Abstract
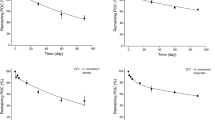
Macrophyte decomposition is a critical process that affects carbon and nutrient cycling, and energy flow, although the majority of the details involved in the process remain unclear. For the present study, a litter bag experiment was conducted to investigate the effects of sediment-borne nutrient and litter quality on the decomposition rates and nutrient release of four macrophyte life forms (emergent macrophyte: Phragmites australis, free-floating macrophyte: Hydrocharis dubia, floating-leaved macrophyte: Nymphoides peltata, submerged macrophyte: Ceratophyllum demersum), and a species mixture. Our results indicated that litter quality significantly influenced macrophyte decomposition and nutrient release. High-quality litter species (high initial nitrogen and phosphorus contents, as well as low C:N, C:P, and N:P ratios) decomposed more rapidly than low-quality litter species, and the initial C:N and C:P ratios, rather than the initial N and P contents, were effective indicators of the decomposition rate of macrophytes. Sediment-borne nutrients had little effect on the decomposition rate, yet a strong effect on the release of N and P, although the interactions between litter quality and sediment-borne nutrients significantly affected the decomposition rate. Three-way ANOVA analysis revealed that the litter quality imparted a more potent effect on the macrophyte decomposition rate and release of N and P than sediment-borne nutrients. These results implied that litter quality interacts with sediment-borne nutrients and may control macrophyte decomposition in shallow lakes.




Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Abelho, M., 2009. Leaf-litter mixtures affect breakdown and macroinvertebrate colonization rates in a stream ecosystem. International Review of Hydrobiology 94: 436–451.
Berglund, S. L. & G. I. Ågren, 2012. When will litter mixtures decompose faster or slower than individual litters? A model for two litters. Oikos 121: 1112–1120.
Bianchini Jr., I., M. B. Cunha-Santino & A. M. Perte, 2008. Oxygen demand during mineralization of aquatic macrophytes from an oxbow lake. Brazilian Journal of Biology 68: 61–67.
Canfield, D. E., B. Thamdrup & E. Kristensen, 2005. Aquatic geimicobiology. Advances in marine biology, Vol. 48. Elsevier, Amsterdam: 424.
Carvalho, P., S. M. Thomaz & L. M. Bini, 2005. Effects of temperature on decomposition of a potential nuisance species: the submerged aquatic macrophyte Egria najas Planchon (Hydrocharitaceae). Brazilian Journal of Biology 65: 51–60.
Chapman, K. J., J. B. Whittaker & O. W. Heal, 1988. Metabolic and faunal activity in litters of tree mixtures compared with pure stands. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment 11: 33–40.
Chapman, S. K., G. S. Newman, S. C. Hart, J. A. Schweitzer & G. W. Koch, 2013. Leaf litter mixtures alter microbial community development: mechanisms for non-additive effects in litter decomposition. PloS One 8: e62671.
Clarke, S. J. & G. Wharton, 2001. Sediment nutrient characteristiccs and aquatic macrophytes in lowland English rivers. The Science of the Total Environment 266: 103–112.
Costantini, M. L., L. Rossi, S. Fazi & D. Rossi, 2009. Detritus accumulation and decomposition in a coastal lake (Acquatina-southern Italy). Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 19: 566–574.
Dang, C. K., M. Schindler, E. Chauvet & M. O. Gessner, 2009. Temperature oscillation coupled with fungal community shifts can modulate warming effects on litter decomposition. Ecology 90: 122–131.
Debusk, W. F. & K. R. Reddy, 2005. Litter decomposition and nutrient dynamics in a phosphorus enriched everglades marsh. Biogeochemistry 75: 217–240.
Federle, T. W., V. L. Mckinley & J. R. Vestal, 1982. Effects of nutrient enrichment on the colonization and decomposition of plant detritus by the microbiota of an arctic lake. Canadian Journal of Microbiology 28: 1199–1205.
Ferreiro, N. A., A. Giorgi, L. Leggieri, C. Feijoó & C. Vilches, 2011. Phosphorus enrichment affects immobilization but not litter decomposition or exoenzymatic activities in a pampean stream. International Review of Hydrobiology 96: 209–220.
Gudasz, C., S. Sobek, D. Bastviken, B. Koehler & L. J. Tranvik, 2015. Temperature sensitivity of organic carbon mineralization in contrasting lake sediments. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences 120: 1215–1225.
