Abstract
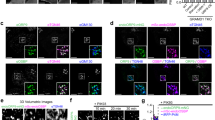
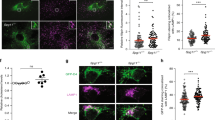
Cholesterol synthesis is a complex, coordinated process involving a series of enzymes. As of today, our understanding of subcellular localization of cholesterol biosynthesis enzymes is far from complete. Considering the complexity and intricacies of this pathway and the importance of functions of DHCR7, DHCR24 and EBP enzymes for human health, we undertook a study to determine their subcellular localization and co-localization. Using expression constructs and antibody staining in cell cultures and transgenic mice, we found that all three enzymes are expressed in ER and nuclear envelope. However, their co-localization was considerably different across the cellular compartments. Furthermore, we observed that in the absence of DHCR7 protein, DHCR24 shows a compensatory upregulation in a Dhcr7−/− transgenic mouse model. The overall findings suggest that the sterol biosynthesis enzymes might not always work in a same functional complex, but that they potentially have different, multifunctional roles that go beyond the sterol biosynthesis pathway. Furthermore, the newly uncovered compensatory mechanism between DHCR7 and DHCR24 could be of importance for designing medications that would improve cholesterol production in patients with desmosterolosis and Smith–Lemli–Opitz syndrome.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson R, Rust S, Ashworth J, Clayton-Smith J, Taylor RL, Clayton PT, Morris AAM (2018) Lathosterolosis: a relatively mild case with cataracts and learning difficulties. JIMD Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/8904_2018_127
Batta AK, Tint GS, Shefer S, Abuelo D, Salen G (1995) Identification of 8-dehydrocholesterol (cholesta-5,8-dien-3 beta-ol) in patients with Smith–Lemli–Opitz syndrome. J Lipid Res 36:705–713
Deng S, Liu H, Qiu K, You H, Lei Q, Lu W (2018) Role of the Golgi apparatus in the blood–brain barrier: Golgi protection may be a targeted therapy for neurological. Dis Mol Neurobiol 55:4788–4801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0691-3
Derry JM et al (1999) Mutations in a delta 8-delta 7 sterol isomerase in the tattered mouse and X-linked dominant chondrodysplasia punctata. Nat Genet 22:286–290. https://doi.org/10.1038/10350
Dietschy JM, Turley SD (2004) Thematic review series: brain lipids. Cholesterol metabolism in the central nervous system during early development and in the mature animal. J Lipid Res 45:1375–1397. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.R400004-JLR200
Hetzer MW (2010) The nuclear envelope. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2:a000539. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a000539
Jiang XS, Backlund PS, Wassif CA, Yergey AL, Porter FD (2010) Quantitative proteomics analysis of inborn errors of cholesterol synthesis: identification of altered metabolic pathways in DHCR7 and SC5D deficiency. Mol Cell Proteomics 9:1461–1475. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M900548-MCP200
Kandutsch AA, Russell AE (1960) Preputial gland tumor sterols. 3. A metabolic pathway from lanosterol to cholesterol. J Biol Chem 235:2256–2261
Kedjouar B et al (2004) Molecular characterization of the microsomal tamoxifen binding site. J Biol Chem 279:34048–34061. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M405230200
Korade Z, Kenworthy AK, Mirnics K (2009) Molecular consequences of altered neuronal cholesterol biosynthesis. J Neurosci Res 87:866–875. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.21917
Kovacs WJ, Olivier LM, Krisans SK (2002) Central role of peroxisomes in isoprenoid biosynthesis. Prog Lipid Res 41:369–391
Krisans SK (1996) Cell compartmentalization of cholesterol biosynthesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 804:142–164
Luu W, Hart-Smith G, Sharpe LJ, Brown AJ (2015) The terminal enzymes of cholesterol synthesis, DHCR24 and DHCR7, interact physically and functionally. J Lipid Res 56:888–897. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M056986
Mazein A, Watterson S, Hsieh WY, Griffiths WJ, Ghazal P (2013) A comprehensive machine-readable view of the mammalian cholesterol biosynthesis pathway. Biochem Pharmacol 86:56–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2013.03.021
