Abstract
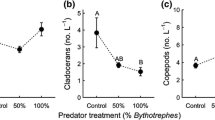
We hypothesized that native Leptodora kindtii would be shorter and have smaller feeding baskets in central Ontario lakes with greater abundances of small-bodied zooplankton prey, and that differences in zooplankton size among lakes could be attributed to the invasive cladoceran Bythotrephes longimanus. We evaluated these conjectures by comparing size metrics of Leptodora and the size of their preferred cladoceran prey in lakes invaded or not by Bythotrephes. Leptodora was less abundant in invaded lakes, but were smaller bodied with smaller feeding baskets only in lakes with long invasion histories. Small cladoceran abundance was greater in non-invaded lakes and was directly related to Leptodora abundance although not to Leptodora size. Mean Leptodora body size declined with increasing abundance of Bythotrephes. We evaluated three possible explanations for these patterns in Leptodora—(a) competition with Bythotrephes for zooplankton prey, (b) direct predation by Bythotrephes, and (c) size-selective predation by fish. While we were unable to unequivocally distinguish among these hypotheses, our observations are most consistent with predation by Bythotrephes changing zooplankton community composition and size structure in a manner that is detrimental to Leptodora. Our results indicate that Bythotrephes invasion may trigger more complex and subtle changes in food webs than previously thought.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrusán, G., 2003. Morphological variation of the predatory cladoceran Leptodora kindtii in relation to prey characteristics. Oecologia 134: 278–283.
Barbiero, R. P. & M. L. Tuchman, 2004. Changes in the crustacean communities of Lakes Michigan, Huron, and Erie following the invasion of the predatory cladoceran Bythotrephes longimanus. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 61: 2111–2125.
Barnhisel, D. R. & W. C. Kerfoot, 2004. Fitting into food webs: behavioural and functional response of young lake trout (Salvelinus namaycush) to an introduced prey, the spiny cladoceran (Bythotrephes cederstroemi). Journal of Great Lakes Research 30(Supp. 1): 300–314.
Branstrator, D. K., 1995. Ecological interactions between Bythotrephes cederstroemi and Leptodora kindtii and the implications for species replacement in Lake Michigan. Journal of Great Lakes Research 21: 670–679.
Branstrator, D. K., 1998. Predicting diet composition from body length in the zooplankton predator Leptodora kindti. Limnology and Oceanography 43: 530–535.
Branstrator, D. K., 2005. Contrasting life histories of the predatory cladocerans Leptodora kindtii and Bythotrephes longimanus. Journal of Plankton Research 27: 569–585.
Bunnell, D. B, B. M. Davis, D. M. Warner, M. A. Chriscinske & E. F. Roseman, 2011. Planktivory in the changing Lake Huron zooplankton community: Bythotrephes consumption exceeds that of Mysis and fish. Freshwater Biology. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2010.02568.x
Dadswell, M. J., 1974. Distribution, ecology, and postglacial dispersal of certain crustaceans and fishes in eastern North America. National Museum of Natural Sciences Publications in Zoology, No. 11, Ottawa.
Foster, S. E., 2007. The co-occurrence and interactions of large invertebrate predators in relation to the Bythotrephes invasion. PhD Dissertation. University of Toronto at Mississauga, Mississauga.
Foster, S. E. & W. G. Sprules, 2009. Effects of the Bythotrephes invasion on native predatory invertebrates. Limnology and Oceanography 54: 757–769.
Foster, S. E. & W. G. Sprules, 2010. Effects of Bythotrephes on the trophic position of native macroinvertebrates. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 67: 58–69.
Herzig, A. & B. Auer, 1990. The feeding behavior of Leptodora kindti and its impact on the zooplankton community of Neusiedler See (Austria). Hydrobiologia 198: 107–117.
Hovius, J. T., B. E. Beisner & K. S. McCann, 2006. Epilimnetic rotifer community responses to Bythotrephes longimanus invasion in Canadian Shield lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 51: 1004–1012.
Laforsch, C. & R. Tollrian, 2004. Inducible defenses in multipredator environments: cyclomorphosis in Daphnia cucullata. Ecology 85: 2302–2311.
Lunte, C. C. & C. Luecke, 1990. Trophic interactions of Leptodora in Lake Mendota. Limnology and Oceanography 35: 1091–1100.
MacIsaac, H. J., J. V. M. Borbely, J. Muirhead & P. A. Graniero, 2004. Backcasting and forecasting biological invasions of inland lakes. Ecological Applications 14: 773–783.
Manca, M. & P. Comoli, 1995. Seasonal changes in size of the feeding basket of Leptodora kindtii (Focke) in Lago Maggiore as related to variations in prey size selection. Limnology and Oceanography 40: 834–838.
