Abstract
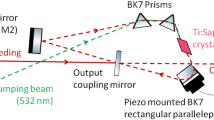
Due to the large absorption cross section for optical transitions into Rydberg and autoionizing states compared to non-resonant ionization, these states are of particular interest for use in efficient laser resonance ionization excitation schemes as used in Resonant Ionization Laser Ion Sources (RILIS). In order to identify these atomic states extensive laser spectroscopy has to be performed. The lasers employed at TRIUMF’s laser ion source are birefringent filter tuned titanium:sapphire (Ti:Sa) lasers which are designed for long term frequency stability rather than continuous tuning. The design and characteristics of a grating tuned, high repetition rate, pulsed Ti:Sa laser for spectroscopy applications are presented. This laser allows fast scans of up to 40 THz with a laser linewidth of approximately 6 GHz. First tests were performed by scanning across the Rydberg series of gallium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bricault, P., et al.: An overview on TRIUMF’s developments on ion sources for radioactive beams. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79, 02A908 (2008)
Scheerer, F., et al.: A chemically selective laser ion-source for online mass separation. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 63, 2831–2833 (1992)
Alkhazov, G.D., et al.: A new highly efficient selective laser ion source. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 280, 141–143 (1989)
Kluge, H.-J., et al.: Laser ion sources. In: Proceedings on Accelerated Radioactive Beams Workshop, Vancouver Island, TRIUMF Proceedings TRI-85-1:119 (1985)
Köster, U.: Resonance ionization laser ion sources. Nucl. Phys., A 701, 441c–451c (2002)
Lassen, J., et al.: Resonant ionization laser ion source project at TRIUMF. Hyperfine Interact. 162, 69–75 (2005)
Demtröder, W.: Laser Spectroscopy. In: Basic Principles, vol. 1, pp. 335–341. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (2008)
Duarte, F.J.: Solid-state multiple-prism grating dye-laser oscillators. Appl. Opt. 33, 3857–3860 (1994)
Duarte, F.J., et al.: Long-pulse narrow-linewidth dispersive solid-state dye laser oscillator. Appl. Opt. 37, 3987–3989 (1998)
Horn, R.E.: Aufbau eines Systems gepulster, abstimmbarer Festkörperlaser zum Einsatz in der Resonanzionisations-Massenspektroskopie. Dissertation, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz (2003) (in German)
Albers, D.: Design, Assembly and characterisation of a double-sided-pumped, high repetition rate titanium sapphire laser systems. Diplom thesis, Fachhochschule Oldenburg/ Ostfriesland/ Wilhelmshaven (2007)
Hänsch, T.W.: Repetitively pulsed tunable dye laser for high resolution spectroscopy. Appl. Opt. 11, 895–989 (1972)
Boyd, R.D., et al.: High-efficiency metallic diffraction gratings for laser applications. Appl. Opt. 34, 1697–1706 (1995)
Hanna, D.C., et al.: A simple beam expander for frequency narrowing of dye lasers. Opt. Quantum Electron. 7, 115–119 (1975)
Prime, E.J., et al.: TRIUMF resonant ionization laser ion source—Ga, Al and Be radioactive ion beam development. Hyperfine Interact. 171, 127–134 (2006)
Ball, G.C., et al.: High-resolution γ-ray spectroscopy: a versatile tool for nuclear β-decay studies at TRIUMF-ISAC. J. Phys., G 31, 1491–1498 (2005)
Geppert, C.: Resonanzionisation zum Nachweis und zur Erzeugung radioaktiver Ionenstrahlen: Vom hochselectiven Ultraspurennachweis zur selektiven on-line Laserionenquelle, Dissertation, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz (2005) (in German)
Lavoie, J.P., et al.: Segmented linear radiofrequency quadrupole/laser ion source project at TRIUMF. Hyperfine Interact. 174, 33–39 (2007)
Sansonetti, J.E., et al.: Handbook of basic atomic spectroscopic data. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 34, 1559–2259 (2005)
Zherikhin, A.N., et al.: Production of photoionic gallium beams through stepwise ionization of atoms by laser radiation. Appl. Phys., B 30, 47–52 (1983)
Buurman, E.P., et al.: On the intercombination line 4s 24p2p − 4s4p 24p in the spectrum of neutral gallium. Z. Phys., D 8, 7–10 (1988)
Saloman, E.B.: A resonance ionization spectroscopy/resonance ionization mass spectrometery data service. V-Data Sheets for Ga, Mn, Sc, and Tl, Spectrochim. Acta. Part B 49, 251–281 (1994)
Baig, M.A., et al.: Autoionization resonances in the 4s-subshell excitation spectrum of gallium. J. Phys., B 24, 3933–3942 (1991)
Davidson, M.D., et al.: Measurements on the quantum defect of the 2S Rydberg series and fine structure of the 2D Rydberg series in the Gallium I spectrum. Z. Phys., D 15, 293–296 (1990)
Shirai, T., et al.: Spectral data for gallium: Ga I through Ga XXXI. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 36, 509–615 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teigelhöfer, A., Bricault, P., Chachkova, O. et al. Grating tuned Ti:Sa laser for in-source spectroscopy of Rydberg and autoionizing states. Hyperfine Interact 196, 161–168 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-010-0171-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-010-0171-x