein 60 in the serum of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. J Rheumatol 26:1306–1311
Argenziano G, Donnarumma G, Iovene MR et al (2003) Incidence of anti-Helicobacter pylori and anti-CagA antibodies in rosacea patients. Int J Dermatol 42:601–604
Baykal C, Buyukbabani N, Akinturk S, Saglik E (2006) Prurigo pigmentosa: not an uncommon disease in the Turkish population. Int J Dermatol 45:1164–1168
Huang X, Qu X, Yan W et al (2010) Iron deficiency anaemia can be improved after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Postgrad Med J 86:272–278
Windle HJ, Kelleher D, Crabtree JE (2007) Childhood Helicobacter pylori infection and growth impairment in developing countries: a vicious cycle? Pediatrics 119:754–759
Rosenstock SJ, Jørgensen T, Andersen LP, Bonnevie O (2000) Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with lifestyle, chronic disease, body-indices, and age at menarche in Danish adults. Scand J Public Health 28:32–40
Wotherspoon AC, Doglioni C, Diss TC et al (1993) Regression of primary low-grade B-cell gastric lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue type after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Lancet (London, England) 342:575–577
Graham DY, Lew GM, Klein PD et al (1992) Effect of treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection on the long-term recurrence of gastric or duodenal ulcer. A randomized, controlled study. Ann Intern Med 116:705–708
Wong BC-Y, Lam SK, Wong WM et al (2004) Helicobacter pylori eradication to prevent gastric cancer in a high-risk region of China: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 291:187–194
Raghunath A, Hungin APS, Wooff D, Childs S (2003) Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: systematic review. BMJ 326:737
Oldenburg B, Diepersloot RJA, Hoekstra JBL (1996) High seroprevalence of Helicobacter pylori in diabetes mellitus patients. Dig Dis Sci 41:458–461
Abdel-Hady H, Zaki A, Badra G et al (2007) Helicobacter pylori infection in hepatic encephalopathy: relationship to plasma endotoxins and blood ammonia. Hepatol Res 37:1026–1033
Kerr JR (2000) An association between sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) and Helicobacter pylori infection. Arch Dis Child 83:429–434
Portnoi VA (1997) Helicobacter pylori infection and anorexia of aging. Arch Intern Med 157:269
Saccà SC, Vagge A, Pulliero A, Izzotti A (2014) Helicobacter pylori infection and eye diseases. Medicine (Baltimore) 93:216
Portal-Celhay C, Perez-Perez GI (2006) Immune responses to Helicobacter pylori colonization: mechanisms and clinical outcomes. Clin Sci 110:305–314
Byrne MF, Kerrigan SW, Corcoran PA et al (2003) Helicobacter pylori binds von Willebrand factor and interacts with GPIb to induce platelet aggregation. Gastroenterology 124:1846–1854
Handin RI (2003) A hitchhiker’s guide to the galaxy—an H. pylori travel guide. Gastroenterology 124:1983–1985
Spaide RF, Yannuzzi LA, Slakter JS et al (1995) Indocyanine green videoangiography of idiopathic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Retina 15:100–110
Talks J, Koshy Z, Chatzinikolas K (2007) Use of optical coherence tomography, fluorescein angiography and indocyanine green angiography in a screening clinic for wet age-related macular degeneration. Br J Ophthalmol 91:600–601
Fanea L, Fagan AJ (2012) Review: magnetic resonance imaging techniques in ophthalmology. Mol Vis 18:2538–2560
Wolff-Korman PG, Kormann BA, Hasenfratz GC, Spengel FA (2009) Duplex and color Doppler ultrasound in the differential diagnosis of choroidal tumors. Acta Ophthalmol 70:66–70
Kim S-W, Oh J, Kwon S-S et al (2011) Comparison of choroidal thickness among patients with healthy eyes, early age-related maculopathy, neovascular age-related macular degeneration, central serous chorioretinopathy, and polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Retina 31:1904–1911
Ulusoy DM, Duru N, Ataş M et al (2015) Measurement of choroidal thickness and macular thickness during and after pregnancy. Int J Ophthalmol 8:321–325
Kim JW, Park MH, Kim YJ, Kim YT (2016) Comparison of subfoveal choroidal thickness in healthy pregnancy and pre-eclampsia. Eye (Lond) 30:349–354
Esmaeelpour M, Považay B, Hermann B et al (2011) Mapping choroidal and retinal thickness variation in type 2 diabetes using three-dimensional 1060-nm optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:5311–5316
Akay F, Gundogan FC, Yolcu U et al (2016) Choroidal thickness in systemic arterial hypertension. Eur J Ophthalmol 26:152–157
Duru N, Altinkaynak H, Erten Ş et al (2016) Thinning of Choroidal thickness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis unrelated to disease activity. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 24:246–253
Altinkaynak H, Duru N, Uysal BS et al (2016) Choroidal thickness in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus analyzed by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 24:254–260
Karalezli A, Eroglu FC, Kivanc T, Dogan R (2014) Evaluation of choroidal thickness using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography in patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: a comparative study. Int J Ophthalmol 7:1030–1034
Mauget-Faÿsse M, Kodjikian L, Quaranta M et al (2002) Helicobacter pylori in central serous chorioretinopathy and diffuse retinal epitheliopathy. Results of the first prospective pilot study. J Fr Ophtalmol 25:1021–1025
Casella AMB, Berbel RF, Bressanim GL et al (2012) Helicobacter pylori as a potential target for the treatment of central serous chorioretinopathy. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 67:1047–1052
Asensio-Sánchez VM, Rodríguez-Delgado B, García-Herrero E et al (2008) Central serous chorioretinopathy as an extradigestive manifestation of Helicobacter pylori gastric infection. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol 83:177–182
Kountouras J, Mylopoulos N, Boura P et al (2001) Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and glaucoma. Ophthalmology 108:599–604
Zeng J, Liu H, Liu X, Ding C (2015) The relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and open-angle glaucoma: a meta-analysis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 56:5238–5245
Franceschi F (2002) Cross-reactivity of anti-CagA antibodies with vascular wall antigens: possible pathogenic link between Helicobacter pylori infection and atherosclerosis. Circulation 106:430–434
Kusters JG, van Vliet AHM, Kuipers EJ (2006) Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Clin Microbiol Rev 19:449–490
Acknowledgements
The authors report no conflict of interests. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interests to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Can, M.E., Kaplan, F.E., Uzel, M.M. et al. The association of Helicobacter pylori with choroidal and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness. Int Ophthalmol 38, 1915–1922 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-017-0677-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-017-0677-1