Mills, E. L., J. M. Casselman, R. Dermott, J. D. Fitzsimons, G. Gal, K. T. Holeck, J. A. Hoyle, O. E. Johannsson, B. F. Lantry, J. C. Makarewicz, E. S. Millard, I. F. Munawar, M. Munawar, R. O’Gorman, R. W. Owens, L. G. Rudstam, T. Schaner & T. J. Stewart, 2003. Lake Ontario: food web dynamics in a changing ecosystem (1970–2000). Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 60: 471–490.
Milne, S. W., B. J. Shuter & W. G. Sprules, 2005. The schooling and foraging ecology of lake herring (Coregonus artedi) in Lake Opeongo, Ontario, Canada. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 62: 1210–1218.
Nero, R. W. & W. G. Sprules, 1986. Zooplankton species abundance and biomass in relation to occurrence of Mysis relicta (Malacostraca, Mysidacea). Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 43: 420–434.
Ontario Ministry of the Environment, 1983. Handbook of analytical methods for environmental samples. Technical Report Ontario Ministry of the Environment, Laboratory Services and Applied Research Branch, Toronto.
Parker Stetter, S. L., L. D. Witzel, L. G. Rudstam, D. W. Einhouse & E. L. Mills, 2005. Energetic consequences of diet shifts in Lake Erie rainbow smelt (Osmerus mordax). Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 62: 145–152.
Prepas, E., 1978. Sugar-frosted Daphnia: improved fixation technique for Cladocera. Limnology and Oceanography 23: 557–559.
R Development Core Team, 2010. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna.
Rivier, I., 1998. The predatory Cladocera (Onychopoda: Podonidae, Polyphemidae, Cercopagidae) and Leptodorida of the world. Backhuys Publishing, Leiden, 214 pp.
Sherwood, G. D., J. Kovecses, A. Hontela & J. B. Rasmussen, 2002. Simplified food webs lead to energetic bottlenecks in polluted lakes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 59: 1–5.
StatSoft, 2001. STATISTICA 6. StatSoft Inc., Tulsa.
Strecker, A. L. & S. E. Arnott, 2008. Invasive predator, Bythotrephes, has varied effects on ecosystem function in freshwater lakes. Ecosystems 11: 490–503.
Strecker, A. L., S. E. Arnott, N. D. Yan & R. Girard, 2006. Variation in the response of crustacean zooplankton species richness and composition to the invasive predator Bythotrephes longimanus. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 63: 2126–2136.
Vanderploeg, H. A., J. R. Liebig & M. Omair, 1993. Bythotrephes predation on Great Lakes’ zooplankton measured by an in situ method: implications for zooplankton community structure. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 127: 1–8.
Wahlström, E. & E. Westman, 1999. Planktivory by the predacious cladoceran Bythotrephes longimanus: effects on zooplankton size structure and abundance. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 56: 1865–1872.
Weisz, E. J. & N. D. Yan, 2010. Relative value of limnological, geographic and human use variables as predictors of the presence of Bythotrephes longimanus in Canadian Shield lakes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 67: 462–472.
Weisz, E. J. & N. D. Yan, 2011. Shifting invertebrate zooplanktivores: watershed-level replacement of the native Leptodora by the non-indigenous Bythotrephes in Canadian Shield lakes. Biological Invasions 13: 115–123.
Welschmeyer, N. A., 1994. Fluorometric analysis of chlorophyll a in the presence of chlorophyll b and pheopigments. Limnology and Oceanography 39: 1985–1992.
Yan, N. D. & T. W. Pawson, 1997. Changes in the crustacean zooplankton community of Harp Lake, Canada, following invasion by Bythotrephes cederstroemi. Freshwater Biology 37: 409–425.
Young, J. D. & N. D. Yan, 2008. Modification of the diel vertical migration of Bythotrephes longimanus by the cold-water planktivore, Coregonus artedi. Freshwater Biology 53: 981–995.
Acknowledgments
We thank K. Krupica and W. B. Wissemeyer for their help in the field and C. Tudorancea and J. Kilgour for counting and measuring zooplankton. N. Collins, B. Shuter, P. Abrams, D, Branstrator, and anonymous reviewers provided helpful comments and editorial corrections. Funding for this project was provided by a Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) Discovery Grant to WGS, a Mary Beatty Scholarship from the University of Toronto Graduate School and other scholarships from the Department of Zoology to SEF, and a NSERC post-graduate scholarship to ALS. S. Arnott provided funding, logistical support, and advice to ALS. We are also grateful to the Ontario Ministry of Environment’s Dorset Environmental Science Center and the Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources Provincial Co-ordination Center for additional field support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: John Havel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foster, S.E., Sprules, W.G. & Strecker, A.L. Effects of Bythotrephes longimanus (Crustacea, Cladocera) on the abundance, morphology, and prey community of Leptodora kindtii (Crustacea, Cladocera). Hydrobiologia 683, 163–172 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-011-0953-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-011-0953-4