Abstract
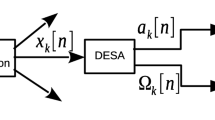
In this paper, we propose a novel multicomponent amplitude and frequency modulated (AFM) signal model for parametric representation of speech phonemes. An efficient technique is developed for parameter estimation of the proposed model. The Fourier–Bessel series expansion is used to separate a multicomponent speech signal into a set of individual components. The discrete energy separation algorithm is used to extract the amplitude envelope (AE) and the instantaneous frequency (IF) of each component of the speech signal. Then, the parameter estimation of the proposed AFM signal model is carried out by analysing the AE and IF parts of the signal component. The developed model is found to be suitable for representation of an entire speech phoneme (voiced or unvoiced) irrespective of its time duration, and the model is shown to be applicable for low bit-rate speech coding. The symmetric Itakura–Saito and the root-mean-square log-spectral distance measures are used for comparison of the original and reconstructed speech signals.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouguelia, M. R., Nowaczyk, S., Santosh, K. C., & Verikas, A. (2018). Agreeing to disagree: Active learning with noisy labels without crowdsourcing. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 9, 1307–1319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-017-0645-0.
Bradbury, J. (2000). Linear predictive coding. http://my.fit.edu/~vkepuska/ece5525/lpc_paper.pdf.
Chu, W. C. (2004). Speech coding algorithms: Foundation and evolution of standardized coders. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Equipments, T. (1990). 40, 32, 24, 16 kbit/s adaptive differential pulse code modulation (adpcm). ITU-T Recommendation, G, 726:59.
Furui, S., & Sondhi, M. M. (1991). Advances in speech signal processing. New York: Marcel Dekker.
Garofolo, J., Lamel, L., Fisher, W., Fiscus, J., Pallett, D., Dahlgren, N., et al. (1993). TIMIT acoustic-phonetic continuous speech corpus. Philadelphia: Linguistic Data Consortium.
George, E. B., & Smith, M. J. T. (1997). Speech analysis/synthesis and modification using an analysis-by-synthesis/overlap-add sinusoidal model. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 5(5), 389–406.
Gray, A., & Markel, J. (1976). Distance measures for speech processing. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 24(5), 380–391.
Hood, A. S., Pachori, R. B., Reddy, V. K., & Sircar, P. (2015). Parametric representation of speech employing multi-component AFM signal model. The International Journal of Speech Technology, 18(3), 287–303.
Jayant, N. S., & Noll, P. (1984). Digital coding of waveforms: Principles and applications to speech and video. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Kay, S. M. (1988). Modern spectral estimation. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Kroon, P., & Deprettere, E. F. (1988). A class of analysis-by-synthesis predictive coders for high quality speech coding at rates between 4.8 and 16 kbit/s. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 6(2), 353–363.
Maragos, P., Kaiser, J. F., & Quatieri, T. F. (1993a). Energy separation in signal modulations with application to speech analysis. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 41(10), 3024–3051.
Maragos, P., Kaiser, J. F., & Quatieri, T. F. (1993b). On amplitude and frequency demodulation using energy operators. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 41(4), 1532–1550.
McAulay, R. J., & Quatieri, T. F. (1984). Magnitude-only reconstruction using a sinusoidal speech model. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP 1984) (pp. 441–444).
McAulay, R. J., & Quatieri, T. F. (1986). Speech analysis/synthesis based on a sinusoidal representation. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 34(4), 744–754.
McAulay, R. J., & Quatieri, T. F. (1990). Pitch estimation and voicing detection based on a sinusoidal speech model. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, (ICASSP 1990) (pp. 249–252).
McAulay, R. J., & Quatieri, T. F. (1992). Low-rate speech coding based on the sinusoidal model. In S. Furui & M. M. Sondhi (Eds.), Advances in speech signal processing. New York: Marcel Dekker. chap 6.
Mowlaee, P., Christensen, M. G., & Jensen, S. H. (2011). New results on single-channel speech separation using sinusoidal modeling. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 19(5), 1265–1277.
Mukherjee, H., Obaidullah, S. M., Santosh, K. C., Phadikar, S., & Roy, K. (2018). Line spectral frequency-based features and extreme learning machine for voice activity detection from audio signal. The International Journal of Speech Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-018-9525-6.
Pachori, R. B., & Sircar, P. (2006). Speech analysis using Fourier-Bessel expansion and discrete energy separation algorithm. In 12th Digital Signal Processing Workshop, 4th Signal Processing Education Workshop (pp. 423–428). IEEE.
Pachori, R. B., & Sircar, P. (2010). Analysis of multicomponent AM-FM signals using FB-DESA method. Digital Signal Processing, 20(1), 42–62.
Potamianos, A., & Maragos, P. (1999). Speech analysis and synthesis using an AM-FM modulation model. Speech Communication, 28(3), 195–209.
Quatieri, T. F., & Danisewicz, R. G. (1990). An approach to co-channel talker interference suppression using a sinusoidal model for speech. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 38(1), 56–69.
Rabiner, L. R., & Juang, B. H. (1993). Fundamentals of speech recognition. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Ramamohan, S., & Dandapat, S. (2006). Sinusoidal model-based analysis and classification of stressed speech. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 14(3), 737–746.
Recommendation G. (1988). Pulse code modulation (PCM) of voice frequencies. Geneva: ITU.
Schroeder, J. (1993). Signal processing via Fourier-Bessel series expansion. Digital Signal Processing, 3(2), 112–124.
Schroeder, M., & Atal, B. (1985). Code-excited linear prediction (CELP): High-quality speech at very low bit rates. In Acoustics, speech, and signal processing, IEEE international conference on ICASSP’85 (Vol. 10, pp. 937–940). IEEE.
Sircar, P., & Saini, R. K. (2007). Parametric modeling of speech by complex AM and FM signals. Digital Signal Processing, 17(6), 1055–1064.
Sircar, P., & Sharma, S. (1997). Complex FM signal model for non-stationary signals. Signal Processing, 57(3), 283–304.
Sircar, P., & Syali, M. S. (1996). Complex AM signal model for non-stationary signals. Signal Processing, 53(1), 35–45.
Spanias, A. S. (1994). Speech coding: A tutorial review. Proceedings of the IEEE, 82(10), 1541–1582.
Tabet, Y., Boughazi, M., & Afifi, S. (2018). Speech analysis and synthesis with a refined adaptive sinusoidal representation. The International Journal of Speech Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-018-9519-4.
Wei, B., & Gibson, J. D. (2001). Comparison of distance measures in discrete spectral modeling. Master’s thesis, Southern Methodist University, Dallas, TX.
Zliobaite, I., Bifet, A., Pfahringer, B., & Holmes, G. (2014). Active learning with drifting streaming data. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 25(1), 27–39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bansal, M., Sircar, P. Low bit-rate speech coding based on multicomponent AFM signal model. Int J Speech Technol 21, 783–795 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-018-9542-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-018-9542-5