Abstract
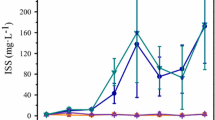
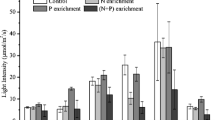
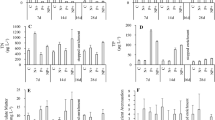
An increased nutrient loading drives eutrophication of lake ecosystems. Nutrient loading has two different origins: (1) internal loading due to nutrients release from sediments and (2) external loading due to nutrients entering the lake ecosystem from catchment and atmospheric deposition. A 10-day mesocosm experiment was conducted to assess the effects of two nutrient origins on algal photosynthetic capacity, biomass, and phytoplankton community composition of Lake Taihu in the Yangtze River zone. The experiment was specifically designed to mimic (1) internal loading including sediment release in both static and turbulent situations, and (2) external loading including addition of P only, N only, and co-addition of both N and P. Sediment resuspension significantly increased nutrient loading and decreased algal photosynthetic capacity. Resuspension brought benthic algae into water column, resulting in an increase of algal biomass. Nutrient addition significantly changed N:P ratios and phytoplankton community composition. Nutrient addition optimized the dominant species. N Addition favored cyanobacteria reproduction, while P addition did not benefit algal growth and chlorophytes was the dominant in summer. With N and P co-addition, both cyanobacteria and chlorophytes were dominant. Hence, a long-term nutrient management strategy for Taihu watershed should reduce the inputs of both N and P.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, J. M., Y. I. Park & W. S. Chow, 1997. Photoinactivation and photoprotection of photosystem II in nature. Physiologia Plantarum 100: 214–223.
Baker, N. R., 2008. Chlorophyll fluorescence: a probe of photosynthesis in vivo. Annual Review of Plant Biology 59: 89–113.
Bledsoe, E. L., E. J. Phlips, C. E. Jett & K. A. Donnelly, 2004. The relationships among phytoplankton biomass, nutrient loading and hydrodynamics in an inner-shelf estuary. Ophelia 58: 29–47.
Bloesch, J., 1995. Mechanisms, measurement and importance of sediment resuspension in lakes. Marine and Freshwater Research 46: 295–304.
Büechel, C. & C. Wilhelm, 1993. In vivo analysis of slow chlorophyll fluorescence induction kinetics in algae: progress, problems and perspectives. Photochemistry and Photobiology 58: 137–148.Boström, B., 1988. Relations between chemistry, microbial biomass and activity in sediments of a sewage-polluted vs a nonpolluted eutrophic lake. SIL Proceedings 1922-2010, 23:1, 451-459.
Carrick, H. J., F. J. Aldridge & C. L. Schelske, 1993. Wind Influences phytoplankton biomass and composition in a shallow, productive lake. Limnology and Oceanography 38: 1179–1192.
Carmichael, W. W., 2001. Health effects of toxin producing cyanobacteria: the cyanoHABs. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment 7: 1393–1407.
Chen, Y. W., B. Q. Qin, K. Teubner & M. T. Dokulil, 2003. Long-term dynamics of phytoplankton assemblages: Microcystis-domination in Lake Taihu, a large shallow lake in China. Journal of Plankton Research 25: 445–453.
Cloern, J. E., 2001. Our evolving conceptual model of the coastal eutrophication problem. Marine Ecology Progress Series 210: 223–253.
Ding, Y. Q., B. Q. Qin, G. W. Zhu, T. F. Wu, Y. P. Wang & L. C. Luo, 2012. Effects of typhoon Morakot on a large shallow lake ecosystem, Lake Taihu, China. Ecohydrology 5: 798–807.
Ding, Y. Q., B. Q. Qin, H. Xu & X. D. Wang, 2016. Effects of sediment and turbulence on alkaline phosphatase activity and photosynthetic activity of phytoplankton in the shallow hyper-eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 23: 183–193.
Ding, Y. Q., B. Q. Qin, J. M. Deng & J. R. Ma, 2017. Effects of episodic sediment resuspension on phytoplankton in Lake Taihu: focusing on photosynthesis, biomass and community composition. Aquatic Sciences 79: 617–629.
