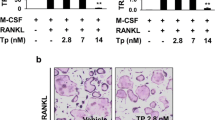
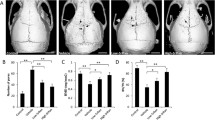
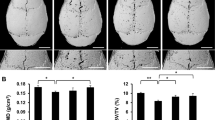
Abstract
The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) pathway is involved in the osteoclast differentiation. The aim of the study was to investigate whether SB203580, a p38 MAPK inhibitor, inhibits wear-debris-induced inflammatory osteolysis in mice. Forty-five mice were implanted with calvaria bone from syngeneic littermates; then, titanium (Ti) particles were injected into established air pouches to provoke inflammatory osteolysis. At 14 days after bone/Ti implantation, pouch membranes with intact bone implants underwent histological and molecular analysis. SB203580 had less effect on MMP-9 and TNF-α expression under wear-debris-induced conditions. SB203580, by inhibiting the expression of p38 MAPK and phospho-p38 MAPK, inhibited Ti particle wear-debris-induced inflammatory osteolysis. It also remarkably decreased the number of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase positive cells in Ti-particle-induced pouch tissues. Results suggest that p38 MAPK may be critical in a murine osteolysis model. SB203580 may notably inhibit wear-debris-induced inflammatory osteolysis by down-regulating expression of MMP-9 and TNF-α via the p38 MAPK pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCE
Mao, X., Pan, X., Peng, X., Cheng, T., and X. Zhang. 2010. Inhibition of titanium particle-induced inflammation by the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in murine macrophage-like RAW 264.7 cells. Inflammation [Epub ahead of print].
Harris, W.H. 2001. Wear and periprosthetic osteolysis: The problem. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 393: 66–70.
Pearl, J.I., T. Ma, A.R. Irani, Z. Huang, W.H. Robinson, R.L. Smith, and S.B. Goodman. 2011. Role of the Toll-like receptor pathway in the recognition of orthopedic implant wear-debris particles. Biomaterials 32: 5535–5542.
Geng, D.C., X.S. Zhu, H.Q. Mao, B. Meng, L. Chen, H.L. Yang, and Y.Z. Xu. 2011. Protection against titanium particle-induced osteoclastogenesis by cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitor. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research. Part A 99: 516–522.
Ingham, E., and J. Fisher. 2005. The role of macrophages in osteolysis of total joint replacement. Biomaterials 26: 1271–1286.
Purdue, P.E., P. Koulouvaris, H.G. Potter, B.J. Nestor, and T.P. Sculco. 2007. The cellular and molecular biology of periprosthetic osteolysis. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 454: 251–261.
Abbas, S., J.C. Clohisy, and Y. Abu-Amer. 2003. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases mediate PMMA-induction of osteoclasts. Journal of Orthopaedic Research 21: 1041–1048.
Rakshit, D.S., K. Ly, T.K. Sengupta, B.J. Nestor, T.P. Sculco, L.B. Ivashkiv, and P.E. Purdue. 2006. Wear debris inhibition of anti-osteoclastogenic signaling by interleukin-6 and interferon-gamma. Mechanistic insights and implications for periprosthetic osteolysis. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume 88: 788–799.
Yamanaka, Y., Y. Abu-Amer, R. Faccio, and J.C. Clohisy. 2006. Map kinase c-JUN N-terminal kinase mediates PMMA induction of osteoclasts. Journal of Orthopaedic Research 24: 1349–1357.
Lee, J.C., J.T. Laydon, P.C. McDonnell, T.F. Gallagher, S. Kumar, D. Green, D. McNulty, M.J. Blumenthal, J.R. Heys, S.W. Landvatter, et al. 1994. A protein kinase involved in the regulation of inflammatory cytokine biosynthesis. Nature 372: 739–746.
Ridley, S.H., S.J. Sarsfield, J.C. Lee, H.F. Bigg, T.E. Cawston, D.J. Taylor, D.L. DeWitt, and J. Saklatvala. 1997. Actions of IL-1 are selectively controlled by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase: Regulation of prostaglandin H synthase-2, metalloproteinases, and IL-6 at different levels. The Journal of Immunology 158: 3165–3173.
Ren, W., S.Y. Yang, and P.H. Wooley. 2004. A novel murine model of orthopaedic wear-debris associated osteolysis. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 33: 349–357.
Suzuki, M., K. Uetsuka, J. Shinozuka, H. Nakayama, and K. Doi. 1998. Changes in location and number of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP)-positive cells during the development of type II collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1 J mice. Experimental Animals 47: 211–214.
