Abstract
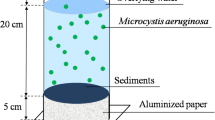
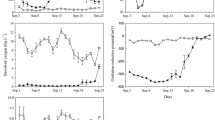
Phytoplankton density and composition, together with phosphorus (P) concentrations and size-fractionated alkaline phosphatase activity (APA), were investigated in dredged and undredged zones in Lake Taihu from January to April 2004. P concentrations were also determined in the corresponding interstitial water. Enzyme Labeled Fluorescence (ELF) was used for localizing extracellular phosphatase on phytoplankton cell membranes in April. The increase in phytoplankton density was paralleled by a significant increase in soluble reactive P (SRP) concentrations in the water column and interstitial water at all sites from January to April, with chlorophyte gradually becoming dominant. In February, at the undredged site, more algae dominated by chlorophyte occurred in overlying water, rather than in the surface, coinciding with higher SRP concentrations in overlying and interstitial water. Therefore, P status in the bottom is important to phytoplankton development in terms of density and composition. Undredged sites had higher SRP concentrations in interstitial water than dredged sites. Furthermore, Higher APA was observed, accompanied by higher dissolved organic P (DOP) and lower total P at the undredged site in February. Enzymatic hydrolysis of DOP may have been an additional source of P for phytoplankton. In April, Schroederia sp. was ELF labeled in surface water at the dredged site, which showed markedly lower SRP concentration, but not at the undredged site with higher SRP concentration. Thus, the dredging might regulate algal density and composition in water column by reducing P bioavailability.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boon, P. I., 1989. Organic matter degradation and nutrient regeneration in Australian freshwaters: I. Methods for exoenzyme assays in turbid aquatic environments. Archiv Fur Hydrobiologie 115: 339–359.
Buergi, H. R., H. Buehrer & B. Keller, 2003. Long-term changes in functional properties and biodiversity of plankton in Lake Greifensee (Switzerland) in response to phosphorus reduction. Aquatic Ecosystem Health and Management 6: 147–158.
Chróst, R. J., W. Siuda & G. Z. halemejko, 1984. Longterm studies on alkaline phosphatase activity (APA) in a lake with fish-aquaculture in relation to lake eutrophication and phosphorus cycle. Archiv Fur Hydrobiologie 70: 1–32.
Cronberg, G., 1982. Changes in the phytoplankton of lake Trummen induced by restoration. Hydrobiologia 86: 185–193.
Gage, M. A. & E. Gorham, 1985. Alkaline phosphatases activity and cellular phosphorus as an index of the phosphorus status of phytoplankton in Minnesota lakes. Freshwater Biology 15: 227–233.
Golterman, H. L., R. S. Clymo & M. A. M. Ohmstad, 1978. Methods for physical and chemical analysis of fresh waters. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, Handbook 8, 2nd edn., 111–117.
Gonzáles-Gil, S., B. Keafer, R. V. M. Jovine, A. Aquilera, S. Lu & D. M. Anderson, 1998. Detection and quantification of alkaline phosphatase in single cells of phosphorus-starved marine phytoplankton. Marine Ecology Progress Series 164: 21–35.
Graham, L. E. & L. W. Wilcox, 2000. Algae. Prentice hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, USA.
Hu, H., R. Li, Y. Wei, C. Zhu, J. Chen & Z. Shi, 1979. Freshwater algae in China. Science Press, Peking (in Chinese).
James, W. F., J. W. Barko, H. L. Eakin & P. W. Sorge, 2002. Phosphorus budget and management strategies for an urban Wisconsin lake. Lake and Reservoir Management 18: 149–163.
Jeppesen, E., P. Kristensen, J. P. Jensen, M. Soendergaard, E. Mortensen & T. Lauridsen, 1990. Recovery resilience following a reduction in external phosphorus loading of shallow, eutrophic Danish lakes: duration, regulating factors and methods for overcoming resilience. 3. Int. Workshop on Ecosystem Research in Freshwater Environment Recovery, 26–29.
Karjalainen, H., S. Seppälä & M. Walls, 1997–1998. Nitrogen, phosphorus and Daphnia grazing in controlling phytoplankton biomass and composition–an experimental study. Hydrobiologia 363: 309–321.
Klotz, R. L., 1985. Influence of light on the alkaline phosphatase activity of Selenastrum capricornutum (Chlorophyceae) in streams. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 42: 384–388.
Knuttila, S., O.-P. Pietil̈ainen & L. Kauppi, 1994. Nutrient balances and phytoplankton dynamics in two agriculturally loaded shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 275/276: 359–369.