Downing, J. A. & E. McCauley, 1992. The nitrogen: phosphorus relationship in lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 37: 936–945.
Duarte, C. M., S. Agusti & S. R. Agawin, 2000. Response of a Mediterranean phytoplankton community to increased nutrient inputs: A mesocosm experiment. Marine Ecology Progress Series 195: 61–70.
Dzialowski, A. R., S. H. Wang, N. C. Lim, J. H. Beury & D. G. Huggins, 2008. Effects of sediment resuspension on nutrient concentrations and algal biomass in reservoirs of the central plains. Lake Reservoir Management 24: 313–320.
Edler, L. & M. Elbrächter, 2010. The Utermöhl method for quantitative phytoplankton analysis. In Karlson, B., C. Cusack & E. Bresnan (eds), Microscopic and Molecular Methods for Quantitative Phytoplankton Analysis. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, Paris: 13–20.
Elmgren, R. & U. Larsson, 2001. Nitrogen and the Baltic Sea: Managing nitrogen in relation to phosphorus. Scientific World 1: 371–377.
Elser, J. J., E. R. Marzolf & C. R. Goldman, 1990. Phosphorus and nitrogen limitation of phytoplankton growth in the freshwaters of North America: A review and critique of experimental enrichments. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 47: 1468–1477.
Falkowski, P. G. & Z. Kolber, 1995. Variations in chlorophyll fluorescence yields in phytoplankton in the world oceans. Australian Journal Plant Physiology 22: 341–355.
Fan, C. X., Y. B. Lou & H. S. Chen, 2000. Approach on estimating storage sludge in Lake Taihu and its distributing characteristics. Shanghai Environmental Sciences 19: 72–75. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Fan, C. X., L. Zhang & B. Q. Qin, 2004. Estimation on dynamic release of phosphorus from wind-induced suspended particulate matter in Lake Taihu. Science in China Series D 47: 710–719.
Gao, G., G. W. Zhu, B. Q. Qin, J. Chen & K. Wang, 2006. Alkaline phosphatase activity and the phosphorus mineralization rate of Lake Taihu. Science in China Series D 49: 176–185.
Gao, L., J. M. Zhou, H. Yang & J. Chen, 2005. Phosphorus fractions in sediment profiles and their potential contributions to eutrophication in Dianchi Lake. Environmental Geology 48: 835–844.
Genty, B., J. M. Briantais & N. R. Baker, 1989. The relationship between the quantum yield of photosynthetic electron transport and quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 990: 87–92.
Gu, T., F. X. Kong & X. Tan, 2011. Investigation on spatio-temporal pattern of cyanobacterial community structure by T-RFLP during overwinter and recruitment period in Taihu Lake. Acta Ecologica Sinica 31: 21–30. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Guildford, S. J. & R. E. Hecky, 2000. Total nitrogen, total phosphorus, and nutrient limitation in lakes and oceans: Is there a common relationship? Limnology and Oceanography 45: 1213–1223.
Guo, L., 2007. Ecology- doing battle with the green monster of Taihu Lake. Science 317: 1166–1166.
Håkanson, L., 1982. Lake bottom dynamics and morphometry: The dynamic ratio. Water Resources Research 18: 1444–1450.
Hamilton, D. P. & S. F. Mitchell, 1997. Wave-induced shear stresses, plant nutrients and chlorophyll in seven shallow lakes. Freshwater Biology 38: 159–168.
Hecky, R., P. Campbell & L. Hendzel, 1993. The stoichiometry of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in particulate matter of lakes and oceans. Limnology and Oceanography 38: 709–724.
Hecky, R. E. & P. Kilhamp, 1988. Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton in freshwater and marine environments: A review of recent evidence on the effects of enrichment. Limnology and Oceanography 33: 796–822.
Heraud, P. & J. Beardall, 2000. Changes in chlorophyll fluorescence during exposure of Dunaliella tertiolecta to UV radiation indicate a dynamic interaction between damage and repair processes. Photosynthysis Research 63: 123–134.
Hu, H., Y. Li, H. Wei & J. Zhu, 1980. Freshwater algae in China. Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Beijing.
Jeppesen, E., J. P. Jensen, M. Sondergaard, K. S. Hansen, P. H. Moller, H. U. Rasmussen, V. Norby & S. E. Larsen, 2003. Does resuspension prevent a shift to a clear state in shallow lakes during reoligotrophication? Limnology and Oceanography 48: 1913–1919.
