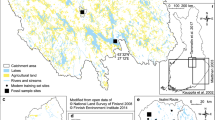
Abstract
Using published paleolimnological results from 14 dimictic calcareous lakes, this study identifies total phosphorous (TP) reference values for the European lake type CB 1. The initial increase in settlement-associated pollen occurred in the catchments between ad ~1000 and ~1820. A departure from diatom-inferred TP reference conditions occurred during periods of increased human activities during Early to Late Medieval Times (ad ~1110–1325; four lakes), early Modern Times (ad ~1575–1600; two lakes), after the 30 years’ war (>ad 1650; two lakes) and during the Anthropocene (after ad ~1850, three lakes). Only one lake continuously has TP reference values until recent days, whilst TP reference values could not be detected in two cases. Thus, we refrain from setting a fixed point in time for defining reference conditions for lakes in the European Central Plains. This study also validates TP reference levels calculated based on common lake models for CB 1-lakes and assesses the range of TP reference levels using paleolimnological diatom studies. The highly variable diatom-inferred TP reference levels only partly support the modelled levels. Thus, we recommend using two subtypes (CB 1a and 1b), based on the watershed to volume ratio to better meet the requirements of lake type-specific reference levels.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, S., 2010. Paltran: WA, WA-PLS, MW for Paleolimnology. R package version 1.3-0. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=paltran.
Alliksaar, T., A. Heinsalu, L. Saarse, J. Salujõe & S. Veski, 2005. A 700-year decadal scale record of lake response to catchment land use from annually laminated lake sediments in southern Estonia. Verhandlungen der Internationalen Vereinigung für Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie 29: 457–460.
Anderson, N. J., I. Renberg & U. Segerström, 1995. Diatom production responses to the development of early agriculture in a boreal forest lake-catchment (Kassjion, northern Sweden). Journal of Ecology 83: 809–822.
Battarbee, R. W., S. Juggins, F. Gasse, N. J. Anderson, H. Bennion & N. G. Cameron, 2000. European Diatom Database (EDDI). An information system for paleoenvironmental reconstruction. European Climate Science Conference, European Commission, Vienna, Austria 1998: 1–10.
Battarbee, R. W., D. T. Monteith, S. Juggins, G. L. Simpson, E. W. Shilland, R. J. Flower & A. M. Kreiser, 2008. Assessing the accuracy of diatom-based transfer functions in defining reference pH conditions for acidified lakes in the United Kingdom. The Holocene 18: 57–67.
Battarbee, R. W., D. Morley, H. Bennion, G. L. Simpson, M. Hughes & V. Bauere, 2011. A palaeolimnological meta-database for assessing the ecological status of lakes. Journal of Paleolimnology 45: 405–414.
Bennion, H. & G. L. Simpson, 2011. The use of diatom records to establish reference conditions for UK lakes subject to eutrophication. Journal of Paleolimnology 45: 469–488.
Bennion, H., R. W. Battarbee, C. D. Sayer, G. L. Simpson & T. A. Davidson, 2011. Defining reference conditions and restoration targets for lake ecosystems using palaeolimnology: a synthesis. Journal of Paleolimnology 45: 533–544.
Birks, H. H., H. J. B. Birks, P. E. Kaland & D. Moe, 1988. The Cultural Landscape—Past, Present and Future. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge: 521 pp.
Bjerring, R., E. G. Bradshaw, S. L. Amsinck, L. S. Johansson, B. V. Odgaard, A. B. Nielsen & E. Jeppsen, 2008. Inferring recent changes in the ecological state of 21 Danish candidate reference lakes (EU Water Framework Directive) using palaeolimnology. Journal of Applied Ecology 45: 1566–1575.
Bradshaw, E. G., P. Rasmussen & B. V. Odgaard, 2005. Mid- to late-Holocene land-use change and lake development at Dallund Sø, Denmark: synthesis of multiproxy data, linking land and lake. The Holocene 15: 1152–1162.
Bradshaw, E. G., A. B. Nielsen & N. J. Anderson, 2006. Using diatoms to assess the impacts of prehistoric, pre-industrial and modern land-use on Danish lakes. Regional Environmental Change 6: 17–24.
