Abstract
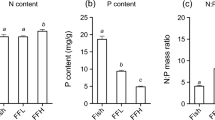
We investigated the roles of a benthivorous (Prochilodus brevis, Steindachner 1875) and a planktivorous (Oreochromis niloticus, Linnaeus, 1758) fish in translocating phosphorus from the benthic to the pelagic habitat of a tropical eutrophic shallow lake and its impact on phytoplankton biomass and water transparency. We performed two field experiments in 20 mesocosms (6 m3) with a 2 × 2 factorial design. Fish presence/absence was manipulated in combination with the presence/absence of a fish cage (4 m3) that prevented fish accessing the sediment. Benthivorous fish increased total phosphorus and chlorophyll a concentrations and decreased water transparency, but only when they had access to the sediment. Planktivorous fish increased the concentration of chlorophyll a without changing total phosphorus concentrations, whether or not they had access to the sediment. Results suggest that only the benthivorous fish increased phytoplankton biomass by translocating phosphorus from benthic to pelagic habitats. However, the planktivorous fish increased phytoplankton biomass by removing zooplankton and recycling nutrients within the pelagic zone. We conclude that removal of either fish species can improve the water quality of eutrophic shallow lakes in tropical regions, but only the removal of benthivorous fish will reduce the internal loading of phosphorus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamek, Z. & B. Marsálek, 2013. Bioturbation of sediments by benthic macroinvertebrates and fish and its implications for pond ecosystems: a review. Aquaculture International 21: 1–17.
Attayde, J. L. & R. F. Menezes, 2008. Effects of fish biomass and planktivore type on plankton communities. Journal of Plankton Research 30: 885–892.
Attayde, J. L., E. H. van Nes, A. I. L. Araujo, G. Corso & M. Scheffer, 2010. Omnivory by planktivores stabilizes plankton dynamics, but may either promote or reduce algal biomass. Ecosystems 13: 410–420.
Bowen, S. H., 1983. Detritivory in neotropical fish communities. Environmental Biology of Fishes 9: 137–144.
Brasil, J., J. L. Attayde, F. R. Vansconcelos, D. D. F. Dantas & V. L. M. Huszar, 2016. Drought-induced water-level reduction favor cyanobacteria blooms in tropical shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 770: 145–164.
Breukelaar, A. W., E. H. R. R. Lammens, J. G. P. Klein Breteler & I. Tátrai, 1994. Effects of benthivorous bream (Abramis brama) and carp (Cyprinus carpio) on sediment resuspension and concentrations of nutrients and chlorophyll a. Freshwater Biology 32: 113–121.
Carpenter, S. R. & K. L. Kitchell, 1993. The Trophic Cascade in Lakes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Cooke, G. D., E. B. Welch, S. A. Peterson & S. A. Nicholas, 2005. Restoration and Management of Lakes and Reservoirs. CRC Press, Boca Raton.
Costa, M. R. A., J. L. Attayde & V. Becker, 2016. Effects of water level reduction on the dynamics of phytoplankton functional groups in tropical semi-arid shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 778: 75–89.
Croel, R. C. & J. M. Kneitel, 2011. Ecosystem-level effects of bioturbation by the tadpole shrimp Lepidurus packardi in temporal pond mesocosm. Hydrobiologia 665: 169–181.
Fernando, C. H., 1994. Zooplankton, fish and fisheries in tropical freshwaters. Hydrobiologia 272: 105–123.
Figueredo, C. C. & A. Giani, 2005. Ecological interactions between Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and phytoplanktonic community of the Furnas Reservoir (Brazil). Freshwater Biology 50: 1391–1403.
Flecker, A. S., 1996. Ecosystem engineering by a dominant detritivore in a diverse tropical stream. Ecology 77: 1845–1854.
Fulton, R. S., W. F. Godwin & M. H. Schaus, 2015. Water quality changes following nutrient loading reduction and biomanipulation in a large shallow subtropical lake, Lake Griffin, Florida, USA. Hydrobiologia 753: 243–263.
González-Bergonzoni, I., M. Meerhoff, T. A. Davidson, F. Teixeira-de Melo, A. Baattrup-Pedersen & E. Jeppesen, 2012. Meta-analysis shows a consistent and strong latitude pattern in fish omnivory across ecosystems. Ecosystems 15: 492–503.
Hansson, L. A. H., H. Annadoter, E. Bergman, S. F. Hamrim, E. Jeppesen, T. Kairesalo, E. Luokkanen, P. A. Nilsson, M. Sondergaard & J. Strand, 1998. Biomanipulation as an application of food-chain theory: constraints, synthesis, and recommendations for temperate lakes. Ecosystem 1: 558–574.
