Abstract
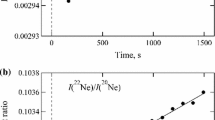
Interest in the triple points of neon isotopes has recently arisen as a result of the multi-institute project to understand how variations in the isotopic composition of natural neon influence the triple-point temperature of a particular sample. Given the challenges in determining with sufficiently low uncertainty both the relative isotopic concentrations, particularly of 22Ne relative to 20Ne, and the temperature differences among cells filled from different gas sources in order to determine the sensitivity coefficient with adequate confidence, modeling of the isotopic influence becomes an attractive alternative for correcting the triple points of “natural” neon samples to a common composition. The modeling requires, among other things, knowledge of the triple-point temperatures of 20Ne and 22Ne. The triple points of these pure neon isotopes have utility in their own right as secondary reference temperatures on the ITS-90, and one or both of these could replace “natural” neon in a revised International Temperature Scale or approximation to the ITS. The neon isotope triple-point temperatures (on the IPTS-68) reported by Furukawa, Kemp, and Sakurai in various publications from 1972 to 1986 predate the ITS-90, and so there is utility in contemporary measurements (on the ITS-90) with gas samples of recent production. At NRC, we find the triple point of 20Ne to be at 24.54230 K (13.80 mK below the triple point of “natural” neon) and that of 22Ne to be at 24.68889 K (132.79 mK above the triple point of “natural” neon), assuming the reference sample of “natural” neon realizes the ideal ITS-90 temperature of 24.5561 K.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Preston-Thomas, Metrologia 27, 3 (1990); Erratum 27, 107 (1990)
de Laeter J.R., Böhlke J.K., De Bièvre P., Hidaka H., Peiser H.S., Rosman K.J.R., Taylor P.D.P.: Pure Appl. Chem. 75, 683 (2003)
Pavese F., Fellmuth B., Hill K.D., Head D., Hermier Y., Lipinski L., Nakano T., Peruzzi A., Sakurai H., Szmyrka-Grzebyk A., Steele A.G., Steur P.P.M., Tamura O., Tew W.L., Valkiers S., Wolber L.: Int. J. Thermophys. 29, 57 (2008). doi:10.1007/s10765-007-0329-1
Furukawa G.T.: Metrologia 8, 11 (1972)
Kemp R.C., Kemp W.R.G.: Metrologia 17, 67 (1981)
Kemp R.C., Sakurai H.: Metrologia 23, 33 (1986)
H. Sakurai, in Temperature Measurement, Proceedings of International Symposium on Temperature Measurement in Industry and Science, ed. by L. Wang, S. Ling (China Academic Publishers, Beijing, 1986), pp. 128–133
Hill K.D., Steele A.G.: Metrologia 42, 278 (2005)
A.G. Steele, in The International Seminar on Low Temperature Thermometry and Dynamic Temperature Measurement, ed. by A. Szmyrka-Grzebyk (DRUK, Wroclaw, Poland, 1997), pp. L42–L53
Wolber L., Fellmuth B.: Int. J. Thermophys. 29, 82 (2008)
Pavese F.: Metrologia 46, 47 (2009)
Fahr M., Rudtsch S.: Int. J. Thermophys. 29, 126 (2008). doi:10.1007/s10765-007-0351-3
Bedford R.E., Bonnier G., Maas H., Pavese F.: Metrologia 33, 133 (1996)
Pavese F., Valkiers S., Steur P.P.M., Ferri D., Giraudi D.: J. Chem. Thermodynamics 42, 1222 (2010)
Clusius K., Flubacher P., Piesbergen U., Schleich K., Sperandio A.: Z. Naturforsch. 15a, 1 (1960)
Gulliver G.H.: J. Inst. Met. 9, 120 (1913)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hill, K.D., Fahr, M. Triple-Point Temperatures of 20Ne and 22Ne. Int J Thermophys 32, 173–188 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-011-0939-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-011-0939-5