Brännvall, M. L., R. Bindler, O. Emteryd & I. Renberg, 2001. Four thousand years of atmospheric lead pollution in northern Europe: a summary from Swedish lake sediments. Journal of Paleolimnology 25: 421–435.
Carvalho, L., A. Solimini, G. Phillips, M. van den Berg, O.-P. Pietiläinen, A. Lyche Solheim, S. Poikane & U. Mischke, 2008. Chlorophyll reference conditions for European lake types used for intercalibration of ecological status. Aquatic Ecology 42: 203–211.
Dreßler, M. & Hübener, Th., 2011. Diatomeenuntersuchungen zur Trophieentwicklung des Rugensees nördlich von Schwerin (Mecklenburg-Vorpommern) während des Holozäns. In Schülke, Almut: Landschaften—Eine archäologische Untersuchung der Region zwischen Schweriner See und Stepenitz. Römisch-Germanische Forschungen, Vol. 68: 337–359.
Dreßler, M., U. Selig, W. Dörfler, S. Adler, H. Schubert & Th Hübener, 2006. Environmental changes and the migration period in Europe by the example of Lake Dudinghausen (northern Germany). Quarternary Research 66: 25–37.
Dreßler, M., A. Schwarz, Th Hübener, S. Adler & B. Scharf, 2011. Use of sedimentary diatoms from multiple lakes to distinguish between past changes in trophic state and climate: evidence for climate change in northern Germany during the past 5,000 years. Journal of Paleolimnology 45: 223–241.
European Union, 2000. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and the council of 23.10.2000 establishing a framework for community action in the field of water policy. Official Journal of the EC L327: 1–72.
Faegri, K. & J. Iversen, 1989. In Faegri, K., P. E. Kaland & K. Krzywinski (eds), Textbook of Pollen Analysis, 4th edn. John Wiley & Sons, New York: 328 pp.
Firbas, F., 1949. Spät- und nacheiszeitliche Waldgeschichte Mitteleuropas nördlich der Alpen 1: Allgemeine Waldgeschichte. Fischer, Jena: 480 pp.
Fritz, S. C., 1989. Lake development and limnological response to prehistoric and historic land-use in Diss, Norfolk, UK. Journal of Ecology 77: 182–202.
Goslar, T., M. Ralska-Jasiewiczowa, B. van Geel, B. Laka, K. Szeroczyäska, L. Chróst & A. Walanus, 1999. Anthropogenic changes in the sediment composition of Lake Gosciaz (central Poland), during the last 330 yrs. Journal of Paleolimnology 22: 171–185.
Guilizzoni, P., A. Marchetto, A. Lami, S. Gerli & S. Musazzi, 2011. Use of sedimentary pigments to infer past phosphorus concentration in lakes. Journal of Paleolimnology 45: 433–445.
Hall, R. I. & J. P. Smol, 2010. Diatoms as indicators of lake eutrophication. In Smol, J. P. & E. F. Stoermer (eds), The Diatoms: Application for the Environmental and Earth Science, 2nd ed. Cambridge University, Cambridge.
Hastie, T. J. & R. J. Tibshiranie, 1990. Generalised Additive Models. Monographs of Statistics and Applied Probability. Chapman & Hall, New York.
Heinsalu, A. & T. Alliksaar, 2009. Palaeolimnological assessment of the reference conditions and ecological status of lakes in Estonia—implications for the European Union Water Framework Directive. Estonian Journal of Earth Sciences 58: 334–341.
Hübener, Th & W. Dörfler, 2004. Reconstruction of the trophic development of the Lake Krakower Obersee (Mecklenburg, Germany) by means of sediment-diatom- and pollen-analysis. Studia Quaternaria 21: 101–108.
Hübener, Th, M. Dreßler, A. Schwarz, K. Langner & S. Adler, 2008. Dynamic adjustment of training sets (‘moving-window’ reconstruction) by using transfer functions in paleolimnology—a new approach. Journal of Paleolimnology 40: 79–95.
Hübener, Th, S. Adler, P. Werner, M. Schult, H. Erlenkeuser, H. Meyer & M. Bahnwart, 2009. A multi-proxy paleolimnological reconstruction of trophic state reference conditions for stratified carbonate-rich lakes in Northern Germany. Hydrobiologia 631: 303–327.
