Abstract
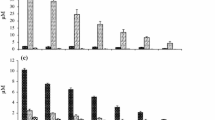
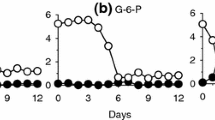
The cosmopolitan alga Phaeocystis globosa forms massive colonies during blooms. In addition to producing haemolytic toxins that affect the ecosystem, centimetre-sized colonies can block nuclear power plant cooling systems. Nitrogen plays a key role in P. globosa blooms; however, the preferred form of inorganic nitrogen taken up by colonies remains unknown. Therefore, we set up four groups with different nitrogen types and levels of enrichment. The culture medium and intracolonial fluid were sampled at different times for the determination of nutrient concentrations to elucidate the nutrient uptake strategy that presumably favours colonies. Although \({{\text{NH}}_{4}}^{ + } {\text{ {-} N}}\) and \({{\text{NO}}_{2}}^{ - } {\text{{-}N}}\) were absorbed by the colonies, \({{\text{NO}}_{3}}^{ - } {\text{{-}N}}\) was the favoured nitrogen, and the average uptake rate of \({{\text{NO}}_{3}}^{ - } {\text{{-}N}}\) was significantly higher than that of \({{\text{NH}}_{4}}^{ + } {\text{{-}N}}\) and \({{\text{NO}}_{2}}^{ - } {\text{{-}N}}\) in each group (P < 0.05). In the enriched groups, the replenishment of \({{\text{NO}}_{3}}^{ - } {\text{{-}N}}\) in the intracolonial fluid was faster than that of \({{\text{NH}}_{4}}^{ + } {\text{{-}N}}\). The symbiotic bacteria and some biochemical processes may explain the differences in the nutrient concentrations inside and outside of the colonies. Considering the high consumption of \({{\text{NO}}_{3}}^{ - } {\text{{-}N}}\) during P. globosa blooms, controlling the concentration of \({{\text{NO}}_{3}}^{ - } {\text{{-}N}}\) is key to preventing P. globosa blooms.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alderkamp, A. C., A. G. J. Buma & M. van Rijssel, 2007. The carbohydrates of Phaeocystis and their degradation in the microbial food web. Biogeochemistry 83: 99–118.
Anderson, D. M., P. M. Glibert & J. M. Burkholder, 2002. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuaries 25: 704–726.
Balode, M., I. Purina, C. Beéchemin & S. Y. Maestrini, 1998. Effects of nutrient enrichment on the growth rates and community structure of summer phytoplankton from the Gulf of Riga, Baltic Sea. Journal of Plankton Research 20: 2251–2272.
Baudoux, A. C. & C. P. D. Brussaard, 2005. Characterization of different viruses infecting the marine harmful algal bloom species Phaeocystis globosa. Virology 341: 80–90.
Baumann, M. E. M., C. Lancelot, F. P. Brandini, E. Sakshaug & D. M. John, 1994. The taxonomic identity of the cosmopolitan prymnesiophyte Phaeocystis: a morphological and ecophysiological approach. Journal of Marine Systems 5: 5–22.
Berman, T., 1997. Dissolved organic nitrogen utilization by an Aphanizomenon bloom in Lake Kinneret. Journal of Plankton Research 19: 577–586.
Cao, X., Z. Yu & L. Qiu, 2017. Field experiment and emergent application of modified clays for Phaeocystis globosa blooms mitigation. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica 48: 753–759. (in Chinese).
Caperon, J. & D. A. Ziemann, 1976. Synergistic effects of nitrate and ammonium ion on the growth and uptake kinetics of Monochrysis lutheri in continuous culture. Marine Biology 36: 73–84.
Chen, S. & K. Gao, 2011. Solar ultraviolet radiation and CO2-induced ocean acidification interacts to influence the photosynthetic performance of the red tide alga Phaeocystis globosa (Prymnesiophyceae). Hydrobiologia 675: 105–117.
Chen, Y., N. Wang, P. Zhang, H. Zhou & L. Qu, 2002. Molecular evidence identifies bloom-forming Phaeocystis (Prymnesiophyta) from coastal waters of southeast China as Phaeocystis globosa. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology 30: 15–22.
Chi, L., X. Song, Y. Yuan, W. Wang, P. Zhou, X. Fan, X. Cao & Z. Yu, 2017. Distribution and key influential factors of dissolved oxygen off the Changjiang River Estuary (CRE) and its adjacent waters in China. Marine Pollution Bulletin 125: 440–450.
Cole, J. J., 1982. Interactions between bacteria and algae in aquatic ecosystems. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 13: 291–314.
Dai, R., P. Wang, P. Jia, Y. Zhang, X. Chu & Y. Wang, 2016. A review on factors affecting microcystins production by algae in aquatic environments. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 32: 1–7.
