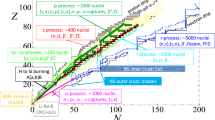
Abstract
Nuclear g factors are of the most accurate probes in modern nuclear physics investigations. Sensitive to the precise structure of the nuclear states, single-particle or collective nature is accessed directly by their measurement. At the border of nuclear existence, key regions of nuclei both neutron-rich and proton-rich are foreseen for studies. The investigations will cover shell structure, magicity, nucleon-nucleon interaction, collectivity, deformation, and shapes. With the new gSPEC project at the GSI/FAIR facility, such investigations are intended to scan various excited states of nuclei along the entire nuclear chart. Currently, the design of a new dedicated experimental apparatus is being performed, including magnetic system and detector R&D, together with feasibility studies of various scientific cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steffen, R.M., Alder, K.: The Electromagnetic Interaction in Nuclear Spectroscopy. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1975)
Goldring, G., Hass, M.: Treatise on Heavy-Ion Science, vol. 3. Plenum, New York (1985)
Neyens, G.: Rep. Prog. Phys. 66, 633 (2003). Erratum 1251 (2003)
Wilhelmy, J.B., et al.: Phys. Rev. C 5, 2041 (1972)
Schmidt-Ott, W.D., et al.: Z. Phys. A 350, 215 (1994)
Sandzelius, M, et al.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 99(02), 2501 (2007)
Hinke, C.B., et al.: Nature 486, 341 (2012)
Cederwall, B, et al.: Nature 469, 68 (2011)
Dillmann, I, et al.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 162503 (2003)
Jungclaus, A, et al.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 132501 (2007)
Stuchbery, A, et al.: Phys. Rev. C 69, 044302 (2004)
Andreev, A, et al.: Nature 405, 430 (2000)
Gaffney, L.P., et al.: Nature 497, 199 (2013)
Möeller, P.: At. Dat. Nucl. Dat. Tabl. 109, 1 (2016)
Gottardo, A, et al.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 162502 (2012)
Neyens, G, et al.: Act. Phys. Pol. B 38, 1237 (2007)
Wollersheim, H.J., et al.: Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 537, 637 (2005)
Ilie, G, et al.: Phys. Lett. B 687, 305 (2010)
Atanasova, L, et al.: Eur. Phys. Lett. 91, 42001 (2010)
Lozeva, R, et al.: Phys. Rev. C 77, 064313 (2008)
Kmiecik, M, et al.: Eur. Phys. J. A 45, 153 (2010)
Ichikawa, Y, et al.: Nat. Phys. 8, 918 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Proceedings of the International Conference on Hyperfine Interactions and their Applications (HYPERFINE 2019), Goa, India, 10–15 February 2019
Edited by S. N. Mishra, P. L. Paulose and R. Palit
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lozeva, R., Stuchbery, A., Gerl, J. et al. gSPEC. Hyperfine Interact 240, 55 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-019-1596-5
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-019-1596-5