Abstract
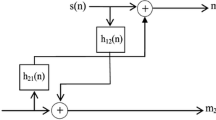
This paper presents a new adaptive blind source separation (BSS) algorithm for acoustic noise reduction and speech enhancement applications in a car framework. The forward BSS structure is often used to separate speech from noise and enhances the speech signal at the output processing. The drawback of most speech enhancement methods that are based on BSS structures is the use of a manual voice activity detection (VAD) system to control the source separation process. In this work, we propose a new algorithm based on the forward BSS structure and an automatic VAD (AVAD) system. The new AVAD system uses an adaptive approach based on a modified normalized least mean square (NLMS) adaptive algorithm to get a new speech enhancement algorithm. This proposed algorithm allows to: (i) reduce the computational complexity of previous techniques based on AVAD system; (ii) enhance the quality of the output speech signal. We have carried out intensive experiments on the proposed algorithm and others state of the art algorithms that use VAD or AVAD systems. In this paper, we show the efficiency of the proposed algorithm in terms of objective and subjective criteria.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albouy, B., & Deville, Y. (2003). Alternative structures and power spectrum criteria for blind segmentation and separation of convolutive speech mixtures. In 4th international symposium on independent component analysis and blind signal separation (ICA) (pp. 361–366), Nara.
Al-Kindi, M. J., & Dunlop, J. (1989). Improved adaptive noise cancellation in the presence of signal leakage on the noise reference channel. Signal Process, 17(3), 241–250.
Araki, S., Makino, S., Aichner, R., Nishikawa, T., & Saruwatari, H. (2003) Subband based blind source separation with appropriate processing for each frequency band. In 4th international symposium on independent component analysis and blind signal separation (pp. 499–504). IEEE ICA 2003, Nara.
Bendoumia, R., & Djendi, M. (2014). Variable step-sizes new efficient two-channel backward algorithm for speech intelligibility enhancement: A subband approach. Applied Acoustics, 76, 209–222.
Bouquin-Jeannès, R. L., Azirani, A. A., & Faucon, G. (1997). Enhancement of speech degraded by coherent and incoherent noise using a cross-spectral estimator. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 5, 484–487.
Charkani, N. H. (1996). Auto-adaptive separation of convolutive mixtures, applications to hand-free telephony in cars, Ph.D. dissertation (in French), National Pollytechnique of Grenoble, France.
Chien, J. T., Lai, P. Y. (2005) Car speech enhancement using a microphone array. International Journal of Speech Technology, 8(1), 79–91.
Combescure, P. (1981). 20 listes de dix phrases phonétiquement équilibrées. Revue d’Acoustique, 56, 34–38.
Darazirar, I., & Djendi, M. (2015). A two-sensor Gauss-Seidel fast affine projection algorithm for speech enhancement and acoustic noise reduction. Applied Acoustics, 96, 39–52.
Deller, J., Proakis, J., & Hansen, J. (1993). Discrete time processing of speech signals. New York: MacMillan Publishing.
Djendi, M. (2010) Advanced techniques for two-microphone noise reduction in mobile communications (Ph.D. dissertation (in French), University of Rennes 1, France, no. 19012010).
Djendi, M., & Bendoumia, R. (2013). A new adaptive filtering subband algorithm for two channel acoustic noise reduction and speech enhancement. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 39(8), 2531–2550.
Djendi, M., & Bendoumia, R. (2014). A new efficient two-channel backward algorithm for speech intelligibility enhancement: A subband approach. Applied Acoustics, 76, 209–222.
Djendi, M., Gilloire, A., & Scalart, P. (2006) Noise cancellation using two closely spaced microphones: Experimental study with a specific model and two adaptive algorithms. In 2006 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing. ICASSP 2006 Proceedings (Vol. 3, pp. 744–747).
Djendi, M., Scalart, P., & Gilloire, A. (2013). Analysis of two-sensors forward BSS structure with post-filters in the presence of coherent and incoherent noise. Speech Communication, 55(10), 975–987.
Djendi, M., Scalart, P., & Gilloire, A. (2013). Analysis of two-sensors forward BSS structurewith post-filters in the presence of coherent and incoherent noise. Speech Communications, 55(10), 975–987.
Djendi, M., & Zoulikha, M. (2014). New automatic forward and backward blind sources separation algorithms for noise reduction and speech enhancement. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 40, 2072–2088.
Duong, Q. K., Ngoc, C., Park, S.-H., & Nam (2008). Application of block on-line blind source separation to acoustic echo cancellation. The Journal of Acoustical Society of Corea, 27(1E), 3 pp. 17–24.
Erik Visser, M., Otsuka, T.-W., & Lee (2003). A spatio-temporal speech enhancement scheme for robust speech recognition in noisy environments. Speech Communications, 41, 393–407.
Haykin, S. (2002). Adaptive filter theory (4th ed.). Upper Saddle River: Prentice-Hall.
Hu, Y., & Loizou, P. C. (2007). Subjective comparison and evaluation of speech enhancement algorithms. Speech Communications, 49, 588–601.
