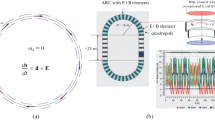
Abstract
Permanent Electric Dipole Moments (EDMs) of elementary particles violate two fundamental symmetries: time reversal invariance (\(\mathcal{T}\)) and parity (\(\mathcal{P}\)). Assuming the \(\mathcal{CPT}\) theorem this implies \(\mathcal{CP}\) violation. The \(\mathcal{CP}\) violation of the Standard Model is orders of magnitude too small to be observed experimentally in EDMs in the foreseeable future. It is also way too small to explain the asymmetry in abundance of matter and anti-matter in our universe. Hence, other mechanisms of \(\mathcal{CP}\) violation outside the realm of the Standard Model are searched for and could result in measurable EDMs. Up to now most of the EDM measurements were done with neutral particles. With new techniques it is now possible to perform dedicated EDM experiments with charged hadrons at storage rings where polarized particles are exposed to an electric field. If an EDM exists the spin vector will experience a torque resulting in change of the original spin direction which can be determined with the help of a polarimeter. Although the principle of the measurement is simple, the smallness of the expected effect makes this a challenging experiment requiring new developments in various experimental areas. Complementary efforts to measure EDMs of proton, deuteron and light nuclei are pursued at Brookhaven National Laboratory and at Forschungszentrum Jülich with an ultimate goal to reach a sensitivity of 10 − 29 e·cm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spergel, D.N., et al., WMAP Collaboration: Astrophys. J. Suppl. 148, 175 (2003) [astro-ph/0302209]
Sakharov, A.D.: Pisma Z. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 5, 32 (1967)
Sakharov, A.D.: JETP Lett. 5, 24 (1967)
Sakharov, A.D.: Sov. Phys. Usp. 34, 392 (1991)
Sakharov, A.D.: Usp. Fiz. Nauk 161, 61 (1991)
Pendlebury, J.M., Hinds, E.A.: Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 440, 471 (2000)
Fukuyama, T.: Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 27, 1230015 (2012). arXiv:1201.4252 [hep-ph]
de Vries, J., Higa, R., Liu, C.-P., Mereghetti, E., Stetcu, I., Timmermans, R.G.E., van Kolck, U.: Phys. Rev., C 84, 065501 (2011). arXiv:1109.3604 [hep-ph]
Bsaisou, J., Hanhart, C., Liebig, S., Meissner, U.-G., Nogga, A., Wirzba, A.: arXiv:1209.6306 [hep-ph]
de Vries, J.: These proceedings
Guo, F.-K., Meissner, U.-G.: Baryon electric dipole moments from strong CP violation. J. High Energy Phys. 1212, 97 (2012)
Le Dall, M., Ritz, A.: These proceedings
Onderwater, C.J.G.: arXiv:1204.2512 [hep-ex]
Baker, C.A., Doyle, D.D., Geltenbort, P., Green, K., van der Grinten, M.G.D., Harris, P.G., Iaydjiev, P., Ivanov, S.N., et al.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 131801 (2006) [hep-ex/0602020]
Griffith, W.C., Swallows, M.D., Loftus, T.H., Romalis, M.V., Heckel, B.R., Fortson, E.N.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 101601 (2009)
Farley, F.J.M., Jungmann, K., Miller, J.P., Morse, W.M., Orlov, Y.F., Roberts, B.L., Semertzidis, Y.K., Silenko, A., et al.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 052001 (2004) [hep-ex/0307006]
Semertzidis, Y.K.: Lect. Notes Phys. 741, 97–113 (2008)
Pondrom, L., Handler, R., Sheaff, M., Cox, P.T., Dworkin, J., Overseth, O.E., Devlin, T., Schachinger, L., et al.: Phys. Rev., D 23, 814 (1981)
Bennett, G.W., et al., Muon (g-2) Collaboration: Phys. Rev., D 80, 052008 (2009). arXiv:0811.1207 [hep-ex]
Thomas, L.H.: Phila. Mag. 3, 1 (1927)
Bargmann, V., Michel, L., Telegdi, V.L.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 2, 435 (1959)
A Proposal to Measure the Proton Electric Dipole Moment with 10 − 29 e·cm Sensitivity, Storage Ring EDM Collaboration BNL (2011)
JEDI Proposal: Search for Permanent Electric Dipole Moments at COSY—step 1: spin coherence and systematic error studies, JEDI Collaboration. http://www2.fz-juelich.de/ikp/jedi/documents/proposals.shtml. Accessed Dec 2012
Lehrach, A., Lorentz, B., Morse, W., Nikolaev, N., Rathmann, F.: arXiv:1201.5773 [hep-ex]
Semertzidis, Y.K.: J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 335, 012012 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
The 5th International Symposium on Symmetries in Subatomic Physics (SSP 2012), Groningen, The Netherlands, 18–22 June 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pretz, J., on behalf of the JEDI collaboration. Measurement of permanent electric dipole moments of charged hadrons in storage rings. Hyperfine Interact 214, 111–117 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-013-0799-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-013-0799-4