Abstract
In this paper, we address the problem of speech enhancement by adaptive filtering algorithms. A particular attention has been paid to the backward blind source separation (BBSS) algorithm and its use in crosstalk resistant speech enhancement applications. In this paper, we propose to implement the BBSS algorithm in the wavelet-domain. The proposed backward wavelet BBSS (WBBSS) algorithm is then used in speech enhancement application when important crosstalk interferences are presents. The new WBBSS algorithm shows better performances in terms of convergence speed and steady state in comparison with the classical BBSS one. The performances properties of the proposed algorithm are evaluated in term of segmental SNR (SegSNR), segmental mean square error (SegMSE), and cepstral distance (CD) criteria. The obtained results have confirmed the best performance of the proposed WBBSS algorithm in a lot of situations when blind noisy observations are available.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BSS:
-
Blind source separation
- BBSS:
-
Backward blind source separation
- DFT:
-
Discrete Fourier transform
- DWT:
-
Discrete wavelet transform
- WBBSS:
-
Wavelet transform of BBSS
- ANC:
-
Adaptive noise cancellation
- LMS:
-
Least mean square
- NLMS:
-
Normalized LMS
- TSNR:
-
Two-step noise reduction
- MSE:
-
Mean square error
- SNR:
-
Signal to noise ratio
- SegSNR:
-
Segmental signal to noise ratio
- MSE:
-
Mean square error
- SegMSE:
-
Segmental mean square error
- CD:
-
Cepstral distance
- dB:
-
Decibel
- VAD:
-
Voice activity detector
- E :
-
Expectation operator
- H:
-
Mixing matrix
- W:
-
Unmixing matrix
- m:
-
Delay index
- n:
-
Discrete time index
- J:
-
DWT scale index
- L:
-
Real and adaptive impulse responses length
- M:
-
Mean averaging value of CD, SegSNR, SegMSE
- fs :
-
Sampling frequency
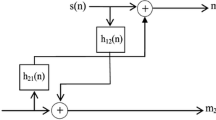
- \({\text{s}}\left( {\text{n}} \right)\) :
-
Speech signal
- \({\text{b}}\left( {\text{n}} \right)\) :
-
Punctual noise
- \({{\text{m}}_{\text{1}}}\left( {\text{n}} \right)\) :
-
First noisy observation
- \({{\text{m}}_{\text{2}}}\left( {\text{n}} \right)\) :
-
Second noisy observation
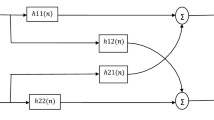
- \({{\text{h}}_{{\text{11}}}}\left( {\text{n}} \right){\text{ and }}{{\text{h}}_{{\text{22}}}}\left( {\text{n}} \right)\) :
-
Direct impulse responses
- \({{\text{h}}_{{\text{12}}}}\left( {\text{n}} \right){\text{ and }}{{\text{h}}_{{\text{21}}}}\left( {\text{n}} \right)\) :
-
Cross-coupling impulse responses
- \(\delta \left( {\text{n}} \right)\) :
-
Dirac impulse
- \({{\text{v}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{(n)}}\) :
-
Estimated speech by forward structure
- \({{\text{v}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(n)}}\) :
-
Estimated noise by forward structure
- \({{\text{w}}_{{\text{12}}}}\left( {\text{n}} \right)\) and \({{\text{w}}_{{\text{21}}}}\left( {\text{n}} \right)\) :
-
Adaptive coefficients
- \({{\mathbf{w}}_{12}}\left( {\text{n}} \right)\) and \({{\mathbf{w}}_{21}}\left( {\text{n}} \right)\) :
-
Adaptive filter vectors
- \({\mathbf{P}}_{{{\text{J, K}}}}^{{\left( {\text{1}} \right)}}\left( {\text{n}} \right)\) :
-
Discrete wavelet transform of \({{\text{m}}_{\text{1}}}\left( {\text{n}} \right)\)
- \({\mathbf{P}}_{{{\text{J, K}}}}^{{\left( {\text{2}} \right)}}\left( {\text{n}} \right)\) :
-
Discrete wavelet transform of \({{\text{m}}_{\text{2}}}\left( {\text{n}} \right)\)
- \({r_{{{\text{v}}_{\text{1}}}{{\text{v}}_{\text{2}}}}}\left( {\text{m}} \right){\text{ }}\) :
-
Cross-correlation between v1(n) and v2(n)
- \({r_{{{\text{v}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{v}}_{\text{1}}}}}\left( {\text{m}} \right)\) :
-
Cross-correlation between v2(n) and v1(n)
- \({\uptheta _1}\) and \({\uptheta _2}\) :
-
Fixed step-sizes of BBSS
- \({\upmu _{12}}{\text{ and }}{\upmu _{21}}\) :
-
Fixed step-sizes of WBBSS
- \({\varsigma _1}\) and \({\varsigma _2}\) :
-
Small positive constant
- \(\upphi \left( {\text{n}} \right)\) :
-
Discret wavelet function
References
Al-Kindi, M. J., & Dunlop, J. (1989). Improved adaptive noise cancellation in the presence of signal leakage on the noise reference channel. Signal Processing, 17(3), 241–250.