Jespersen, A. M. & K. Christoffersen, 1987. Measurements of chlorophyll a from phytoplankton using ethanol as extraction solvent. Archiv Fur Hydrobiologie 109: 445–454.
Jin, X. C. & Q. Y. Tu, 1990. Standard of Lake Eutrophication Survey of China. China Environmental Science Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese).
Kamp-Nielsen, L., 1975. A kinetic approach to the aerobic sediment–water exchange of phosphorus in Lake Esrom. Ecological Modelling 1: 153–160.
Kolber, Z. & P. G. Falkowski, 1993. Use of active fluorescence to estimate phytoplankton photosynthesis in situ. Limnology and Oceanography 38: 1646–1665.
Kristensen, P., M. Søndergaard & E. Jeppesen, 1992. Resuspension in a shallow eutrophic lake. Hydrobiologia 228: 101–109.
Lai, G. Y., G. Yu & F. Gui, 2006. Preliminary study on assessment of nutrient transport in the Taihu Basin based on SWAT modeling. Science in China Series D 49: 135–145.
Lewis, W. M. & A. W. Wurtsbaugh, 2008. Control of lacustrine phytoplankton by nutrients: Erosion of the phosphorus paradigm. International Review of Hydrobiology 93: 446–465.
Li, Y., M. Horsman, B. Wang, N. Wu & C. Q. Lan, 2008. Effects of nitrogen sources on cell growth and lipid accumulation of green alga Neochloris oleoabundans. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 81: 629–636.
Luo, L. C., B. Q. Qin, G. W. Zhu, X. J. Sun, D. L. Hong, Y. J. Gao & R. Xie, 2006. Nutrient fluxes induced by disturbance in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu. Science inChina Series D 49: 186–192.
Luo, L. C., B. Q. Qin, L. Y. Yang & Y. Z. Song, 2007. Total inputs of phosphorus and nitrogen by wet deposition into Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 581: 63–70.
Ma, J. R., J. D. Brookes, B. Q. Qin, H. W. Paerl, G. Gao, P. Wu, W. Zhang, J. M. Deng, G. W. Zhu , Y. L. Zhang, H. Xu & H. L. Niu, 2014. Environmental factors controlling colony formation in blooms of the cyanobacteria Microcystis spp. in Lake Taihu, China. Harmful Algae 31: 136–142.
Ma, J. R., B. Q. Qin, P. Wu, J. Zhou, C. Niu, J. M. Deng & H. L. Niu, 2015. Controlling cyanobacterial blooms by managing nutrient ratio and limitation in a large hypereutrophic lake: Lake Taihu, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences 27: 80–86.
McCarthy, M. J., P. J. Lavrentyev, L. Y. Yang, L. Zhang, Y. W. Chen, B. Q. Qin & W. S. Gardner, 2007. Nitrogen dynamics relative to microbial food web structure in a subtropical, shallow, well-mixed, eutrophic lake (Taihu Lake, China). Hydrobiologia 581: 195–207.
Niemistö, J. & J. Horppila, 2007. The contribution of ice cover to sediment resuspension in a shallow temperate lake: possible effects of climate change on internal nutrient loading. Journal of Environmental Quality 36: 1318–1323.
Niemistö, J., H. Holmroos, Z. Pekcan-Hekim & J. Horppila, 2008. Interactions between sediment resuspension and sediment quality decrease the TN: TP ratio in a shallow lake. Limnology and Oceanography 53: 2407–2415.
Nixdorf, B. & R. Deneke, 1997. Why “very shallow” lakes are more successful opposing reduced nutrients loads. Hydrobiologia 342(343): 269–284.
Nixon, S. W., 1995. Coastal marine eutrophication: A definition, social causes, and future concerns. Ophelia 41: 199–219.
Paerl, H. W., 2008. Nutrient and other environmental controls of harmful cyanobacterial blooms along the fresh watere marine continuum. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 619: 216–241.
Paerl, H. W., 2009. Controlling eutrophication along the freshwater -Marine continuum: dual nutrient (N and P) reductions are essential. Estuaries and Coasts 32: 593–601.
