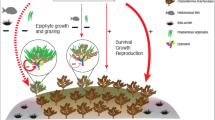
Abstract
The presence of the stoloniferous hydroid Obelia geniculata (L.) had no effect on the pigment concentration or nitrogen status of underlying blade tissue of the giant kelp Macrocystis pyrifera (L.) C. Agardh. The sheet-like colonies of the bryozoan Membranipora membranacea (L.) markedly reduced the pigment concentration of colonized blade tissue, but only during winter. Reductions in pigment concentration are most likely a result of damage to underlying tissue due to some factor related to the presence of bryozoan colonies on blade surfaces. Blade tissue colonized by M. membranacea also had higher δ15N signatures than surrounding bryozoan-free tissue, possibly indicating the provision of nitrogen to M. pyrifera by bryozoan colonies. Results show that seasonal changes in nitrogen and colony size can strongly modify the effect of epifauna on macroalgae they colonize. Unlike bryozoans, hydroid colonies provided no barrier to nitrogen uptake by colonized M. pyrifera tissue and enhanced ammonium uptake was observed for tissue colonized by O. geniculata during nitrogen limitation. Epifauna with stoloniferous growth forms such as hydroids are more likely to have benign or even mutualistic relationships with macroalgae they colonize than the sheet-like colonies of bryozoans.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. E. Arnold S. L. Manley (1985) ArticleTitleCarbon allocation in Macrocystis pyrifera (Phaeophyta): intrinsic variability in photosynthesis and respiration Journal of Phycology 21 154–167 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXitVWgtrs%3D
H. L. Barrales C. S. Lobban (1975) ArticleTitleThe comparative ecology of Macrocystis pyrifera, with emphasis on the forests of Chubut, Argentina Journal of Ecology 63 657–677
B. B. Bernstein N. Jung (1979) ArticleTitleSelective pressures and coevolution in a kelp canopy community in Southern California Ecological Monographs 49 335–355
M. T. Brown M. A. Nyman J. A Keogh N. K. M. Chin (1997) ArticleTitleSeasonal growth of the giant kelp Macrocystis pyrifera in New Zealand Marine Biology 129 417–424 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002270050182
R. H. Bustamante G. M. Branch S. Eekhout (1995) ArticleTitleMaintenance of an exceptional intertidal grazer biomass in South Africa: subsidy by subtidal kelps Ecology 76 2315–2329
J. M. Cancino J. Muñoz M. Muñoz M. C. Orellana (1987) ArticleTitleEffects of the bryozoan Membranipora tuberculata (Bosc.) on the photosynthesis and growth of Gelidium rex Journal of Experimental Marine Biology Ecology 113 105–112
A. R. O. Chapman J. S. Craigie (1977) ArticleTitleSeasonal growth in Laminaria longicruris: Relations with dissolved inorganic nutrients and internal reserves of nitrogen Marine Biology 40 197–205 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00390875 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2sXktlGqtbo%3D
N. K. M. Chin (1989) Seasonal growth and photosynthesis of Macrocystis University of Otago Dunedin, New Zealand 112
H. Christie N. M. Jørgensen K. M. Norderhaug E. Waage-Neilsen (2003) ArticleTitleSpecies distribution and habitat exploitation of fauna associated with kelp, Laminaria hyperborea, along the Norwegian Coast Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 83 687–699 Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0025315403007653h
P. K. Dayton (1985) ArticleTitleEcology of kelp communities Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 16 215–245 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.es.16.110185.001243
M. E. Burgh ParticleDe P. V. Fankboner (1978) ArticleTitleA nutritional association between the bull kelp Nereocystis luetkeana and its epizoic bryozoan Membranipora membranacea Oikos 31 69–72
J. Dixon S. C. Schroeter J. Kastendiek (1981) ArticleTitleEffects of the encrusting bryozoan, Membranipora membranacea, on the loss of blades and fronds by the giant kelp Macrocystis pyrifera (Laminariales) Journal of Phycology 17 341–345 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.0022-3646.1981.00341.x
G. S. Dieckmann (1980) ArticleTitleAspects of the ecology of Laminaria pallida (Grev.) J. Ag. off the Cape Peninsula (South Africa). I. Seasonal growth Botanica Marina 23 579–585
D. O. Duggins C. A. Simenstad J. A. Estes (1989) ArticleTitleMagnification of secondary production by kelp detritus in coastal marine ecosystems Science 245 170–173
D. O. Duggins J. E. Eckman A. T. Sewell (1990) ArticleTitleEcology of understory environments. II. Effects of kelps on recruitment of benthic invertebrates Journal of Experimental Marine Biology of Ecology 143 27–45