Bactor, P., & Garg, A. (2012). Different techniques for the enhancement of the intelligibility of a speech signal. International Journal of Engineering Research and Development, 2(2), 57–64.
Benesty, J., & Cohen, I. (2017). Multichannel speech enhancement in the STFT domain. In J. Benesty, & I. Cohen (Eds.), Canonical correlation analysis in speech enhancement, Springer briefs in electrical and computer engineering (pp. 79–101). New York: Springer.
Boll, SF (1979). Suppression of acoustic noise in speech using spectral subtraction. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 27, 113–120.
Bouzid, A., & Ellouze, N. (2016). Speech enhancement based on wavelet packet of an improved principal component analysis. Journal Computer Speech and Language, 35, 58–72.
Cappé, O. (1994). Elimination of the musical noise phenomenon with the Ephraïm and Malah noise suppressor. IEEE Transactions on Speech Audio Processing, 2(2), 345–349.
Davila, C. E. (1984). A subspace approach to estimation of autoregressive parameters from noisy measurements. IEEE Transaction on Signal processing, 46, 531–534.
Dixit, S., & Mulge, M. Y. (2014). Review on speech enhancement techniques, International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing, 3(8), 285–290.
Djendi, M., Bensafia, S., & Safi, M. (2016). A frequency co-channel adaptive algorithm for speech quality enhancement, In International Conference on Engineering and MIS (ICEMIS).
Djendi, M., Khemies, F., & Morsli, A. (2015). A Frequency Domain Adaptive Decorrelating Algorithm for Speech Enhancement. In International Conference on Speech and Computer, SPECOM 2015, pp. 51–54.
Djendi, M., Scalart, P., & Gilloire, A. (2006). Noise cancellation using two closely spaced microphones: Experimental study with a specific model and two adaptive algorithms. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Vol. 3, pp. 744–747.
Djendi, M., & Scalart, P. (2012). Double Pseudo Affine Projection algorithm for speech enhancement and acoustic noise reduction. 2012 Proceedings of the 20th European, Romania, Bucharest, Vol. 1, pp. 2080–2084.
Djendi, M., Scalart, P., & Gilloire, A. (2013). Analysis of two-sensor forward BSS structure with post-filters in the presence of coherent and incoherent noise. Speech Communication, 55(10), 975–987.
Doclo, S., & Moonen, M. (2002). GSVD-based optimal filtering for signal and multi-microphone speech enhancement. IEEE Transaction on Signal processing, 50, 2230–2244.
Dong, J., Wei, X. P., & Zhang, Q. (2009). Speech enhancement algorithm based on high-order Cumulant parameter estimation. International Journal of Innovative Computing information and Control, 5, 2725–2733.
Ephraim, Y., LevAri, H., Roberts, W. J. J. (2014). A brief survey of speech enhancement. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 10, 104–106.
Ephraim, Y., & Malah, D. (1984). Speech enhancement using a minimum mean-square error short-time spectral amplitude estimator. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 32(6), 1109–1121.
Ephraim, Y., & Malah, D. (1985). Speech enhancement using a minimum mean-square error log-spectral amplitude estimator. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, ASSP-33(2), 443–445.
Ghribi, K., Djendi, M., & Berkani, D. (2016). A wavelet-based forward BSS algorithm for acoustic noise reduction and speech enhancement. Applied Acoustics, 105, 55–66.