Labry, C., A. Herbland & D. Delmas, 2002. The role of phosphorus on planktonic production of the Gironde plume waters in the Bay of Biscay. Journal of Plankton Research 24: 97–117.
Lessmann, D., A. Fyson & B. Nixdorf, 2003. Experimental eutrophication of a shallow acidic mining lake and effects on the phytoplankton. Hydrobiologia 506–509: 753–758.
Levine, M. A. & S. C. Whalen, 2001. Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton production in Alaskan Arctic foothill lakes. Hydrobiologia 455: 189–201.
Murphy, J. & P. Riley, 1962. A modified single solution method of the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta 27: 1–36.
Nedoma, J., A. Štrojsová, J. Vrba, J. Komárková & K. Šimek, 2003. Extracellular phosphatase activity of natural plankton studied with ELF97 phosphate: fluorescence quantification and labelling kinetics. Environmental Microbiology 5: 462–472.
Nuernberg, G. K, R. W. Bachmann, J. R. Jones, R. H. Peters & D. M. Soballe, 1995. Modeling phosphorus in lakes with possible sediment P release, case studies. Lake and Reservoir Management 11(2): 176.
Ortega-Mayagoitial, E., C. Rojo & M. A. Rodrigo, 2003. Controlling factors of phytoplankton assemblages in wetlands: an experimental approach. Hydrobiologia 502: 177–186.
Overbeck, J., 1991. Early studies on ecto- and extracellular enzymes in aquatic environments. In Chróst, R. J. (ed.), Microbial enzymes in aquatic environments. Springer Verlag, New York, 29–59.
Pan, Y. D., R. Stevenson, V. Jan, S. J. Panchabi & C. J. Richardson, 2000. Changes in algal assemblages along observed and experimental phosphorus gradients in a subtropical wetland, USA. Freshwater Biology 44: 339–353.
Pillsbury, R. W., R. L. Lowe, Y. D. Pan & J. L. Greenwood, 2002. Changes in the benthic algal community and nutrient limitation in Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron, during the invasion of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). Journal of the North American Benthological Society 21: 238–252.
Pollingher, U., 1986. Non-siliceous algae in a five meter core from Lake Kinneret (Israel). Hydrobiologia 143: 213–216.
Poulickova, A., L. Pechar & M. Kummel, 1998. Influence of sediment removal on fishpond phytoplankton. Archiv Fur Hydrobiologie Supplement 124: 107–120.
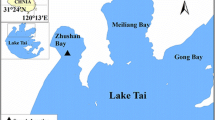
Qin, B., P. Xu, Q. Wu, L. Luo & Y. Zhang, 2007. Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 581: 3–14.
Rengefors, K., K. Pettersson, T. Blenckner & D. M. Anderson, 2001. Species-specific alkaline phosphatase activity in freshwater spring phytoplankton: application of a novel method. Journal of Plankton Research 23: 435–443.
Roberts, E., J. Kroker, S. Koerner & A. Nicklisch, 2003. The role of periphyton during the re-colonization of a shallow lake with submerged macrophytes. Hydrobiologia 506–509: 525–530.
Sala, M. M. & H. Guede, 1995. Influence of algae and crustacean zooplankton on patterns of microbial hydrolytic enzyme activities––an experimental approach. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 48: 143–154.
Štrojsová, A., J. Vrba, J. Nedoma, J. Komárková & P. Znachor, 2003. Seasonal study on expression of extracellular phosphatases in the phytoplankton of an eutrophic reservoir. European Journal of Phycology 38: 295–306.
Vrba, J., J. Komárková & V. Vyhnálek, 1993. Enhanced activity of alkaline phosphatases––phytoplankton response to epilimnetic phosphorus depletion. Water Science and Technology 28: 15–24.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Basic Research and Development Program (2002CB412304) and the grant (2002AA601013). We also obliged to the funds from the National Science Foundation of China (20177033). This work was partly supported by Sino-Czech Scientific and Technological Cooperation––project No. 36–20. We would like to thank Jaroslav Vrba, Alena Štrojsová and Feng Weisong for their methodical help and providing facilities to use epifluorescence microscope. Many thanks are given to Li Jianqiu for the sample preparations and to Liu Jingyuan for the review of this manuscript. The thanks also go to Li Lin, Zeng hui for their kind helps in sample collecting.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, X., Song, C., Li, Q. et al. Dredging effects on P status and phytoplankton density and composition during winter and spring in Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 581, 287–295 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0516-2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0516-2