M. S. Foster (1975) ArticleTitleRegulation of algal community development in a Macrocystis pyrifera forest Marine Biology 32 331–342
M. S. Foster D. R. Schiel (1985) The ecology of giant kelp forests in California: a community profile. Biological Report 85 (7.2) U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Washington, D.C
J.-P. Gattuso M. Frankignoulle R. Wollast (1998) ArticleTitleCarbon and carbonate metabolism in coastal aquatic systems Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 29 405–434 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.29.1.405
V. A. Gerard (1984) ArticleTitleThe light environment in a giant kelp forest: influence of Macrocystis pyrifera on spatial and temporal variability Marine Biology 84 189–195 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00393004
V. A. Gerard (1986) ArticleTitlePhotosynthetic characteristics of giant kelp (Macrocystis pyrifera) determined in situ Marine Biology 90 473–482 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00428571
V. A. Gerard K. H. Mann (1979) ArticleTitleGrowth and production of Laminaria longicruris (Phaeophyta) populations exposed to different intensities of water movement Journal of Phycology 15 33–41 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.0022-3646.1979.00033.x
L. Hagermann (1966) ArticleTitleThe macro- and microfauna associated with Fucus serratus (L.), with some ecological remarks Ophelia 3 1–43
K. C. Haines P. A. Wheeler (1978) ArticleTitleAmmonium and nitrate uptake by Hypnea musciformis (Rhodophyta) and Macrocystis pyrifera (Phaeophyta) Journal of Phycology 14 319–324 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1cXlvFeqtLg%3D
M. D. Hanisak (1983) The nitrogen relationships of marine macroalgae E. J. Carpenter D. G. Capone (Eds) Nitrogen in the Marine Environment Academic Press New York 699–730
M. D. Hanisak (1993) ArticleTitleNitrogen release from decomposing seaweeds: species and temperature effects Journal of Applied Phycology 5 175–181
C. D. Hepburn (2003) The influence of sessile epifauna on the ecology and physiology of the giant kelp Macrocystis pyrifera (L.) C. Agardh University of Otago Dunedin, New Zealand 178
C. D. Hepburn C. L. Hurd (2005) ArticleTitleA conditional mutualism between the giant kelp Macrocystis pyrifera and colonial epifauna Marine Ecology Progress Series 302 37–48
R. C. Highsmith (1985) ArticleTitleFloating and algal rafting as potential dispersal mechanisms in brooding invertebrates Marine Ecology Progress Series 25 169–175
C. L. Hurd K. M. Durante F. S. Chia P. J. Harrison (1994) ArticleTitleEffect of bryozoan colonization on inorganic nitrogen acquisition by the kelps Agarum fimbriatum and Macrocystis integrifolia Marine Biology 121 167–173 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00349486
C. L. Hurd K. M. Durante P. J. Harrison (2000) ArticleTitleInfluence of bryozoan colonization on the physiology of the kelp Macrocystis integrifolia (Laminariales, Phaeophyta) from nitrogen-rich and -poor sites in Barkley Sound, British Columbia, Canada Phycologia 39 435–440
J. G. Jennings P. D. Steinberg (1997) ArticleTitlePhlorotannins versus other factors affecting epiphyte abundance on the kelp Ecklonia radiata Oecologia 109 461–473 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004420050106
J. M. Kain (1975) ArticleTitleThe biology of Laminaria hyperborean. 7. Reproduction of the sporophyte Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 55 567–582
C. D. Kopczak (1994) ArticleTitleVariability of nitrate uptake capacity in Macrocystis pyrifera (Laminariales, Phaeophyta) with nitrate and light availability Journal of Phycology 30 573–580 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.0022-3646.1994.00573.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXht1agtLk%3D
W. J. Lambert P. S. Levin J. Berman (1992) ArticleTitleChanges in the structure of a New England (USA) kelp bed: the effects of an introduced species Marine Ecology Progress Series 88 303–307
M. Littler D. Littler (1999) ArticleTitleBlade abandonment/proliferation: a novel mechanism for rapid epiphyte control in marine macrophytes Ecology 80 1736–1746
K. H. Mann (1988) ArticleTitleProduction and use of detritus in various freshwater, estuarine and coastal marine ecosystems Limnology and Oceanography 33 145–158
J. M. Mercado R. Carmona F. X. Niell (1998) ArticleTitleBryozoans increase available CO2 for photosynthesis in Gelidium sesquipedale (Rhodophyceae) Journal of Phycology 34 925–927 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1529-8817.1998.340925.x