Dortch, Q., 1990. The interaction between ammonium and nitrate uptake in phytoplankton. Marine Ecology Progress Series 61: 183–201.
Dortch, Q. & H. L. Conway, 1984. Interactions between nitrate and ammonium uptake: variation with growth rate, nitrogen source and species. Marine Biology 79: 151–164.
Hai, D. N., N. N. Lam & J. W. Dippner, 2010. Development of Phaeocystis globosa blooms in the upwelling waters of the South Central coast of Viet Nam. Journal of Marine Systems 83: 253–261.
Hamm, C. E., 2000. Architecture, ecology and biogeochemistry of Phaeocystis colonies. Journal of Sea Research 43: 307–315.
Hamm, C. E., D. A. Simson, R. Merkel & V. Smetacek, 1999. Colonies of Phaeocystis globosa are protected by a thin but tough skin. Marine Ecology Progress Series 187: 101–111.
He, C., S. Xu, S. Song & C. Li, 2019. The spatial-temporal distributions of heterotrophic bacteria in seawater of the northern Beibu Gulf. Acta Oceanologica Sinica 41: 94–108. (in Chinese).
Hu, J., H. Zhang, L. Li, Y. Wang & M. Zhao, 2016. Seasonal changes of organic matter origins and anammox activity in the Changjiang Estuary deduced from multi-biomarkers in suspended particulates. Science China Earth Sciences 59: 1339–1352.
Jiang, X. & N. Jiao, 2016. Nitrate assimilation by marine heterotrophic bacteria. Science China Earth Sciences 59: 477–483.
Klein Breteler, W. C. M. & M. Koski, 2003. Development and grazing of Temora longicornis (Copepoda, Calanoida) nauplii during nutrient limited Phaeocystis globosa blooms in mesocosms. Hydrobiologia 491: 185–192.
Lancelot, C., N. Gypens, G. Billen, J. Garnier & V. Roubeix, 2007. Testing an integrated river-ocean mathematical tool for linking marine eutrophication to land use: The Phaeocystis-dominated Belgian coastal zone (Southern North Sea) over the past 50 years. Journal of Marine Systems 64: 216–228.
Larson, A., M. M. Kirk & D. L. Kirk, 1992. Molecular phylogeny of the volvocine flagellates. Molecular Biology & Evolution 9: 85–105.
Lee, J., A. E. Parker, F. P. Wilkerson & R. C. Dugdale, 2015. Uptake and inhibition kinetics of nitrogen in Microcystis aeruginosa: results from cultures and field assemblages collected in the San Francisco Bay Delta, CA. Harmful Algae 47: 126–140.
Lunau, M., M. Voss, M. Erickson, C. Dziallas, K. Casciotti & H. Ducklow, 2013. Excess nitrate loads to coastal waters reduces nitrate removal efficiency: mechanism and implications for coastal eutrophication. Environmental Microbiology 15: 1492–1504.
Madhupratap, M., S. Sawant & M. Gauns, 2000. A first report on a bloom of the marine prymnesiophycean, Phaeocystis globosa from the Arabian Sea. Oceanologica Acta 23: 83–90.
Mayers, J. J., K. J. Flynn & R. J. Shields, 2014. Influence of the N:P supply ratio on biomass productivity and time-resolved changes in elemental and bulk biochemical composition of Nannochloropsis sp. Bioresource Technology 169: 588–595.
Nejstgaard, J. C., K. W. Tang, M. Steinke, J. Dutz, M. Koski, E. Antajan & J. D. Long, 2007. Zooplankton grazing on Phaeocystis: a quantitative review and future challenges. Biogeochemistry 83: 147–172.
Ohmori, M., K. Ohmori & H. Strotmann, 1977. Inhibition of nitrate uptake by ammonia in a blue-green alga, Anabaena cylindrica. Archives of Microbiology 114: 225–229.
Ploug, H., W. Stolte & B. B. Jørgensen, 1999. Diffusive boundary layers of the colony-forming plankton alga Phaeocystis sp.-implications for nutrient uptake and cellular growth. Limnology & Oceanography 44: 1959–1967.
Powell, N., A. N. Shilton, S. Pratt & Y. Chisti, 2008. Factors influencing luxury uptake of phosphorus by microalgae in waste stabilization ponds. Environmental Science & Technology 42: 5958–5962.
Qi, Y., J. Chen, Z. Wang, N. Xu, Y. Wang, P. Shen, S. Lu & I. J. Hodgkiss, 2004. Some observations on harmful algal bloom (HAB) events along the coast of Guangdong, southern China in 1998. Hydrobiologia 512: 209–214.
Riegman, R., A. A. M. Noordeloos & G. C. Cadée, 1992. Phaeocystis blooms and eutrophication of the continental coastal zones of the North Sea. Marine Biology 112: 479–484.
