Abstract.
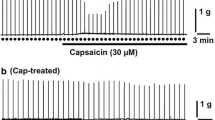
We investigated the role of capsaicin-sensitive afferent neurons in receptive relaxation of the rat stomach in response to distension. Under urethane anesthesia, a balloon with barostat was inserted through the pylorus and placed in the forestomach. Isobaric distension was performed in a stepwise increment of 2 mmHg, each lasting for 2 min, while the corresponding intragastric volume was recorded. Gastric distension produced the intraballoon volume in a progressive manner with saturation, suggesting the occurrence of receptive relaxation of the stomach during distension. Intragastric application of capsaicin significantly enhanced the degree of receptive relaxation. The capsaicin-induced enhancement of receptive relaxation was totally abolished by bilateral vagotomy as well as chemical ablation of capsaicin-sensitive afferent neurons. Likewise, the enhanced receptive relaxation in response to stomach distension was also significantly attenuated by pretreatment of the animals with NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME, an inhibitor of nitric oxide (NO) synthase), calcitonin gene related peptide (CGRP)8-37 (CGRP antagonist), indomethacin and ONO-8711 (EP1 receptor antagonist). These results suggest that capsaicin significantly enhanced the receptive relaxation induced by gastric distention through both vagal nerves and capsaicin-sensitive afferent neurons. This process is intervened by endogenous NO and CGRP in addition to prostaglandins (PGs), and the effect of PGs may be mediated by EP1 receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 9 October 2006; accepted 10 November 2006
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taniguchi, M., Mashita, Y., Matsuzaka, Y. et al. Role of capsaicin-sensitive afferent neurons in receptive relaxation induced by gastric distension in rats. Inflammopharmacol 15, 273–277 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-007-1586-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-007-1586-0