Abstract
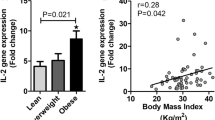
Objective Recent studies have revealed a link between toll-like receptors (TLRs), Kruppel-like factors (KLFs), and the adipose tissue inflammation associated with obesity. TLR4 is associated with chronic inflammation in obesity. KLF7 is known to play an important role in the differentiation of adipocytes, but its role in visceral adipose tissue inflammation has not yet been investigated. Thus, the objective of this study was to determine the correlation of TLR4 and KLF7 in inflammation induced by obesity. Methods A total of 32 Wistar male rat subjects were fed in the center for experimental animals of Shihezi University. The rats were divided into normal control (NC) and high-fat diet (HFD) group. Surgical instruments were used to collect rats’ visceral adipose tissue samples in the 10th week after HFD feeding. Ninety-five Uygur subjects between 20 and 90 years old were enrolled in the present study. The subjects were divided into two groups: the normal control group (NC, 18.0 kg/m2 ≤ BMI ≤ 23.9 kg/m2, n = 50) and the obesity group (OB, BMI ≥ 28 kg/m2, n = 45), and visceral adipose tissue was collected from the subjects. Anthropometric and clinical parameters were measured using standard procedures; biochemical indices were detected using the glucose oxidase-peroxidase method and a standardized automatic biochemistry analyzer; the plasma levels of inflammatory factors and adipocytokines were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA); the mRNA and protein expression levels of key genes involved in the inflammatory signaling pathway were measured by real-time PCR and Western blot. Results In rats, compared with the NC group, the weight, Lee’s index, waist circumference, visceral fat mass, and the plasma level of Glu, TG, FFA, and TNF-α were higher in the HFD group, while the plasma levels of LPT and APN were significantly lower in the HFD group in the 10th week. Furthermore, compared with the NC group, visceral adipose tissue’s mRNA expression levels of TLR4, KLF7, and SRC were higher in the HFD group, and KLF7 was significantly positively correlated with LDL, TLR4, SRC, and IL-6 (P < 0.05). Meanwhile, in the Uygur population, the plasma levels of TG, LDL, and TNF-α in the OB group were significantly higher than those in the NC group (P < 0.05). Moreover, compared with the NC group, visceral adipose tissue’s mRNA expression levels of TLR4, KLF7, and SRC were significantly higher in the OB group (P < 0.05), and KLF7 was significantly positively correlated with TC, TLR4, MYD88, SRC, and IL-6 (P < 0.05); the protein expression levels of TLR4 and KLF7 were significantly higher than those in the NC group (P < 0.05). Conclusion Higher expression of TLR4 and KLF7 may play a vital role in the process of inflammation induced by obesity in visceral adipose tissue.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kotas, M.E., and R. Medzhitov. 2015. Homeostasis, inflammation, and disease susceptibility. Cell 160(5): 816–827.
Ding, J., L.M. Reynolds, T. Zeller, et al. 2015. Alterations of a cellular cholesterol metabolism network are a molecular feature of obesity-related Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes 64(10): 3464–3474.
Chalmem, J., and M.E. Cooper. 2008. UKPDS and the legacy effect. New England Journal of Medicine 359: 1618–1620.
Park, Mi-Young, and Seong Taek Mun. 2014. Carnosic acid inhibits TLR4-MyD88 signaling pathway in LPS-stimulated 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Nutrition Research and Practice 8(5): 516–520.
Cullberg, K.B., J.O. Larsen, S.B. Pedersen, et al. 2014. Effects of LPS and dietary free fatty acids on MCP-1 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and macrophages in vitro. Nutrition and Diabetes 4(3): e113.
Bieker, J.J. 2001. Krüppel-like factors: three fingers in many pies. Journal of Biological Chemistry 276(37): 34355–34358.
McConnell, Beth B., and Vincent W. Yang. 2010. Mammalian Krüppel-Like Factors in Health and Diseases. Physiological Reviews 90(4): 1337–1381.
Zhang, J., Z. Zhang, Y. Ding, et al. 2015. Adipose tissues characteristics of normal, obesity, and Type 2 diabetes in uygurs population. Journal of Diabetes Research 2015: 905042.
Gupta, S., A.K. Gupta, M. Verma, et al. 2016. A study to compare the plasma glucose level obtained in sodium fluoride and citrate buffer tubes at a tertiary care hospital in Punjab. International Journal of Applied and Basic Medical Research 6(1): 50–53.
Jagannadham, J., H.K. Jaiswal, S. Agrawal, et al. 2016. Comprehensive map of molecules implicated in obesity. PLoS One 11(2), e0146759.
Chathyan, P., J.B. Clifford, and R.G. Helen. 2015. Aging, adipose tissue, fatty acids and inflammation. Biogerontology 16(2): 235–248.
Gaur, A., G.K. Pal, P.H. Ananthanarayanan, et al. 2014. Role of Ventromedial hypothalamus in high fat diet induced obesity in male rats: association with lipid profile, thyroid profile and insulin resistance. Annals of Neurosciences 21(3): 104–107.
Li, Q., and I.M. Verma. 2002. NF-kB regulation in the immune system. Nature Reviews Immunology 2(10): 725–734.
Poulain, L., V. Richard, P. Lévy, et al. 2015. Toll-like receptor-4 mediated inflammation is involved in the cardiometabolic alterations induced by intermittent hypoxia. Mediators of Inflammation 2015: 620258.
Zhang, J., W. Dou, E. Zhang, et al. 2014. Paeoniflorin abrogates DSS-induced colitis via a TLR4-dependent pathway. American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 306(1): G27–36.
Jiao, Hao, Zhang Yang, Zhibo Yan, et al. 2013. Caveolin-1 Tyr14 phosphorylation induces interaction with TLR4 in endothelial cells and mediates MyD88-dependent signaling and sepsis-induced lung inflammation. Journal of Immunology 191(12): 619–9. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1300873.
Chen, L., Y.M. Dai, C.B. Ji, et al. 2014. MiR-146b is a regulator of human visceral preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation and its expression is altered in human obesity. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 393(1–2): 65–74.
Kawamura, Y., Y. Tanaka, R. Kawamori, et al. 2006. Overexpression of Kruppel-like factor 7 regulates adipocytokine gene expressions in human adipocytes and inhibits glucose-induced insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cell line. Molecular Endocrinology 20(4): 844–856.
Wang, X., Q.W. Shen, J. Wang, et al. 2016. KLF7 regulates satellite cell quiescence in response to extracellular signaling. Stem Cells. doi:10.1002/stem.2346.
Mreich, E., X.M. Chen, A. Zaky, et al. 2015. The role of Krüppel-like factor 4 in transforming growth factor-β-induced inflammatory and fibrotic responses inhuman proximal tubule cells. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology 42(6): 680–686.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81360142), the Program for High-Level Personnel Start at Shihezi University (nos. RCZX201230, gxjs2012-zdgg02), and the Applied basic research project of Xinjiang corps (2015AG016).
Authors’ Contribution
Cuizhe Wang and Xiaodan Ha contributed equally to the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Cuizhe Wang and Xiaodan Ha contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Ha, X., Li, W. et al. Correlation of TLR4 and KLF7 in Inflammation Induced by Obesity. Inflammation 40, 42–51 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0450-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0450-z