Hu, Y., & Loizou, P. C. (2008). Evaluation of objective quality measures for speechenhancement. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 16(1), 229–238.
Ikeda, S., & Sugiyama, A. (1999). An adaptive noise canceller with low signal-distorsion in the presence of crosstalk. IEICE Transactions on Fundamentals, E82-A, 1517–1525.
ITU (2001) Perceptual Evaluation of Speech Quality (PESQ), and Objective Method for End-to-End Speech Quality Assessment of Narrowband Telephone Networks and Speech Codecs. ITU-T Recommendation.
ITU-T (1996). Methods for subjective determination of transmission quality. Geneva: International Telecommunications Union (ITU-T) Recommendation.
Kazuhiro, K. (2012) Subjective quality measurement of speech its evaluation, estimation applications (1st ed.). Berlin: Springer.
Kocinski, J. (2008). Speech intelligibility improvement using convolutive blind source separation assisted by denoising algorithms. Speech Commununications, 50(1), 29–37.
Kocinski, J., & Sek, A. P. (2005). Speech intelligibility in various spatial configurations of background noise. Archives of Acoustics, 30(2), 173–191.
Lee, K. A., & Gan, W. S. (2004) Improving convergence of the NLMS algorithm using constrained subband updates. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 11(9), 736–739.
Lepauloux, L., Sound recording distant by system multi-sensors. Application tospoken communication in noisy environment (Ph.D. dissertation (in French), University of Rennes 1, France, no. 4156).
Ma, J., Hu, Y., & Loizou, P. C. (2009). Objective measures for predicting speech intelligibilityin noisy conditions based on new band-importance functions. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 125(5), 3387–3405.
Marwa, A., Abd El-Fattah, M. A., Dessouky, M. I., Abbas, A. M., Diab, S. M., El-Rabaie, E. M., et al. (2014). Speech enhancement with an adaptive Wiener filter. International Journal of Speech Technology, 17(1), 53–64.
Mayyas, K. (2004). Fast implementation of a subband adaptive algorithm for acoustic echo cancellation. Journal of Electrical Engineering-Bratislava, 55(5–6), 113–121.
Meyer, J., & Simmer, K. U. Multi-channel speech enhancement in a car environment using Wiener filtering and spectral subtraction. In 1997 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (Vol. 2, pp. 1167–1170).
Navarro, L. (2007). Représentation tridimensionnelle de la phase dans un plan temps fréquence-Contribution à l’analyse des signaux quasi-stationnaires (Ph.D. dissertation (in French), University of Saint-Étienne, France, no. 461 IVS).
Parra, L., & Spence, C. (2000). Convolutive blind separation of nonstationary sources. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 8(3), 320–327.
Kunche, P., Sasi Bhushan Rao, G., Reddy, K. V. V. S, & Uma Maheswari R. (2015) A new approach to dual channel speech enhancement based on hybrid PSOGSA. International Journal of Speech Technology, 18(1), 45–56.
Rabiner, L., & Juang, B.-H. (1993). Fundamentals of speech recognition. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
Sayed, A. H. (2003). Fundamentals of adaptive filtering. New York: Wiley.
Scalart, P., & Lepauloux L. (2010) On the convergence behavior of recursive adaptive noise cancellation structure in the presence of crosstalk. In Conference of sensor signal processing for defence (SSPD 2010) (pp. 1–4).
Scalart, P., & Filho, J. (1996) Speech enhancement based on a priori signal to noise estimation. In 1996 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (pp. 629–32).
Selvi, R. S., & Suresh, G. R. (2016). Hybridization of spectral filtering with particle swarm optimization for speech signal enhancement. International Journal of Speech Technology, 19(1), 19–31.
Sullivan, T. M. (1996). Multi-microphone correlation-based processing for robust automatic speech recognition (Dissertation, Ph. D., Carnegie Mellon University). http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~robust.
Trawicki Marek, B., & Johnson Michael, T. (2012). Distributed multichannel speech enhancement with minimum mean-square error short-time spectral amplitude, log-spectral amplitude, and spectral phase estimation. Signal Processing, 92, 345–356.
Tsujikawa, M., & Iso K.-I. (2004). Hands-free speech recognition using blind source separation post-processed by two-stage spectral subtraction. In INTERSPEECH 2004 - ICSLP, 8th international conference on spoken language processing (pp. 2073–2076), Jeju Island, Korea
Van Gerven, S.,& Van Compernolle, D. (1992) Feedforward and feedback in symmetric adaptive noise canceller: stability analysis in a simplified case. In Eusipco 92, European signal processing conference (pp. 1081–1084). Brussels.
Van Gerven, S., & Van Compernolle, D. (1995). Signal separation by symmetric adaptive decorrelation: Stability, convergence, and uniqueness. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 74(3), 1602–1612.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zoulikha, M., Djendi, M. A new robust forward BSS adaptive algorithm based on automatic voice activity detector for speech quality enhancement. Int J Speech Technol 21, 1007–1020 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-018-9555-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-018-9555-0