Abstract
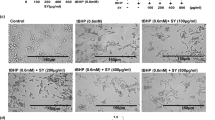
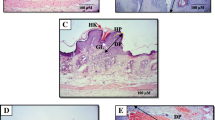
Baicalein, one of the four major flavanoids extracted from the root of Scutellaria baicalensis, has been shown to exert chemopreventive effect against several cancers, including skin cancer. However, the precise mechanisms remain to be elucidated. In the present study, we investigated the chemopreventive activity of baicalein against 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA)/12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-mediated skin tumorigenesis in C57BL/6 mice. We found that topical treatment with baicalein resulted in a significant inhibitory effect on DMBA/TPA-mediated tumor promotion. Furthermore, we observed that baicalein suppressed cell proliferation and promoted apoptosis in DMBA/TPA-mediated group. Additionally, pretreatment with baicalein inhibited the production of inflammatory cells in DMBA/TPA-induced skin/tumors. Further experiments showed that baicalein reduced TPA-induced skin hyperplasia as well as infiltration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in the dermis. In conclusion, our data suggest that baicalein inhibits DMBA/TPA-induced skin tumorigenesis by suppressing proliferation and inflammation and promoting apoptosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaudhary, S.C., M.S. Siddiqui, M. Athar, and M.S. Alam. 2012. Geraniol inhibits murine skin tumorigenesis by modulating COX-2 expression, Ras-ERK1/2 signaling pathway and apoptosis. Journal of Applied Toxicology. doi:10.1002/jat.2739.
Abel, E.L., J.M. Angel, K. Kiguchi, and J. DiGiovanni. 2009. Multi-stage chemical carcinogenesis in mouse skin: fundamentals and applications. Nature Protocols 4(9): 1350–1362. doi:10.1038/nprot.2009.120.
Kemp, C.J. 2005. Multistep skin cancer in mice as a model to study the evolution of cancer cells. Seminars in Cancer Biology 15(6): 460–473. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2005.06.003.
DiGiovanni, J. 1991. Modification of multistage skin carcinogenesis in mice. Progress in Experimental Tumor Research 33: 192–229.
Chaudhary, S.C., M.S. Alam, M.S. Siddiqui, and M. Athar. 2009. Chemopreventive effect of farnesol on DMBA/TPA-induced skin tumorigenesis: involvement of inflammation, Ras-ERK pathway and apoptosis. Life Sciences 85(5–6): 196–205. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2009.05.008.
Bickers, D.R., and M. Athar. 2006. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of skin disease. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology 126(12): 2565–2575. doi:10.1038/sj.jid.5700340.
Chun, K.S., S.H. Kim, Y.S. Song, and Y.J. Surh. 2004. Celecoxib inhibits phorbol ester-induced expression of COX-2 and activation of AP-1 and p38 MAP kinase in mouse skin. Carcinogenesis 25(5): 713–722. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgh076.
Afaq, F., M. Saleem, C.G. Krueger, J.D. Reed, and H. Mukhtar. 2005. Anthocyanin- and hydrolyzable tannin-rich pomegranate fruit extract modulates MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways and inhibits skin tumorigenesis in CD-1 mice. International Journal of Cancer 113(3): 423–433. doi:10.1002/ijc.20587.
Giri, U., S.D. Sharma, M. Abdulla, and M. Athar. 1995. Evidence that in situ generated reactive oxygen species act as a potent stage I tumor promoter in mouse skin. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 209(2): 698–705. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1995.1555.
Hoellen, F., K. Kelling, C. Dittmer, K. Diedrich, M. Friedrich, and M. Thill. 2011. Impact of cyclooxygenase-2 in breast cancer. Anticancer Research 31(12): 4359–4367.
Zhang, H., Y. Xu, Z. Zhang, R. Liu, and B. Ma. 2012. Association between COX-2 rs2745557 polymorphism and prostate cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Immunology 13: 14. doi:10.1186/1471-2172-13-14.
Diduk, S.V., K.V. Smirnova, and V.E. Gurtsevich. 2012. COX-2 as an early diagnostic marker of virus-associated human malignant neoplasms. Voprosy Virusologii 57(2): 4–8.
Chang, M.S., B.C. Chen, M.T. Yu, J.R. Sheu, T.F. Chen, and C.H. Lin. 2005. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate upregulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human pulmonary epithelial cells via Ras, Raf-1, ERK, and NF-kappaB, but not p38 MAPK, pathways. Cellular Signalling 17(3): 299–310. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2004.07.008.