Heal, O. W., J. M. Anderson & M. J. Swift, 1997. Plant litter quality and decomposition: an historical overview. In Cadish, G. & K. E. Giller (eds), Driven by nature plant litter quality and decomposition. CAB International, Wallingford: 3–30.
Hoorens, B., R. Aerts & M. Stroetenga, 2003. Does initial litter chemistry explain litter mixture effects on decomposition? Oecologia 137: 578–586.
Jonsson, M. & D. A. Wardle, 2008. Context dependency of litter-mixing effects on decomposition and nutrient release across a long-term chronosequence. Oikos 117: 1674–1682.
Kominoski, J. S., C. M. Pringle, B. A. Ball, M. A. Bradford & D. C. Coleman, 2007. Nonadditive effects of leaf litter species diversity on breakdown dynamics in a detritus-based stream. Ecology 88: 1167–1176.
Lan, Y., B. Cui, Z. You, X. Li, Z. Han, Y. Zhang & Y. Zhang, 2012. Litter decomposition of six macrophytes in a eutrophic shallow lake (Baiyangdian Lake, China). Clean - Soil, Air, Water 40: 1159–1166.
Lecerf, A., G. Marie, J. S. Kominoski, C. J. LeRoy, C. Bernadet & C. M. Swan, 2011. Incubation time, functional litter diversity, and habital characteristics predict litter mixing effects on decomposition. Ecology 92: 160–169.
Lemley, D. A., G. C. Snow & L. R. D. Human, 2014. The decomposition of estuarine macrophytes under different temperature regimes. Water SA 40: 117–124.
Li, C., B. Wang, C. Ye & Y. Ba, 2014. The release of nitrogen and phosphorus during the decomposition process of submerged macrophyte (Hydrilla verticillata Royle) with different biomass levels. Ecological Engineering 70: 268–274.
Li, X., B. Cui, Q. Yang, H. Tian, Y. Lan, T. Wang & Z. Han, 2012. Detritus quality controls macrophyte decomposition under different nutrient concentrations in a eutrophic shallow lake, North China. PloS One 7: e42042.
Li, X., B. Cui, Q. Yang, Y. Lan, T. Wang & Z. Han, 2013. Effects of plant species on macrophyte decomposition under three nutrient conditions in a eutrophic shallow lake, North China. Ecological Modelling 252: 121–128.
Longhi, D., M. Bartoli & P. Viaroli, 2008. Decomposition of four macrophytes in wetland sediments: Organic matter and nutrient decay and associated benthic processes. Aquatic Botany 89: 303–310.
Murray, L. G., S. M. Mudge, A. Newton & J. D. Icely, 2006. The effect of benthic sediments on dissolved nutrient concentrations and fluxes. Biogeochemistry 81: 159–178.
Pagioro, T. A. & S. M. Thomaz, 1999. Decomposition of Eichhornia azurea from limnologically different environments of the upper Parana river floodplain. Hydrobiologia 411: 45–51.
Paul, E. A. & F. E. Clark, 1989. Soil microbiology and biochemistry. Academic Press, San Diego: 5–10.
Rejmánková, E. & K. Houdková, 2006. Wetland plant decomposition under different nutrient conditions: what is more important, litter quality or site quality? Biogeochemistry 80: 245–262.
Rosemond, A. D., C. M. Swan, J. S. Kominoski & S. E. Dye, 2010. Non-additive effects of litter mixing are suppressed in a nutrient-enriched stream. Oikos 119: 326–336.
Royer, T. V. & G. W. Minshall, 2001. Effects of nutrient enrichment and leaf quality on the breakdown of leaves in a hardwater stream. Freshwater Biology 46: 603–610.
Song, N., Z. S. Yan, H. Y. Cai & H. L. Jiang, 2013. Effect of temperature on submerged macrophyte litter decomposition within sediments from a large shallow and subtropical freshwater lake. Hydrobiologia 714: 131–144.
Villar, C. A., L. de Cabo, P. Vaithiyanathan & C. Bonetto, 2001. Litter decomposition of emergent macrophytes in a floodplain marsh of the Lower Parana’ River. Aquatic Botany 70: 105–116.
Yu, H., C. Ye, X. Song & J. Liu, 2010. Comparative analysis of growth and physio-biochemical responses of Hydrilla verticillata to different sediments in freshwater microcosms. Ecological Engineering 36: 1285–1289.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31270261) and (31570366).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Handling editor: Chris Joyce
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Hao, T., Deng, X. et al. Effects of sediment-borne nutrient and litter quality on macrophyte decomposition and nutrient release. Hydrobiologia 787, 205–215 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2961-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2961-x