K. J. McGlathery M. F. Pederson J. Borum (1996) ArticleTitleChanges in intracellular nitrogen pools and feed back controls on nitrogen uptake in Chaetomorpha linum (Chlorophyta) Journal of Phycology 32 393–401 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.0022-3646.1996.00393.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xktlygurc%3D
J. Muñoz J. M. Cancino M. X. Molina (1991) ArticleTitleEffect of encrusting bryozoans on the physiology of their algal substratum Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 71 877–882
R. C. Oswald N. Telford R. Seed C. M. Happey-Wood (1984) ArticleTitleThe effect of encrusting bryozoans on the photosynthetic activity of Fucus serratus L Estuarine Coastal Shelf Science 19 697–702
R. C. Oswald R. Seed (1986) ArticleTitleOrganisation and seasonal progression within the epifaunal communities of coastal macroalgae Cahiers De Biologie Marine 27 29–40
M. F. Pederson (1994) ArticleTitleTransient ammonium uptake in the macroalga Ulva lactuca (Chlorophyta): nature, regulation, and consequences for choice of measuring technique Journal of Phycology 30 980–986
T. A. Probyn A. R. O. Chapman (1983) ArticleTitleSummer growth of Chordaria flagelliformis (O.F. Muell) C. Ag.: physiological strategies in a nutrient stressed environment Journal of Experimental Marine Biology of Ecology 73 243–271
J. Ramus M. Venable (1987) ArticleTitleTemporal ammonium patchiness and growth rate in Codium and Ulva (Ulvophyceae) Journal of Phycology 23 518–523 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXht1yls70%3D
D. C. Reed M. S. Foster (1984) ArticleTitleThe effects of canopy shading on growth in a giant kelp forest Ecology 65 937–948
B. Saier A. S. Chapman (2004) ArticleTitleCrusts of the alien bryozoan Membranipora membranacea can negatively impact spore output from native kelps (Laminaria longicruris) Botanica Marina 47 265–271 Occurrence Handle10.1515/BOT.2004.031
R. E. Scheibling A. W. Hennigar T. Balch (1999) ArticleTitleDestructive grazing, epiphytism, and disease: the dynamics of sea urchin–kelp interactions in Nova Scotia Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science 56 2300–2314 Occurrence Handle10.1139/cjfas-56-12-2300
R. Seed R. J. O’Connor (1981) ArticleTitleCommunity organization in marine algal epifaunas Annual Review of Ecology Systematics 12 49–74
G. R. Seely M. J. Duncan W. E. Vidaver (1972) ArticleTitlePreparative and analytical extraction of brown pigments from brown algae with dimethyl sulfoxide Marine Biology 12 184–188 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00350754 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE38XktVarsrk%3D
R. S. Steneck et al. (2002) ArticleTitleKelp forest ecosystems: biodiversity, stability, resilience and future Environmental Conservation 29 436–459 Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0376892902000322
R. B. Taylor R. G. Cole (1994) ArticleTitleMobile epifauna on subtidal brown seaweeds in northeastern New Zealand Marine Ecology Progress Series 115 271–282
R. B. Taylor T. A. V. Rees (1998) ArticleTitleExcretory products of mobile epifauna as a nitrogen source for seaweeds Limnology Oceanography 43 600–606 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXlsFWqsbw%3D
D. W. Towle J. S. Pearse (1973) ArticleTitleProduction of the giant kelp, Macrocystis, estimated by in situ incorporation of 14C in polyethylene bags Limnology Oceanography 18 155–159 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3sXhsVGgtLY%3D
B. I. Tussenbroek Particlevan (1989) ArticleTitleSeasonal growth and composition of fronds of Macrocystis pyrifera in the Falkland Islands Marine Biology 100 419–430 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00391158
W. N. Wheeler (1980) ArticleTitlePigment content and photosynthetic rates of the fronds of Macrocystis pyrifera Marine Biology 56 97–102 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3cXkvFajs7o%3D
P. L. Yoshioka (1982) ArticleTitleRole of planktonic and benthic factors in the population dynamics of the bryozoan Membranipora membranacea Ecology 63 457–468
R. C. Zimmerman J. N. Kremer (1984) ArticleTitleEpisodic nutrient supply to a kelp forest ecosystem in Southern California Journal of Marine Research 42 591–604
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hepburn, C.D., Hurd, C.L. & Frew, R.D. Colony Structure and Seasonal Differences in Light and Nitrogen Modify the Impact of Sessile Epifauna on the Giant Kelp Macrocystis pyrifera (L.) C Agardh. Hydrobiologia 560, 373–384 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-1573-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-1573-7