Goldsworthy, R. L. (2014). Two-microphone spatial filtering improves speech reception for cochlear-implant users in reverberant conditions with multiple noise sources. Trends in Hearing, 18, 1–13.
Hu, Y., & Loizou, P. C. (2007). A comparative intelligibility study of single-microphone noise reduction algorithms. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 122(3), 1777–1786.
Hu, Y., & Loizou, P. C. (2008). Evaluation of objective quality measures for speech enhancement. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 16(1), 229–238.
Jin, Y. G., Shin, J. W., & Kim, N. S. (2014). Spectro-temporal filtering for multichannel speech enhancement in short-time Fourier transform domain. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 21(3), 352–355.
Jutten, C., & Herrault, J. (1991). Blind separation of sources: an adaptive algorithm based on neuromimetic architecture. Signal Processing, 24, 1–10.
Lee, G., & Dae Na, S. (2016). Seong K2, Cho JH3, Nam Kim M4. Wavelet speech enhancement algorithm using exponential semi-soft masks filtering. Bioengineered, 7(5), 352–356.
Lee, K. A., & Gan, W. S. (2004). Improving convergence of the NLMS algorithm using constrained subband updates. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 11(9), 736–739.
Loizou, P. C. (2007). Speech enhancement: Theory and practice (pp. 589–599). Boca Raton, FL: Taylor and Francis.
Mansour, A., Jutten, C., & Loubaton, P. (1996). Subspace method for blind separation of sources and for a convolutive mixture model. Signal processing VIII, theories and applications (pp. 2081–2084).
Nguyen Thi, H. L., & Jutten, C. (1995). Blind sources separation for convolutive mixtures. Signal Processing, 45, 209–229.
Plapous, C., Marro, C., Scalart, P. (2005). Speech enhancement using harmonic regeneration, In IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, Signal Processing, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1, pp. 157–160.
Plapous, C., Marro, C., Scalart, P., Mauuary, L., & Two-Step, A. (2004). Noise reduction technique. In IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, Signal Processing, Montral, Quebec Canada, 1, pp. 289–292.
Scalart, P., Filho, J. (1996). Speech enhancement based on a priori signal to noise estimation. In International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing. pp. 629–632.
Selva Nidhyananthan, S., Shantha Selva Kumari, R., & Arun Prakash, A. (2014). A review on speech enhancement algorithms and why to combine with environment classification. International Journal of Modern Physics C, 25(10), 210–225.
Tong, R., Bao, G., & Ye, Z. (2015). A higher order subspace algorithm for multichannel speech enhancement. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 22(11), 2004–2008.
Van Gerven, S., & Van Compernolle, D. (1992). Feed forward and feedback in symmetric adaptive noise canceller: Stability analysis in a simplified case. In European Signal Processing Conference, Brussels, Belgium. pp. 1081–1084.
Weinstein, E., Feder, M., & Oppenheim, A. V. (1993). Multi-channel signal separation by decorrelation. IEEE Transactions on Speech Audio Processing, 1(4), 405–413.
Widrow, B., & Stearns, S. D. (1985). Adaptive signal processing, Upper Saddle River: Prentice-Hall.
Widrow, B., Goodlin, R. C. (1975). Adaptive noise cancelling: Principles and applications. Proceedings of the IEEE, 63, 1692–1716.
Wolfe, P. J., & Godsill, S. J. (2003). Efficient alternatives to the Ephraim and Malah suppression rule for audio signal enhancement. EURASIP Journal on Applied Signal Processing, 10, 1043–1051.
Zhang, Y., & Zhao, Y. (2012). Real and imaginary modulation spectral subtraction for speech enhancement. Journal on Speech Communication, 55(6), 509–522.
Zoulikha, M., & Djendi, M. (2016). A new regularized forward blind source separation algorithm for automatic speech quality enhancement. Applied Acoustics, 112, 192–200.
Zoulikha, M., Djendi, M., Djendi, M., & Zoulikha, M. (2014). New automatic forward and backward blind sources separation algorithms for noise reduction and speech enhancement. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 40, 2072–2088.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Djendi, M. An efficient wavelet-based adaptive filtering algorithm for automatic blind speech enhancement. Int J Speech Technol 21, 355–367 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-018-9514-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-018-9514-9