Gallo, J., P. Kaminek, V. Ticha, P. Rihakova, and R. Ditmar. 2002. Particle disease. A comprehensive theory of periprosthetic osteolysis: A review. Biomedical Papers of the Medical Faculty of the University Palacky, Olomouc, Czech Republic 146: 21–28.
Dorr, L.D., Z. Wan, C. Shahrdar, L. Sirianni, M. Boutary, and A. Yun. 2005. Clinical performance of a Durasul highly cross-linked polyethylene acetabular liner for total hip arthroplasty at five years. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume 87: 1816–1821.
Ren, W., X.H. Li, B.D. Chen, and P.H. Wooley. 2004. Erythromycin inhibits wear debris-induced osteoclastogenesis by modulation of murine macrophage NF-kappaB activity. Journal of Orthopaedic Research 22: 21–29.
von Knoch, F., A. Heckelei, C. Wedemeyer, G. Saxler, G. Hilken, F. Henschke, F. Loer, and M. von Knoch. 2005. The effect of simvastatin on polyethylene particle-induced osteolysis. Biomaterials 26: 3549–3555.
Goodman, S.B., and T. Ma. 2010. Cellular chemotaxis induced by wear particles from joint replacements. Biomaterials 31: 5045–5050.
Shimizu, S., N. Okuda, N. Kato, S.R. Rittling, A. Okawa, K. Shinomiya, T. Muneta, D.T. Denhardt, M. Noda, K. Tsuji, and Y. Asou. 2010. Osteopontin deficiency impairs wear debris-induced osteolysis via regulation of cytokine secretion from murine macrophages. Arthritis and Rheumatism 62: 1329–1337.
Vattakuzhi, Y., Abraham, S.M., Freidin, A., Clark, A.R., and N.J. Horwood. 2012. Dual specificity phosphatase 1 null mice exhibit spontaneous osteolytic disease and enhanced inflammatory osteolysis in experimental arthritis. Arthritis Rheum [Epub ahead of print].
Seo, S.W., D. Lee, H. Minematsu, A.D. Kim, M. Shin, S.K. Cho, D.W. Kim, J. Yang, and F.Y. Lee. 2010. Targeting extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling has therapeutic implications for inflammatory osteolysis. Bone 46: 695–702.
Wei, S., and G.P. Siegal. 2007. p38 MAPK as a potential therapeutic target for inflammatory osteolysis. Advances in Anatomic Pathology 14: 42–45.
Goodman, S.B., M. Trindade, T. Ma, M. Genovese, and R.L. Smith. 2005. Pharmacologic modulation of periprosthetic osteolysis. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 430: 39–45.
Nawrocki, B., M. Polette, H. Burlet, P. Birembaut, and J.J. Adnet. 1999. Expression of gelatinase A and its activator MT1-MMP in the inflammatory periprosthetic response to polyethylene. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 14: 288–294.
Ono, K., and J. Han. 2000. The p38 signal transduction pathway: Activation and function. Cellular Signalling 12: 1–13.
Welkoborsky, H.J. 2011. Current concepts of the pathogenesis of acquired middle ear cholesteatoma. Laryngo- Rhino- Otologie 90: 38–48.
Goodman, S.B., T. Ma, J. Spanogle, R. Chiu, K. Miyanishi, K. Oh, P. Plouhar, S. Wadsworth, and R.L. Smith. 2007. Effects of a p38 MAP kinase inhibitor on bone ingrowth and tissue differentiation in rabbit chambers. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research. Part A 81: 310–316.
Yasuda, S., H. Sugiura, H. Tanaka, S. Takigami, and K. Yamagata. 2011. p38 MAP kinase inhibitors as potential therapeutic drugs for neural diseases. Central Nervous System Agents in Medicinal Chemistry 11: 45–59.
Triantaphyllopoulos, K., L. Madden, I. Rioja, D. Essex, J. Buckton, R. Malhotra, K. Ray, M. Binks, and E.M. Paleolog. 2010. In vitro target validation and in vivo efficacy of p38 MAP kinase inhibition in established chronic collagen-induced arthritis model: a pre-clinical study. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 28: 176–185.
Hollenbach, E., M. Neumann, M. Vieth, A. Roessner, P. Malfertheiner, and M. Naumann. 2004. Inhibition of p38 MAP kinase- and RICK/NF-kappaB-signaling suppresses inflammatory bowel disease. The FASEB Journal 18: 1550–1552.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the Interdisciplinary (Engineering–Medical) Research Fund of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (No. YG2011MS30), the Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau Science Fund for Young Scholars (No. 2010QJ036A), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81171688).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, D., Guo, Y., Mao, X. et al. Inhibition of p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Down-regulates the Inflammatory Osteolysis Response to Titanium Particles in a Murine Osteolysis Model. Inflammation 35, 1798–1806 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-012-9500-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-012-9500-3