Jones, P. D. & R. S. Bradley, 1992. Climatic variations over the last 500 years. In Bradley, R. S. & P. D. Jones (eds), Climate Since ad 1500. Routledge, London, New York: 649–665.
Juggins, S., 2013. Quantitative reconstructions in palaeolimnology: new paradigm or sick science? Quaternary Science Reviews 64: 20–32.
Juggins, S., N. J. Anderson, J. M. Ramstack Hobbs & A. J. Heathcote, 2013. Reconstructing epilimnetic total phosphorus using diatoms: statistical and ecological constraints. Journal of Paleolimnology 49: 373–390.
Kalbe, L. & H. Werner, 1974. Das Sediment des Kummerower Sees. Untersuchungen des Chemismus und der Diatomeenflora. Internationale Revue der Gesamten Hydrobiologie 596: 755–782.
Kirilova, E., O. Heiri, D. Enters, H. Cremer, A. F. Lotter, B. Zolitschka & Th Hübener, 2009. Climate-induced changes in the trophic status of a Central Europe lake. Journal of Limnology 68: 71–82.
Krammer, K., 1997a. Die cymbelloiden Diatomeen. Eine Monographie der weltweit bekannten Taxa, Teil 1 Allgemeines und Encyonema Part. Bibliotheca Diatomologica 36, Cramer Berlin, Stuttgart.
Krammer, K., 1997b. Die cymbelloiden Diatomeen, Eine Monographie der weltweit bekannten Taxa, Teil 2 Encyonema Part. Encyonopsis and Cymbellopsis. Bibliotheca Diatomologica 37, Cramer, Berlin, Stuttgart.
Krammer, K., 2000. In Lange-Bertalot, H. (ed.), The Genus Pinnularia. Diatoms of Europe 1. A.R.G. Gantner Verlag, Ruggel.
Krammer, K., 2002. In Lange-Bertalot, H. (ed.), Cymbella. Diatoms of Europe 3. ARG Gantner Verlag, Ruggel.
Krammer, K., 2003. In Lange-Bertalot, H. (ed.), Cymbopleura, Delicata, Navicymbula, Gophocymbelloides, Afrocymbella. Diatoms of Europe 4. A.R.G. Gantner Verlag, Ruggel.
Krammer, K. & H. Lange-Bertalot, 1986. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Bacillariophyceae, Vol. 2, 1st ed. Fischer, Jena.
Krammer, K. & H. Lange-Bertalot, 1988. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Bacillariophyceae, Vol. 2, 2nd ed. Fischer, Jena.
Krammer, K. & H. Lange-Bertalot, 1991a. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Bacillariophyceae, Vol. 2, 3rd ed. Fischer, Jena.
Krammer, K. & H. Lange-Bertalot, 1991b. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Bacillariophyceae, Vol. 2, 4th ed. Fischer, Jena.
Küster, H., 1996. Geschichte der Landschaft Mitteleuropas. Beck Verlag, Munchen: 423 pp.
Küster, M., W. Jahnke, H. Meyer, S. Lorenz, R. Lampe, Th Hübener & A. M. Klammt, 2012. Zur jungquartären Landschaftsentwicklung der Mecklenburgischen Kleinseenplatte. Geomorphologische, bodenkundliche und limnogeologische Untersuchungen am Krummen See bei Blankenförde (Mecklenburg). Forschung und Monitoring 3: 1–79.
Lamp, H. H., 1965. The early medieval warm epoch and its sequel. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 1: 13–37.
Lampe, R., S. Lorenz, W. Janke, H. Meyer, M. Küster, T. Hübener & A. Schwarz, 2009. Zur Landschafts- und Gewässergeschichte der Müritz Umweltgeschichtlich orientierte Bohrungen 2004–2006 zur Rekonstruktion der nacheiszeitlichen Entwicklung. Forschung und Monitoring 2: 1–95.
Lang, G., 1994. Quartäre Vegetationsgeschichte Europas. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena: 462 pp.
Lange-Bertalot, H. & G. Moser, 1994. Brachysira, Monographie der Gattung. Bibliotheca Diatomologica, Vol. 29. Cramer, Berlin, Stuttgart.
