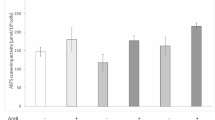
Abstract
Adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effect by inhibition of the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) pathway and is involved in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation. Cell-death-inducing DFF45-like effector C (CIDEC) can directly down-regulate AMPK activity through interacting with AMPKα subunit. However, whether the AMPK or CIDEC is involved in LPS-induced inflammation in renal tubular epithelial cells is still unknown. Therefore, we studied the role of AMPK and CIDEC in LPS-treated NRK-52E cells. Our results showed that LPS could up-regulate the expression of CIDEC in vitro and in vivo. Silencing CIDEC by CIDEC-siRNA could restore expression of phosphorylated-AMPKα which was decreased by LPS, suppress LPS-induced NF-κB pathway activation, and TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β production in NRK-52E cells. Furthermore, silencing CIDEC also partially alleviated LPS-induced epithelial cells apoptosis. In conclusion, the results demonstrated that CIDEC/AMPK signaling pathway played an important role in LPS-induced inflammation and epithelial cells apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
KDIGO AKI Guideline Work Group. 2012. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney International 2 (Suppl): 1.
Odutayo, A., C.X. Wong, M. Farkouh, et al. 2017. AKI and long-term risk for cardiovascular events and mortality. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 28: 377–387.
RR Acedillo, R., E. Mcarthur Wald, et al. 2017. Characteristics and outcomes of patients discharged home from an emergency department with AKI. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 12: 1215–1225.
Zarjou, A., and A. Agarwal. 2011. Sepsis and acute kidney injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 22: 999–1006.
Hotchkiss, R.S., and I.E. Karl. 2003. The pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. The New England Journal of Medicine 348: 138–150.
Rabb, H., M.D. Griffin, D.B. Mckay, et al. 2016. Inflammation in AKI: current understanding, key questions and knowledge gaps. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 27 (2): 371–379.
RW Schrier, W., B. Poole Wang, et al. 2004. Acute renal failure: definitions, diagnosis, pathogenesis, and therapy. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 114 (1): 5–14.
Souza, A.C., R.A. Volpini, M.H. Shimizu, et al. 2012. Erythropoietin prevents sepsis-related acute kidney injury in rats by inhibiting NF-kappaB and upregulating endothelial nitric oxide synthase. American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology 302 (8): F1045.
Zhang, L., D. Sun, Y. Bao, Y. Shi, Y. Cui, and M. Guo. 2017. Nerolidol protects against LPS-induced acute kidney injury via inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signaling. Phytotherapy Research 31 (3): 459–465.
Su, R.Y., Y. Chao, T.Y. Chen, D.Y. Huang, and W.W. Lin. 2007. 5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside sensitizes TRAIL- and TNF{alpha}-induced cytotoxicity in colon cancer cells through AMP-activated protein kinase signaling. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics 6 (5): 1562–1571.
Zhao, X., J.W. Zmijewski, E. Lorne, et al. 2008. Activation of AMPK attenuates neutrophil proinflammatory activity and decreases the severity of acute lung injury. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 295 (3): L497–L504.
Lv, H., Q. Liu, Z. Wen, H. Feng, X. Deng, and X. Ci. 2017. Xanthohumol ameliorates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury via induction of AMPK/GSK3β-Nrf2 signal axis. Redox Biology 12 (C): 311–324.
Xing, J., Q. Wang, K. Coughlan, B. Viollet, C. Moriasi, and M.H. Zou. 2013. Inhibition of AMP-activated protein kinase accentuates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung endothelial barrier dysfunction and lung injury in vivo. American Journal of Pathology. 182 (3): 1021–1030.
Giri, S., N. Nath, B. Smith, et al. 2004. 5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-4-ribofuranoside inhibits proinflammatory response in glial cells: a possible role of AMP-activated protein kinase. Journal of Neuroscience. 24 (2): 479–487.
Lee, D.U., Y.S. Ko, H.J. Kim, et al. 2017. 13-Ethylberberine reduces HMGB1 release through AMPK activation in LPS-activated RAW264.7 cells and protects endotoxemic mice from organ damage. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 86: 48–56.
Y, Xu, Gu Y, G. Liu, et al. 2015. Cidec promotes the differentiation of human adipocytes by degradation of AMPKalpha through ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1850 (12): 2552–2562.