Kalra, N., K. Bhui, P. Roy, S. Srivastava, J. George, S. Prasad, and Y. Shukla. 2008. Regulation of p53, nuclear factor kappaB and cyclooxygenase-2 expression by bromelain through targeting mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in mouse skin. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 226(1): 30–37. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2007.08.012.
Arora, N., M.P. Bansal, and A. Koul. 2011. Azadirachta indica exerts chemopreventive action against murine skin cancer: studies on histopathological, ultrastructural changes and modulation of NF-kappaB, AP-1, and STAT1. Oncology Research 19(5): 179–191.
Kaur, J., M. Sharma, P.D. Sharma, and M.P. Bansal. 2008. Chemopreventive activity of lantadenes on two-stage carcinogenesis model in Swiss albino mice: AP-1 (c-jun), NFkappaB (p65) and P53 expression by ELISA and immunohistochemical localization. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 314(1–2): 1–8. doi:10.1007/s11010-008-9758-9.
Shao, Z.H., C.Q. Li, T.L. Vanden Hoek, L.B. Becker, P.T. Schumacker, J.A. Wu, A.S. Attele, and C.S. Yuan. 1999. Extract from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi attenuates oxidant stress in cardiomyocytes. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology 31(10): 1885–1895. doi:10.1006/jmcc.1999.1021.
Lee, M.J., C.J. Wang, Y.Y. Tsai, J.M. Hwang, W.L. Lin, T.H. Tseng, and C.Y. Chu. 1999. Inhibitory effect of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-caused tumor promotion in benzo[a]pyrene-initiated CD-1 mouse skin by baicalein. Nutrition and Cancer 34(2): 185–191. doi:10.1207/S15327914NC3402_9.
Wang, L., Y. Ling, Y. Chen, C.L. Li, F. Feng, Q.D. You, N. Lu, and Q.L. Guo. 2010. Flavonoid baicalein suppresses adhesion, migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Letters 297(1): 42–48. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2010.04.022.
Chen, F.L., X.Z. Wang, J.Y. Li, J.P. Yu, C.Y. Huang, and Z.X. Chen. 2008. 12-lipoxygenase induces apoptosis of human gastric cancer AGS cells via the ERK1/2 signal pathway. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 53(1): 181–187. doi:10.1007/s10620-007-9841-1.
Wei, X., W. Guo, S. Wu, L. Wang, P. Huang, J. Liu, and B. Fang. 2010. Oxidative stress in NSC-741909-induced apoptosis of cancer cells. Journal of Translational Medicine 8: 37. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-8-37.
Lea, M.A., C. Ibeh, J.K. Deutsch, I. Hamid, and C. desBordes. 2010. Inhibition of growth and induction of alkaline phosphatase in colon cancer cells by flavonols and flavonol glycosides. Anticancer Research 30(9): 3629–3635.
Lee, H.Z., H.W. Leung, M.Y. Lai, and C.H. Wu. 2005. Baicalein induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human lung squamous carcinoma CH27 cells. Anticancer Research 25(2A): 959–964.
Takahashi, H., M.C. Chen, H. Pham, E. Angst, J.C. King, J. Park, E.Y. Brovman, H. Ishiguro, D.M. Harris, H.A. Reber, O.J. Hines, A.S. Gukovskaya, V.L. Go, and G. Eibl. 2011. Baicalein, a component of Scutellaria baicalensis, induces apoptosis by Mcl-1 down-regulation in human pancreatic cancer cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1813(8): 1465–1474. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.05.003.
Taniguchi, H., T. Yoshida, M. Horinaka, T. Yasuda, A.E. Goda, M. Konishi, M. Wakada, K. Kataoka, T. Yoshikawa, and T. Sakai. 2008. Baicalein overcomes tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance via two different cell-specific pathways in cancer cells but not in normal cells. Cancer Research 68(21): 8918–8927. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1120.
Shieh, D.E., L.T. Liu, and C.C. Lin. 2000. Antioxidant and free radical scavenging effects of baicalein, baicalin and wogonin. Anticancer Research 20(5A): 2861–2865.
Huang, W.H., A.R. Lee, P.Y. Chien, and T.C. Chou. 2005. Synthesis of baicalein derivatives as potential anti-aggregatory and anti-inflammatory agents. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 57(2): 219–225. doi:10.1211/0022357055371.