LAWA—Länderarbeitsgemeinschaft Wasser, 1999. Gewässerbewertung—stehende Gewässer. Kulturbuchverlag, Berlin.
LAWA—Länderarbeitsgemeinschaft Wasser, 2007. Rahmenkonzeption Monitoring Teil B Bewertungsgrundlagen und Methodenbeschreibungen. Arbeitspapier II Hintergrund- und Orientierungswerte für physikalisch-chemische Komponenten.
Leira, M., P. Jordan, D. Taylor, C. Dalton, H. Bennion, N. Rose & K. Irvine, 2006. Assessing the ecological status of candidate reference lakes in Ireland using palaeolimnology. Journal of Applied Ecology 43: 816–827.
Levkov, Z., 2009. In Lange-Bertalot, H. (ed.), Amphora sensu lato. Diatoms of Europe 5. A.R.G. Gantner Verlag, Ruggel.
Mathes, J., G. Plambeck & J. Schaumburg, 2002. Das Typisierungssystem für stehende Gewässer in Deutschland mit Wasserflächen ab 0.5 km2 zur Umsetzung der Wasserrahmenrichtlinie. Aktuelle Reihe Brandenburgische Technische Universität Cottbus 5: 15–23.
Mietz, O. & H. Vietinghoff, 1994. Zu den funktionellen Abhängigkeiten zwischen morphometrischen topographischen und trophischen Kriterien von Seen. Wasserwirtschaft 84: 662–667.
Nadeau, M.-J., P. M. Grootes, M. Schleicher, P. Hasselberg, A. Rieck & M. Bitterling, 1998. Sample throughput and data quality at the Leibniz-Labor AMS facility. Radiocarbon 40: 239–245.
Ohle, W., 1973. Rasante Eutrophierung des Großen Plöner Sees in frühgeschichtlicher Zeit. Naturwissenschaften 60: 47.
Ohle, W., 1979. Ontogeny of the Lake Grosser Plöner See. Paleolimnology of Lake Biwa and the Japanese Pleistocene. Kyoto University: 3–33.
Poikane, S., M. H. Alves, C. Argillier, M. van den Berg, F. Buzzi, E. Hoehn, C. de Hoyos, I. Karottki, C. Laplace-Treyture, A. Lyche Solheim, J. Ortiz-Casas, I. Ott, G. Phillips, A. Pilke, A. Pàdua, S. Remec-Rekar, U. Riedmüller, J. Schaumburg, M. S. Serrano, H. Soszka, D. Tierney, G. Urbanic & G. Wolfram, 2010. Defining chlorophyll-a reference conditions in European lakes. Environmental Management 45: 1286–1298.
Preußische Landesaufnahme, 1888. Messtischblatt 2439 Karow. http://www.geoportal-mv.de/.
Räsänen, J., T. Kaupilla & V. P. Salonen, 2006. Sediment-based investigation of naturally or historically eutrophic lakes-implications for lake management. Journal of Lake Management 79: 253–265.
Rasmussen, P. & N. J. Anderson, 2005. Natural and anthropogenic forcing of aquatic macrophyte development in a shallow Danish lake during the last 7000 years. Journal of Biogeography 32: 1993–2005.
Robbins, A. & D. N. Edgington, 1975. Determination of recent sedimentation rates in Lake Michigan using Pb-210 and Cs-137. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 39: 285–304.
Rosèn, P., R. Bindler, T. Korsman, T. Mighall & K. Bishop, 2011. The complementary power of pH and lake water organic carbon reconstructions for discerning the influences on surface waters across decadal to millennial time scales. Biogeosciences 8: 2439–2466.
Ruddiman, W. F., 2003. The anthropogenic greenhouse era began thousands of years ago. Climatic Change 61: 261–293.
Schwarz, A., 2006. Rekonstruktion der Entwicklung des Schulzensees und des Tiefen Sees (Mecklenburg-Vorpommern) seit dem Spätglazial mittels Diatomeenanalyse unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Trophiegeschichte. Greifswalder Geographische Arbeiten 41: 1–166.