Paerl, H. W., R. S. Fulton, P. H. Moisander & J. Dyble, 2001. Harmful freshwater algal blooms, with an emphasis on cyanobacteria. The Scientific World 1: 76–113.
Paerl, H. W., H. Xu, M. J. McCarthy, G. W. Zhu, B. Q. Qin, Y. P. Li & W. S. Gardner, 2011. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hypereutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): The need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Research 45: 1973–1983.
Palmer-Felgate, E. J., R. J. G. Mortimer, M. D. Krom & H. P. Jarvie, 2011. Internal loading of phosphorus in a sedimentation pond of a treatment wetland: effect of a phytoplankton crash. Science of the total environment 409: 2222–2232.
Ogilvie, B. G. & S. F. Mitchell, 1998. Does sediment resuspension have persistent effects on phytoplankton? Experimental studies in three shallow lakes. Freshwater Biology 40: 51–63.
Oxborough, K., A. R. M. Hanlon, G. J. C. Underwood & N. R. Baker, 2000. In vivo estimation of the photosystem II photochemical efficiency of individual microphytobenthic cells using high-resolution imaging of chlorophyll a fluorescence. Limnology and Oceanography 45: 1420–1425.
Qin, B. Q., W. P. Hu, G. Gao, L. C. Luo & J. S. Zhang, 2004. Dynamics of sediment resuspension and the conceptual schema of nutrient release in the large shallow Lake Taihu, China. Chinese Science Bulletin 49: 54-64.Qin, B. Q., G. W. Zhu, G. Gao, Y. L. Zhang, W. Li, H. W. Paerl & W. W. Carmichael, 2010. A drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environmental Management 45: 105–112.
Qin, B. Q., P. Z. Xu, Q. L. Wu, L. C. Luo & Y. L. Zhang, 2007. Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 581: 3–14.
Regel, R. H., J. D. Brookes & G. G. Ganf, 2004. Vertical migration, entrainment and photosynthesis of the freshwater dinoflagellate Peridinium cinctum in a shallow urban lake. Journal of Plankton Research 26: 143–157.
Rosenberg, J. N., G. A. Oyler, L. Wilkinson & M. J. Betenbaugh, 2008. A green light for engineered algae: redirecting metabolism to fuel a biotechnology revolution. Current Opinion in Biotechnology 19: 430–436.
Scheffer, M., 1998. Ecology of Shallow Lakes. Chapman and Hall, New York.
Schindler, D. W., 1977. The evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science 195: 260–262.
Schindler, D. W., R. E. Hecky, D. L. Findlay, M. P. Stainton, B. P. Parker, M. J. Paterson, K. G. Beaty, M. Lyng & S. E. M. Kasian, 2008. Eutrophication of lakes cannot be controlled by reducing nitrogen input: Results of a 37 year whole ecosystem experiment. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 105: 11254–11258.
Schreiber, U., 1994. New emitter detector cuvette assembly for measuring modulated chlorophyll fluorescence of highly diluted suspensions in conjunction with the standard PAM fluorometer. Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung C 49: 646–656.
Schreiber, U., J. F. Müller, A. Haugg & R. Gademann, 2002. New type of dual-channel PAM chlorophyll fluorometer for highly sensitive water toxicity biotests. Photosynthesis research 74: 317–330.
Smayda, T. J. & C. S. Reynolds, 2001. Community assembly in marine phytoplankton: Application of recent models to harmful dinoflagellate blooms. Journal of Plankton Research 23: 447–461.
Smith, V. H., 1990. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and nitrogen fixation in lacustrine and estuarine ecosystems. Limnology and Oceanography 35: 1852–1859.
Smith, V. H., 2003. Eutrophication of freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems: A global problem. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 10: 126–139.
Smith, V. H., 2006. Responses of estuarine and coastal marine phytoplankton to nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment. Limnology and Oceanography 51: 377–384.
Søndergaard, M., J. P. Jensen & E. Jeppesen, 2003. Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 506–509: 135–145.
Vanni, M. J. & J. Temte, 1990. Seasonal patterns of grazing and nutrient limitation of phytoplankton in a eutrophic lake. Limnology and Oceanography 35: 697–709.
