Abstract
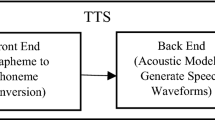
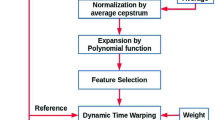
One of the main applications of time alignment is parallel corpus based voice conversion. In the literature, various methods such as dynamic time warping (DTW) and hidden Markov model have been suggested for time alignment of two speech signals. In this paper, we introduce some modifications to DTW in order to decrease the time alignment error. These modifications are refinement, which is done by exerting a threshold, normalization, and comparisons between the preceding and the following frames to make sound correspondence between two different parallel corpus-based speakers’ speeches. Evaluation of this approach which has been done on some corpus sentences indicates a significant improvement of time alignment. At least about 4% and in some cases 15% decrease of error in comparison with DTW has been achieved.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arslan, L. M., & Talkin, D. (1998). Speaker transformation using sentence HMM based alignments and detailed prosody modification. ICASSP.
Dengï, Y., & Byrne, W. (2008). HMM word and phrase alignment for statistical machine translation. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 16, 494–507.
Homayounpour, M. (2009) Text to speech conversion. Tehran: Amirkabir University of Technology.
Latsch, V. L., & Sergio, L. N. (2011). Pitch-synchronous time alignment of speech signals for prosody transplantation. IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems (ISCAS).
Rabiner, L., & Juang, B. H. (1993). Fundamentals of Speech Recognition. Upper Saddle: Prentice Hall.
Rabiner, L. R. (1989). A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech. Proceedings of the IEEE.
Sayadian, A., & Mozaffari, F. (2017). A novel method for voice conversion based on non-parallel corpus. International Journal of Speech Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-017-9430-4
Seara, R., et al. (2016). Enhanced CORILGA: introducing the automatic phonetic alignment tool for continuous speech. LREC.
Stainhaouer, G. N., & Carayannis, G. (1990). New parallel implementations for DTW algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics Speech Signal Processing, 38, 4.
Tinati, M., & Farhid, M. (2007) A novel method for improvement of the quality of voice conversion systems. 13th national computer engineering conference of Iran.
Torkkola, K. (1988). Automatic alignment of speech with phonetic transcriptions in real time. Proceedings of IEEE.
Wang, T., & Cuperman, V. (1998). Robust voicing estimation with dynamic time warping. Proceedings of IEEE..
Yfantis, E. A., Lazarakis, T., & Angelopoulos, A. (1998). On time alignment and metric algorithms for speech recognition. Proceedings of IEEE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mozaffari, F., Sayadian, A. Improvement of time alignment of the speech signals to be used in voice conversion. Int J Speech Technol 21, 79–84 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-018-9490-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-018-9490-0