Abstract
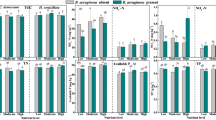
Freshwater snails and submerged macrophytes are both important aquatic biological groups. The presence of freshwater snails might affect the growth of submerged macrophytes in term of their feeding behavior and metabolism. Bellamya aeruginosa (Reeve) is an important freshwater snail for most of Chinese waters and rarely grazes submerged macrophytes. We expected this snail species would benefit the growth of submerged macrophytes. We conducted a control experiment to study effects of nutrient enrichment in the water column and B. aeruginosa absence/presence on growth and carbon (C), nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) stoichiometric characteristics of three submerged macrophytes, Ceratophyllum demersum (L.), Hydrilla verticillata (L. f.) Royle, and Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara. The results indicated that both nutrient enrichment and B. aeruginosa presence affected the biomass and C, N, and P stoichiometric characteristics of submerged macrophytes. However, the effects of nutrient enrichment were relative larger than those of B. aeruginosa presence. B. aeruginosa could promote the biomass of V. natans in low nutrient levels but did not significantly affect the biomass of the other two macrophytes. B. aeruginosa presence increased the N contents of H. verticillata and V. natans, decreased the P contents of V. natans, and had negligible effects on C. demersum. Our study highlights that the effects of B. aeruginosa on submerged macrophytes were very complicated. More studies still should be done in order to give a scientific advice on how these two biological groups are combined used in the restoration of degraded aquatic ecosystems.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Best, E. P. H., 1980. Effects of nitrogen on the growth and nitrogenous compounds of Ceratophyllum demersum. Aquatic Botany 8: 197–206.
Brönmark, C., 1985. Interactions between macrophytes, epiphytes and herbivores: an experimental approach. Oikos 45: 26–30.
Cai, Y., Q. Xue, J. Xu, L. Zhang, Z. Gong & K. Acharya, 2016. Widespread natural intraspecific variation in tissue stoichiometry of two freshwater molluscs: effect of nutrient enrichment. Ecological Indicators 66: 583–591.
Cao, T., L. Ni, P. Xie, J. Xu & M. Zhang, 2011. Effects of moderate ammonium enrichment on three submersed macrophytes under contrasting light availability. Freshwater Biology 56: 1620–1629.
Cao, Y., W. Li & E. Jeppesen, 2014. The response of two submerged macrophytes and periphyton to elevated temperatures in the presence and absence of snails: a microcosm approach. Hydrobiologia 738: 49–59.
Carpenter, S. R. & D. M. Lodge, 1986. Effects of submersed macrophytes on ecosystem processes. Aquatic Botany 26: 341–370.
Denny, P., 1972. Sites of nutrient absorption in aquatic macrophytes. Journal of Ecology 60: 819–829.
Fu, H., G. Yuan, T. Cao, L. Ni, M. Zhang & S. Wang, 2012. An alternative mechanism for shade adaptation: implication of allometric responses of three submersed macrophytes to water depth. Ecological Research 27: 1087–1094.
Gross, E. M., D. Erhard & E. Iványi, 2003. Allelopathic activity of Ceratophyllum demersum, L. and Najas marina, ssp. intermedia, (Wolfgang) Casper. Hydrobiologia 506: 583–589.
Gu, Q., M. Husemann, B. Ding, Z. Luo & B. Xiong, 2015. Population genetic structure of Bellamya aeruginosa (Mollusca: Gastropoda: Viviparidae) in China: weak divergence across large geographic distances. Ecology & Evolution 5: 4906–4919.
Han, S., S. Yan, K. Chen, Z. Zhang, R. Zed, J. Zhang, W. Song & H. Liu, 2010. 15N isotope fractionation in an aquatic food chain: Bellamya aeruginosa (Reeve) as an algal control agent. Journal of Environmental Sciences 22(2): 242–247.
Huang, X., 2000. Survey, Observation and Analysis of Lake Ecology. Standards Press of China, Beijing. (In Chinese).
Jeppesen, E., Søndergaard Ma, Søndergaard Mo & K. Christoffersen (eds), 1997. The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes. Springer-Verlag, New York: 423.
Kuo, S., 1996. Phosphorus. Methods of Soil Analysis Part 3: Chemical Methods. Soil Science Society of America, Madison: 869–919.
Langeland, K. A., 1996. Hydrilla verticillata (LF) Royle (Hydrocharitaceae),” the perfect aquatic weed”. Castanea 61: 293–304.
Li, D., R. A. Erickson, S. Tang, Y. Zhang, Z. Niu, H. Liu & H. Yu, 2016. Structure and spatial patterns of macrobenthic community in Tai Lake, a large shallow lake, China. Ecological Indicators 61: 179–187.