Wang, Z.Q., Y. Yu, X.H. Zhang, et al. 2010. Human adenovirus 36 decreases fatty acid oxidation and increases de novo lipogenesis in primary cultured human skeletal muscle cells by promoting Cidec/FSP27 expression. International Journal of Obesity. 34 (9): 1355–1364.
Tilyek, A., C. Chai, X. Hou, B. Zhou, C. Zhang, Z. Cao, and B. Yu. 2016 Feb 3. The protective effects of Ribes diacanthum pall on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 178: 297–306.
Cerdá, J., N. Lameire, P. Eggers, et al. 2008. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 3 (3): 881–886.
Leemans, J.C., L.M. Butter, G.J.D. Teske, et al. 2012. The toll interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) 8/single Ig domain IL-1R-related molecule modulates the renal response to bacterial infection. Infection & Immunity. 80: 3812–3820.
Ho, A., and C.C. Wong. 2008. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha up-regulates the expression of CCL2 and adhesion molecules of human proximal tubular epithelial cells through MAPK signaling pathways. Immunobiology 213: 533–544.
Meng, X.M., D.J. Nikolicpaterson, and H.Y. Lan. 2014. Inflammatory processes in renal fibrosis. Nature Reviews. Nephrology 10: 493–503.
Filiopoulos, V., and D. Vlassopoulos. 2009. Inflammatory syndrome in chronic kidney disease: pathogenesis and influence on outcomes. Inflammation & Allergy Drug Targets 8 (5): 369–382.
Xu, C., A. Chang, B.K. Hack, M.T. Eadon, S.L. Alper, and P.N. Cunningham. 2014. TNF-mediated damage to glomerular endothelium is an important determinant of acute kidney injury in sepsis. Kidney international. 85: 72–81.
Tian, Y., J. Ma, W. Wang, L. Zhang, J. Xu, K. Wang, and D. Li. 2016. Resveratrol supplement inhibited the NF-κB inflammation pathway through activating AMPKα-SIRT1 pathway in mice with fatty liver. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 422 (1–2): 75–84.
Wan, L., S.M. Bagshaw, C. Langenberg, et al. 2008. Pathophysiology of septic acute kidney injury: what do we really know? Critical Care Medicine. 36 (4 Suppl): 198–203.
Cantaluppi, V., A.D. Quercia, S. Dellepiane, et al. 2012. New mechanisms and recent insights in the pathogenesis of acute kidney injury (AKI). Giornale Italiano Di Nefrologia Organo Ufficiale Della Società Italiana Di. Nefrología 29 (5): 535.
Langenberg, C., S.M. Bagshaw, C.N. May, and R. Bellomo. 2008. The histopathology of septic acute kidney injury: a systematic review. Critical Care. 12 (2): R38.
Lerolle, N., D. Nochy, E. Guérot, P. Bruneval, J.Y. Fagon, J.L. Diehl, and G. Hill. 2010 Mar. Histopathology of septic shock induced acute kidney injury: apoptosis and leukocytic infiltration. Intensive Care Medicine 36 (3): 471–478.
Bae, Eun Hui, Jin Kim In, Hong Sang Choi, et al. 2018 Mar. Tumor necrosis factor α-converting enzyme inhibitor attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced reactive oxygen species and mitogen-activated protein kinase expression in human renal proximal tubule epithelial cells. Korean Journal Physiology & Pharmacology 22 (2): 135–143.
Liu, K., S. Zhou, J.Y. Kim, K. Tillison, D. Majors, D. Rearick, J.H. Lee, R.F. Fernandez-Boyanapalli, K. Barricklow, M.S. Houston, and C.M. Smas. 2009. Functional analysis of FSP27 protein regions for lipid droplet localization, caspase-dependent apoptosis, and dimerization with CIDEA. American Journal of Physiology Endocrinology & Metabolism. 297 (6): E1395.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Lixue Chen, Xiaojuan Deng, and jun He at the central laboratory of the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University for their assistance while we conducted our experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J. He and B. Zhang conceived the study and designed the experiments. J. He, B. Zhang performed all of the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. H. Gan reviewed and revised the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, J., Zhang, B. & Gan, H. CIDEC Is Involved in LPS-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis in Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells. Inflammation 41, 1912–1921 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0834-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0834-3