Rousseau, V., M. J. Chrétiennot-Dinet, A. Jacobsen, P. Verity & S. Whipple, 2007. The life cycle of Phaeocystis: state of knowledge and presumptive role in ecology. Biogeochemistry 83: 29–47.
Smith Jr., W. O., X. Liu, K. W. Tang, L. M. DeLizo, N. H. Doan, N. L. Nguyen & X. Wang, 2014. Giantism and its role in the harmful algal bloom species Phaeocystis globosa. Deep-Sea Research Part II 101: 95–106.
Solomonson, L. P. & M. J. Barber, 1990. Assimilatory nitrate reductase: functional properties and regulation. Annual Review of Plant Biology 41: 225–253.
Tan, S., X. Hu, P. Yin & L. Zhao, 2016. Photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative stress to the toxic Phaeocystis globosa caused by a diketopiperazine isolated from products of algicidal bacterium metabolism. Journal of Microbiology 54: 364–375.
Tang, K. W., 2003. Grazing and colony size development in Phaeocystis globosa (Prymnesiophyceae): the role of a chemical signal. Journal of Plankton Research 25: 831–842.
Tang, D. L., H. Kawamura, H. Doan-Nhu & W. Takahashi, 2004. Remote sensing oceanography of a harmful algal bloom off the coast of southeastern Vietnam. Journal of Geophysical Research 109: 1–7.
Terry, K. L., 1982. Nitrate uptake and assimilation in Thalassiosira weissflogii and Phaeodactylum tricornutum: interactions with photosynthesis and with the uptake of other ions. Marine Biology 69: 21–30.
Van Boekel, W. H. M. & M. J. W. Veldhuis, 1990. Regulation of alkaline phosphatase synthesis in Phaeocystis sp. Marine Ecology Progress Series 61: 281–289.
Van Rijssel, M., I. Janse, D. J. B. Noordkamp & W. W. C. Gieskes, 2000. An inventory of factors that affect polysaccharide production by Phaeocystis globosa. Journal of Sea Research 43: 297–306.
Veldhuis, M. J. W., C. P. D. Brussaard & A. A. M. Noordeloos, 2005. Living in a Phaeocystis colony: a way to be a successful algal species. Harmful Algae 4: 841–858.
Wan, X. S., H. X. Sheng, M. Dai, Y. Zhang, D. Shi, T. W. Trull, Y. Zhu, M. W. Lomas & S. J. Kao, 2018. Ambient nitrate switches the ammonium consumption pathway in the euphotic ocean. Nature Communications 9: 1–9.
Wang, Y., H. Tang, L. Jiang & S. Li, 2006. Effects of nitrate on the growth and nitrate reductase activity in Phaeocystis globosa. Chinese Bulletin of Botany 23: 138–144. (in Chinese).
Wang, X., Y. Wang & W. O. Smith Jr., 2011. The role of nitrogen on the growth and colony development of Phaeocystis globosa (Prymnesiophyceae). European Journal of Phycology 46: 305–314.
Wang, W., Z. Yu, X. Song, Y. Yuan, Z. Wu, P. Zhou & X. Cao, 2018. Intrusion pattern of the offshore kuroshio branch current and its effects on nutrient contributions in the East China Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans 123: 1–13.
Xu, X., Z. Yu, L. He, F. Cheng, X. Cao & X. Song, 2017. Nano- and microphytoplankton community characteristics in brown tide bloom-prone waters of the Qinhuangdao coast, Bohai Sea, China. Science China Earth Sciences 60: 1189–1200.
Yu, Z., X. Song, X. Cao & Y. Liu, 2017. Mitigation of harmful algal blooms using modified clays: theory, mechanisms, and applications. Harmful Algae 69: 48–64.
Zhang, H., Y. Peng, S. Zhang, G. Cai, Y. Li, X. Yang, K. Yang, Z. Chen, J. Zhang, H. Wang, T. Zheng & W. Zheng, 2016. Algicidal effects of prodigiosin on the harmful algae Phaeocystis globosa. Frontiers in Microbiology 7: 1–10.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Guangxi Academy of Sciences and Guangxi Fangchenggang Nuclear Power Co., Ltd., for instrument employed. The authors sincerely thank Dr. Wentao Wang and Liyan He from Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao for their valuable and constructive suggestions, which helped us to considerably improve the manuscript. This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFC1404300), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41706133), the Aoshan Talents Cultivation Program supported by Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (2017ASTCP-OS16), the NSFC-Shandong Joint Fund for Marine Science Research Centers (U1606404), and the Taishan Scholars Climbing Program of Shandong Province of the year 2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Judit Padisák
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, X., Wu, Z., Song, X. et al. Nutritional strategy for the preferential uptake of \({{\text{NO}}_{3}}^{ - } {\text{{-}N}}\) by Phaeocystis globosa. Hydrobiologia 846, 109–122 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-019-04055-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-019-04055-6