Mitsche MA, McDonald JG, Hobbs HH, Cohen JC (2015) Flux analysis of cholesterol biosynthesis in vivo reveals multiple tissue and cell-type specific pathways. Elife 4:e07999. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.07999
Moebius FF, Fitzky BU, Lee JN, Paik YK, Glossmann H (1998) Molecular cloning and expression of the human delta7-sterol reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:1899–1902
Paik YK, Billheimer JT, Magolda RL, Gaylor JL (1986) Microsomal enzymes of cholesterol biosynthesis from lanosterol. Solubilization and purification of steroid 8-isomerase. J Biol Chem 261:6470–6477
Porter FD, Herman GE (2011) Malformation syndromes caused by disorders of cholesterol synthesis. J Lipid Res 52:6–34. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.R009548
Rath A, Glibowicka M, Nadeau VG, Chen G, Deber CM (2009) Detergent binding explains anomalous SDS-PAGE migration of membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:1760–1765. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0813167106
Rittenberg D, Borek E, Bloch K (1946) Synthesis of cholesterol in liver slices. Fed Proc 5:151
Robertson KA, Ghazal P (2016) Interferon control of the sterol metabolic network: bidirectional molecular circuitry-mediating host. Protect Front Immunol 7:634. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2016.00634
Robertson KA et al (2016) An interferon regulated microRNA provides broad cell-intrinsic antiviral immunity through multihit host-directed targeting of the sterol pathway. PLoS Biol 14:e1002364. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1002364
Rossi M et al (2007) Clinical phenotype of lathosterolosis. Am J Med Genet A 143A:2371–2381. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.31929
Schaaf CP et al (2011) Desmosterolosis-phenotypic and molecular characterization of a third case and review of the literature. Am J Med Genet A 155A:1597–1604. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.34040
Sharpe LJ, Wong J, Garner B, Halliday GM, Brown AJ (2012) Is seladin-1 really a selective Alzheimer’s disease indicator? J Alzheimers Dis 30:35–39. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2012-111955
Smith DW, Lemli L, Opitz JM (1964) A newly recognized syndrome of multiple congenital anomalies. J Pediatr 64:210–217
Worman HJ, Evans CD, Blobel G (1990) The lamin B receptor of the nuclear envelope inner membrane: a polytopic protein with eight potential transmembrane domains. J Cell Biol 111:1535–1542
Zerenturk EJ, Sharpe LJ, Ikonen E, Brown AJ (2013) Desmosterol and DHCR24: unexpected new directions for a terminal step in cholesterol synthesis Prog Lipid Res 52:666–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2013.09.002
Zerenturk EJ, Sharpe LJ, Brown AJ (2014) DHCR24 associates strongly with the endoplasmic reticulum beyond predicted membrane domains: implications for the activities of this multi-functional enzyme. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20130127
Zolotushko J et al (2011) The desmosterolosis phenotype: spasticity, microcephaly and micrognathia with agenesis of corpus callosum and loss of white matter. Eur J Hum Genet 19:942–946. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2011.74
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by The National Institutes of Health, NIMH MH110636 (KM) and MN067234 (KM). Katalin Koczok was the Rosztoczy Foundation scholar.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10735_2018_9807_MOESM1_ESM.pptx
Supplementary Figure 1. Co-localization of fluorescently tagged recombinant proteins and antibody staining. In this validation study, Neuro2a cells were transiently transfected with EGFP-DHCR7, EGFP-DHCR24 and ptdTomato-EBP fusion constructs. Cells were labeled with anti-DHCR7, anti-DHCR24 and anti-EBP antibodies, respectively, in order to verify antibody specificity and analyzed by confocal microscopy. Nuclei were visualized by Hoechst dye. Original images were collected with a 60× oil objective. Calibration bar, 5 µm. Note that the recombinant proteins and antibody staining fully co-localize. (PPTX 2331 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koczok, K., Gurumurthy, C.B., Balogh, I. et al. Subcellular localization of sterol biosynthesis enzymes. J Mol Hist 50, 63–73 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-018-9807-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-018-9807-y