Verburg, P., J. Horrox, E. Chaney, J. Rutherford, J. Quinn & R. Wilcock, 2013. Nutrient ratios, differential retention, and the effect on nutrient limitation in a deep oligotrophic lake. Hydrobiologia 718: 119–130.
Wang, X. D., B. Q. Qin, G. Gao & H. W. Paerl, 2010. Nutrient enrichment and selective predation by zooplankton promote Microcystis (Cyanobacteria) bloom formation. Journal of Plankton Research 32: 457–470.
White, S., A. Anandraj & F. Bux, 2011. PAM fluorometry as a tool to assess microalgal nutrient stress and monitor cellular neutral lipids. Bioresource Technology 102: 1675–1682.
Wu, T. F., B. Q. Qin, G. W. Zhu, L. C. Luo, Y. Q. Ding & G. Bian, 2013. Dynamics of cyanobacterial bloom formation during short-term hydrodynamic fluctuation in a large shallow, eutrophic, and wind-exposed Lake Taihu, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 20: 8546–8556.
Wu, X. D., F. X. Kong & X. L. Zhang, 2008. Comparison of overwintering and recruitment of Cyanobacteria in Taihu Lake and Chaohu Lake. Huan Jing Ke Xue 29: 1313-1318 (Press in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu, H., H. W. Paerl, B. Q. Qin, G. W. Zhu & G. Gao, 2010. Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnology and Oceanography 55: 420–432.
Xu, H., H. W. Paerl, B. Q. Qin, G. W. Zhu, N. S. Hall & Y. Wu, 2015. Determining critical nutrient thresholds needed to control harmful cyanobacterial blooms in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Environmental Science and Technology 49: 1051–1059.
Xu, P. Z. & B. Q. Qin, 2005. Water quantity and pollutant fluxes of the surrounding rivers of Lake Taihu during the hydrological year of 2001-2002. Journal of Lake Sciences 17: 213-218 (Press in Chinese with English abstract).
You, B. S., J. C. Zhong, C. X. Fan, T. C. Wang, L. Zhang & S. M. Ding, 2007. Effects of hydrodynamics processes on phosphorus fluxes from sediment in large, shallow Taihu Lake. Journal of Environmental Sciences 19: 1055–1060.
Zhang, L., X. Gu, C. X. Fan, J. G. Shang, Q. S. H. Shen, Zh D Wang & J. Shen, 2010. Impact of different benthic animals on phosphorus dynamics across the sediment-water interface. Journal of Environmental Sciences 22: 1674–1682.
Zhang, L., J. G. Shang, W. He, B. S. You & C. X. Fan, 2014. The role of tubificid worms (Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri) in sediment resuspension: a microcosm study. Annales de Limnologie - International Journal of limnology 50: 253–260.
Zhang, M., F. X. Kong, X. D. Wu & P. Xing, 2008. Different photochemical responses of phytoplankters from the large shallow Taihu Lake of subtropical China in relation to light and mixing. Hydrobiologia 603: 267–278.
Zhu, G. W., B. Q. Qin & G. Gao, 2005. Direct evidence of phosphorus outbreak release from sediment to overlying water in a large shallow lake caused by strong wind wave disturbance. Chinese Science Bulletin 50: 577–582.
Zhu, G. W., B. Q. Qin, G. Gao, L. Zhang, L. C. Luo & Y. L. Zhang, 2007. Effects of hydrodynamics on phosphorus concentrations in water of Lake Taihu, a large, shallow, eutrophic lake of China. Hydrobiologia 581: 53–61.
Zhu, G. W., F. Wang, G. Gao & B. Q. Qin, 2008. Hypoxia and its environmental influences in large, shallow, and eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Verhandlungen des Internationalen Verein Limnologie 30: 361–365.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Lake Taihu Laboratory for Lake Ecosystem Research which provided the experiment platform. This work was funded through the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41501518, 41621002), Sino-French international collaborative research project (41661134036) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20140184). And it also was supported by State Key Laboratory of Lake Science and Environment (2016SKL006) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2014QNA86).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Judit Padisák
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Y., Xu, H., Deng, J. et al. Impact of nutrient loading on phytoplankton: a mesocosm experiment in the eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 829, 167–187 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-018-3830-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-018-3830-6