Li, K., Z. Liu, Y. Hu & H. Yang, 2009. Snail herbivory on submerged macrophytes and nutrient release: implications for macrophyte management. Ecological Engineering 35: 1664–1667.
Li, W., T. Cao, L. Ni, G. Zhu, X. Zhang, H. Fu, X. Song & P. Xie, 2015. Size-dependent C, N and P stoichiometry of three submersed macrophytes along water depth gradients. Environmental Earth Sciences 74: 3733–3738.
Li, W., J. Zhong, G. Yuan, H. Fu, H. Fan, L. Ni, P. Xie & T. Cao, 2017. Stoichiometric characteristics of four submersed macrophytes in three plateau lakes with contrasting trophic statuses. Ecological Engineering 99: 265–270.
Lombardo, P. & G. D. Cooke, 2004. Resource use and partitioning by two co-occurring freshwater gastropod species. Archiv Fur Hydrobiologie 159(2): 229–251.
McCollum, E. W., L. B. Crowder & S. A. McCollum, 1998. Complex interactions of fish, snails, and littoral zone periphyton. Ecology 79: 1980–1994.
Mo, S., X. Zhang, Y. Tang, Z. Liu & N. Kettridge, 2017. Effects of snails, submerged plants and their coexistence on eutrophication in aquatic ecosystems. Knowledge & Management of Aquatic Ecosystems 418: 44.
Persson, J., P. Fink, A. Goto, J. M. Hood, J. Jonas & S. Kato, 2010. To be or not to be what you eat: regulation of stoichiometric homeostasis among autotrophs and heterotrophs. Oikos 119: 741–751.
Pieczyńska, E., 2003. Effect of damage by the snail Lymnaea, (Lymnaea) stagnalis, (L.) on the growth of Elodea canadensis, Michx. Aquatic Botany 75: 137–145.
Phillips, G., N. Willby & B. Moss, 2016. Submerged macrophyte decline in shallow lakes: what have we learnt in the last forty years? Aquatic Botany 135: 37–45.
Rattray, M. R., C. Howard-Williams & J. M. A. Brown, 1991. Sediment and water as sources of nitrogen and phosphorus for submerged rooted aquatic macrophytes. Aquatic Botany 40: 225–237.
Rosemond, A. D., P. J. Mulholland & J. W. Elwood, 1993. Top-down and bottom-up control of stream periphyton: effects of nutrients and herbivores. Ecology 74: 1264–1280.
Rybak, J. I., 2002. The release of phosphorus and nitrogen by living and decomposing snails. Polish Academy of Sciences 50(1): 17–24.
Scheffer, M., M. R. Redelijkheid & F. Noppert, 1992. Distribution and dynamics of submerged vegetation in a chain of shallow eutrophic lakes. Aquatic Botany 42: 199–216.
Sheldon, S. P., 1987. The effects of herbivorous snails on submerged macrophyte communities in Minnesota Lakes. Ecology 68: 1920–1931.
Sterner, R. W. & J. J. Elser, 2002. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements From Molecules to the Biosphere. Princeton University Press, Princeton.
Underwood, G. J. C., 1991. Growth enhancement of the macrophyte Ceratophyllum demersum in the presence of the snail Planorbis planorbis: the effect of grazing and chemical conditioning. Freshwater Biology 26: 325–334.
Xie, Y., S. An & B. Wu, 2005. Resource allocation in the submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans related to sediment type, rather than water-column nutrients. Freshwater Biology 50: 391–402.
Zheng, Z., J. Lv, K. Lu, C. Jin, J. Zhu & X. Liu, 2011. The Impact of snail (Bellamya aeruginosa) bioturbation on sediment characteristics and organic carbon fluxes in an eutrophic pond. Clean-Soil Air Water 39: 566–571.
Zhu, J., K. Lu & X. Liu, 2013. Can the freshwater snail Bellamya aeruginosa (Mollusca) affect phytoplankton community and water quality? Hydrobiologia 707: 147–157.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the anonymous reviewers and editors, who kindly provided helpful comments and constructive suggestions. This study was co-funded by the Science and Technology Program Project of Jiangxi province, China (20161BBG70048), the Open Foundation of Chinese Ministry of Water Resources Research Center of Poyang Lake Water Resources and Water Environment (ZXKT201708), and 2017 National Students’ Platform for Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (201711319006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Handling editor: Zhengwen Liu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Fu, H., Li, Y. et al. Effects of nutrient enrichment and Bellamya aeruginosa (Reeve) presence on three submerged macrophytes. Hydrobiologia 833, 95–105 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-019-3884-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-019-3884-0