Iglesias, C., N. Mazzeo, M. Meerhoff, G. Lacerot, J. M. Clemente, F. Scasso, C. Kruk, G. Goyenola, J. García-Alonso, S. L. Amsinck, J. C. Paggi, S. J. Paggi & E. Jeppesen, 2011. High predation is of key importance for dominance of small-bodied zooplankton in warm shallow lakes: evidence from lakes, fish exclosures, and surface sediment. Hydrobiologia 667: 133–147.
Jeppesen, E., M. Meerhoff, B. A. Jakobsen, R. S. Hansen, M. Søndergaard, J. P. Jensen, T. L. Lauridesen, N. Mazzeo & C. W. C. Branco, 2007. Restoration of shallow lakes by nutrient control and biomanipulatio – the successful strategy varies with lake size and climate. Hydrobiologia 581: 269–285.
Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, T. L. Lauridsen, T. A. Davidson, L. Zhengwen, N. Mazzeo, C. Trochine, K. Özkan, H. S. Jensen, D. Trolle, F. L. R. M. Starling, X. Lazzaro, L. S. Johansson, R. Bjerring, L. Liboriussen, S. E. Larsen, F. Landkildehus, S. Egemose & M. Meerhoff, 2012. Biomanipulation as a restoration tool to combat eutrophication: recent advances and future challenges. Advances in Ecological Research 47: 411–473.
Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard & Z. Liu, 2017. Lake restoration and management in a climate change perspective: an introduction. Water 9: 1–8.
Jespersen, A. M. & K. Christoffersen, 1988. Measurements of chlorophyll α from phytoplankton using ethanol as extraction solvent. Archives of Hydrobiologia 109: 445–454.
Jiménez-Montealegre, R., M. Verdegem, J. E. Zamora & J. A. J. A. J. Verreth, 2002. Organic matter sedimentation and resuspension in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) ponds during a production cycle. Aquacultural Engineering 26: 1–12.
Joyni, M. J., B. M. Kurup & Y. Avnimelech, 2011. Bioturbation as a possible means for increase production and improving pond soil characteristic in shrimp-fish brackish water ponds. Aquaculture 318: 464–470.
Kosten, S., V. L. M. Huszar, E. Bécares, L. S. Costa, E. Van Donk, L.-A. Hansson, E. Jeppesen, C. Kruk, G. Lacerot, N. Mazzeo, L. Meester, B. Moss, M. Lürling, T. Nõges, S. Romo & M. Scheffer, 2012. Warmer, climate, boost cyanobacterial dominance in shallow lakes. Global Change Biology 18: 118–126.
Kristensen, E., G. Penha-Lopes, M. Delefosse, T. Valdemarsen, C. O. Qintana & G. T. Banta, 2012. What is bioturbation? The need for a precise definition of for fauna in aquatic sciences. Marine Ecology Progress Series 446: 285–302.
Lacerot, G., 2010. Effects of climate on size structure and functioning of aquatic food webs. PhD thesis, Wageningen University: 98.
Lazzaro, X., 1997. Do the trophic cascade hypothesis and classical biomanipulation approaches apply to tropical lakes reservoirs? Verhandlungen Internationale Vereinigung fuer Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie 26: 719–730.
Lazzaro, X. & F. Starling, 2005. Using biomanipulation to control eutrophication in a shallow tropical urban reservoir (Lago Paranoá, Brazil). In Reddy, M. V. (ed.), Restoration and Management of Tropical Eutrophic Lakes. Oxford & IBH Publ. Co. Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi and Science Publishers Inc., New Hampshire: 361–387.
Mehner, T., J. Benndorf, P. Kasprzak & R. Koschel, 2002. Biomanipulation of lake ecosystems: successful application and expanding complexity in the underlying science. Freshwater Biology 47: 2453–2465.
Meijer, M.-L., M. W. de Haan, A. W. Breukelaar & H. Buiteveld, 1990. Is reduction of the benthivorous fish an important cause of high transparency following biomanipulation in shallow lakes? Hydrobiologia 200(201): 303–316.
Menezes, R. F., J. L. Attayde & F. R. Vasconcelos, 2010. Effects of omnivorous filter-feeding fish and nutrient enrichment on the plankton community and water transparency in a tropical reservoir. Freshwater Biology 55: 767–779.
Misson, B., M. Sabart, C. Amblard & D. Latour, 2011. Involvement of microcystins and colony size in benthic recruitment of the cyanobacterium Microcystis (Cyanophyceae). Journal of Phycology 47: 42–51.
Montoya, J. V., D. L. Roelke, K. O. Winemiller, J. B. Cotner & J. A. Snider, 2006. Hydrological seasonality and benthic algal biomass in a Neotropical floodplain river. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 25: 157–170.