Simpson, G. L. & N. J. Anderson, 2009. Deciphering the effect of climate change and separating the influence of confounding factors in sediment core records using additive models. Limnology and Oceanography 54(6, part 2): 2529–2541.
Smol, J. P., 2008. Pollution of Lakes and Rivers—A Paleoenvironmental Perspective. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford.
Søndergaard, M., E. Jeppesen, J. P. Jensen & S. L. Amsinck, 2005. Water Framework Directive: ecological classification of Danish lakes. Journal of Applied Ecology 42: 616–629.
Stuiver, M., P. J. Reimer, E. Bard, J. W. Beck, G. S. Burr, K. H. Hughen, B. Kromer, G. McCormac, J. van der Plicht & M. Spurk, 1998. IntCal98 radiocarbon age calibration, 24,000–0 cal BP. Radiocarbon 40: 1041–1083.
Szeroczynska, K., 1991. Impact of prehistoric settlements on the Cladocera in the sediments of Lakes Suszek, Blgdowo, and Skrzetuszewskie. Hydrobiologia 225: 105–114.
ter Braak, C. J. F. & S. Juggins, 1993. Weighted averaging partial least squares regression (WA-PLS): an improved method for reconstructing environmental variables from species assemblages. Hydrobiologia 269(270): 485–502.
Umweltministerium Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, 2003. Die Naturschutzgebiete in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Demmler Verlag.
UNSCEAR, 2000. Sources and effects of ionizing radiation. In UNSCEAR 2000 Report to the General Assembly, Technical Paper, U.N. Science Commission. On the Effects of Atom. Radiation, Vienna. Vol. I: Sources, Annex C: Exposures from Man-made Sources of Radiation.
Vollenweider, R. A. & K. Kerekes, 1982. Eutrophication of Waters Monitoring. Assessment and Control. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Paris.
von Wiebeking, K. F. & F. Engel, 1786. Historischer Atlas von Mecklenburg. Bölau-Verlag 1962, reprint.
Wallin, M., T. Wiederholm & R. K. Johnson, 2003. Guidance on Establishing Reference Conditions and Ecological Status Class Boundaries for Inland Surface Waters. WFD Working Group 2.3, Version 7.0—Reference Conditions for Inland Surface Waters (REFCOND).
WFD-Intercalibration Technical Report, 2006. European Environmental NGO Technical Review of the Water Framework Directive Intercalibration Process. RSPB, Pond Conservation and the European Environmental Bureau.
Wieckowska, M., W. Dörfler & W. Kirlis, 2012. Vegetation and settlement history of the past 9000 years as recorded by lake deposits from Großer Eutiner See (Northern Germany. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology 174: 79–90.
Wood, S. N., 2006. Generalized Additive Models: An Introduction with R. Chapman and Hall, CRC, Boca Raton.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Jürgen Mathes (Ministry for Agriculture, Environment and Consumer Protection of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Germany) for providing morphometric and limnologic variables of the lakes as well as actual measurements and assessments. Kirsten Langner and Anna-Marie Klammt (lab ‘phycology’ of Rostock University) analysed diatom samples from lakes DRE and GÜL, respectively. Sediment chemical data were analysed by Uwe Selig (Rostock University) and Hinrich Meyer (University of Greifswald), pollen by Walter Dörfler (University of Kiel) and Manuela Schult (University of Greifswald) and macrorests by Dierk Michaelis (University of Greifswald). 210Pb/137Cs and 14C-AMS analysis were conducted by Helmut Erlenkeuser, Pieter M. Grootes and Matthias Huels (University of Kiel). For coring we used the help and equipment from Burkhardt Scharf (Bremen), Walter Dörfler and Oliver Nelle (both University of Kiel), Reinhardt Lampe and Sebastian Lorenz (both University of Greifswald). Three anonymous journal reviewers provided many constructive comments and suggestions on an earlier version of this paper. We would also like to thank Francine Forrest (LimnoLogic Solutions Ltd) for reviewing the English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Koen Martens
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hübener, T., Adler, S., Werner, P. et al. Identifying reference conditions for dimictic north German lowland lakes: implications from paleoecological studies for implementing the EU-Water Framework Directive. Hydrobiologia 742, 295–312 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-1992-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-1992-4