Wang, J., Y. Yu, F. Hashimoto, Y. Sakata, M. Fujii, and D.X. Hou. 2004. Baicalein induces apoptosis through ROS-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction pathway in HL-60 cells. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 14(4): 627–632.
Huang, H.C., L.M. Hsieh, H.W. Chen, Y.S. Lin, and J.S. Chen. 1994. Effects of baicalein and esculetin on transduction signals and growth factors expression in T-lymphoid leukemia cells. European Journal of Pharmacology 268(1): 73–78.
Huang, H.C., H.R. Wang, and L.M. Hsieh. 1994. Antiproliferative effect of baicalein, a flavonoid from a Chinese herb, on vascular smooth muscle cell. European Journal of Pharmacology 251(1): 91–93.
Pidgeon, G.P., M. Kandouz, A. Meram, and K.V. Honn. 2002. Mechanisms controlling cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis after 12-lipoxygenase inhibition in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Research 62(9): 2721–2727.
Piao, Y.S., Y.C. Du, H. Oshima, J.C. Jin, M. Nomura, T. Yoshimoto, and M. Oshima. 2008. Platelet-type 12-lipoxygenase accelerates tumor promotion of mouse epidermal cells through enhancement of cloning efficiency. Carcinogenesis 29(2): 440–447. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgm274.
Chandrashekar, N., A. Selvamani, R. Subramanian, A. Pandi, and D. Thiruvengadam. 2012. Baicalein inhibits pulmonary carcinogenesis-associated inflammation and interferes with COX-2, MMP-2 and MMP-9 expressions in-vivo. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 261(1): 10–21. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2012.02.004.
Davis, T.W., B.S. Zweifel, J.M. O’Neal, D.M. Heuvelman, A.L. Abegg, T.O. Hendrich, and J.L. Masferrer. 2004. Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 by celecoxib reverses tumor-induced wasting. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 308(3): 929–934. doi:10.1124/jpet.103.063099.
Kawamori, T., C.V. Rao, K. Seibert, and B.S. Reddy. 1998. Chemopreventive activity of celecoxib, a specific cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, against colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Research 58(3): 409–412.
Harris, R.E., G.A. Alshafie, H. Abou-Issa, and K. Seibert. 2000. Chemoprevention of breast cancer in rats by celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor. Cancer Research 60(8): 2101–2103.
Fischer, S.M., H.H. Lo, G.B. Gordon, K. Seibert, G. Kelloff, R.A. Lubet, and C.J. Conti. 1999. Chemopreventive activity of celecoxib, a specific cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, and indomethacin against ultraviolet light-induced skin carcinogenesis. Molecular Carcinogenesis 25(4): 231–240. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2744(199908)25:4<231::AID-MC1>3.0.CO;2-F.
Kamp, D.W., E. Shacter, and S.A. Weitzman. 2011. Chronic inflammation and cancer: the role of the mitochondria. Oncology (Williston Park, N.Y.) 25(5): 400–410. 413.
Vendramini-Costa, D.B., and J.E. Carvalho. 2012. Molecular link mechanisms between inflammation and cancer. Current Pharmaceutical Design
Schluter, C., M. Duchrow, C. Wohlenberg, M.H. Becker, G. Key, H.D. Flad, and J. Gerdes. 1993. The cell proliferation-associated antigen of antibody Ki-67: a very large, ubiquitous nuclear protein with numerous repeated elements, representing a new kind of cell cycle-maintaining proteins. The Journal of Cell Biology 123(3): 513–522.
Gerdes, J., L. Li, C. Schlueter, M. Duchrow, C. Wohlenberg, C. Gerlach, I. Stahmer, S. Kloth, E. Brandt, and H.D. Flad. 1991. Immunobiochemical and molecular biologic characterization of the cell proliferation-associated nuclear antigen that is defined by monoclonal antibody Ki-67. American Journal of Pathology 138(4): 867–873.
Balkwill, F., and L.M. Coussens. 2004. Cancer: an inflammatory link. Nature 431(7007): 405–406. doi:10.1038/431405a.
Prescott, S.M., and F.A. Fitzpatrick. 2000. Cyclooxygenase-2 and carcinogenesis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1470(2): M69–M78.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (State Education Ministry, IRT0760 and Education Department of Liaoning Province, 2006T133, 2008T193, LR201040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, GZ., Liu, CH., Wei, B. et al. Baicalein Inhibits DMBA/TPA-Induced Skin Tumorigenesis in Mice by Modulating Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Inflammation. Inflammation 36, 457–467 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-012-9566-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-012-9566-y