Murphy, J. & J. P. Riley, 1962. A modified single-solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta 27: 31–36.
Okun, N., J. Brasil, J. L. Attayde & I. A. S. Costa, 2008. Omnivory does not prevent trophic cascades in pelagic food webs. Freshwater Biology 53: 129–138.
Pearl, H. W. & J. Huisman, 2008. Blooms Like It Hot. Science 320: 57–58.
Rao, W., J. Ning, P. Zhong, E. Jeppesen & Z. Liu, 2015. Size-dependent feeding of omnivorous Nile Tilapia in a macrophyte-dominated lake: implications for lake management. Hydrobiologia 749: 125–134.
Rondel, C., R. Arfi, D. Corbin, F. Le Bihan, E. H. Ndour & X. Lazzaro, 2008. A cyanobacterial bloom prevents fish trophic cascades. Freshwater Biology 53: 637–651.
Roozen, F. C. J. M., M. Lurling, H. Vlek, E. A. J. Van der Pouw Kraan, B. W. Ibelings & M. Scheffer, 2007. Resuspension of algal cells by benthivorous fish boosts phytoplankton biomass and alters community structure in shallow lakes. Freshwater Biology 52: 977–987.
Schaus, M. H. & M. J. Vanni, 2000. Effects of gizzard shad on phytoplankton and nutrient dynamics: role of sediment feeding and fish size. Ecology 81: 1701–1719.
Scheffer, M., 1998. The Ecology of Shallow Lakes. Chapman & Hall, London: 357.
Scheffer, M., R. Portielje & L. Zambrano, 2003. Fish facilitate wave resuspension of sediment. Limnology and Oceanography 48: 1920–1926.
Søndergaard, M., L. Liboriussen, A. R. Pedersen & E. Jeppesen, 2008. Lake restoration by fish removal: long-term effects in 36 Danish lakes. Ecosystems 1: 1291–1305.
Starling, F., M. Beveridge, X. Lazzaro & D. Baird, 1998. Silver carp biomass effects on the plankton community in Paranoa reservoir (Brazil) and an assessment of its potential for improving water quality in lacustrine environments. International Review of Hydrobiology 83: 499–507.
Starling, F., X. Lazzaro, C. Cavalcanti & R. Moreira, 2002. Contribution of omnivorous tilapia to eutrophication of a shallow tropical reservoir: evidence from a fish kill. Freshwater Biology 47: 2443–2452.
Taylor, B., A. Flecker & R. Hall, 2006. Loss of a harvested fish species disrupts carbon flow in a diverse tropical river. Science 313: 833–836.
Valderrama, J. C., 1981. The simultaneous analysis of total N and P in natural waters. Marine Chemical 10: 109–122.
Vanni, M. J., 2002. Nutrient cycling by animals in freshwater ecosystems. Annual Revision of Ecology and Systematic 33: 341–370.
Yu, J., Z. Liu, K. Li, F. Chen, B. Guan, Y. Hu, P. Zhong, Y. Tang, X. Zhao, H. He, H. Zeng & E. Jeppesen, 2016. Restoration of shallow lakes in subtropical and tropical China: response of nutrients and water clarity to biomanipulation by fish removal and submerged plant transplantation. Water 8: 1–13.
Zambrano, L. & D. Hinojosa, 1999. Direct and indirect effects of carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) on macrophyte and benthic communities in experimental shallow ponds in central Mexico. Hydrobiologia 408(409): 131–138.
Zambrano, L., M. Scheffer & M. Martínez-Ramos, 2001. Catastrophic response of lakes to benthivorous fish introduction. Oikos 94: 344–350.
Zhang, X., P. Xie & X. Huang, 2008. A review of nontraditional biomanipulation. The Scientific World Journal 8: 1184–1196.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Vanessa Becker and Andre Amado for their logistic support to the laboratory analyses. The authors greatly appreciate all insights and contributions from the two anonymous reviewers. They also thank the Brazilian Science Foundation (CNPq – www.cnpq.gov.br) for their financial support to JLA (CNPq/ICMBio number 13/2011) and the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES-www.capes.gov.br) for the Ph.D. grants given to DDFD and PLR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: S. Nandini, S.S.S. Sarma, Erik Jeppesen & Linda May / Shallow Lakes Research: Advances and Perspectives
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dantas, D.D.F., Rubim, P.L., de Oliveira, F.A. et al. Effects of benthivorous and planktivorous fish on phosphorus cycling, phytoplankton biomass and water transparency of a tropical shallow lake. Hydrobiologia 829, 31–41 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-018-3613-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-018-3613-0