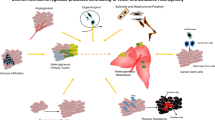
Abstract
Chemokines are a class of functional chemotactic peptides that contribute to a number of tumor-related processes. They are functionally defined as soluble factors that are able to control the directional migration of leukocytes, in particular, during infection and inflammation. It appears, however, that the biological effects mediated by chemokines are far more complex, and virtually all cells, including many tumor cell types, can express chemokines and chemokine receptors. A growing body of evidence indicates that they also contribute to a number of tumor-related processes, such as tumor cell growth, angiogenesis/angiostasis, local invasion, and mediate organ-specific metastases of cancer. The CXC chemokine class is a subfamily of a large family of chemokines. During the occurrence and development of tumor cells, this chemokine class is often accompanied by a series of molecular and biological changes. The CXC chemokine subfamily is closely related to the body’s immune response to tumors and biological behaviors of tumors. In this paper, CXC chemokines and their role in the progression and treatment of tumors will be reviewed.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GPCR:
-
G protein-coupled receptor
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- INF:
-
Interferon
- HHV-8:
-
Human herpes virus 8
- MGSA:
-
Melanocyte growth stimulatory activity
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- SCID:
-
Severe combined immunodeficiency
- TKRs:
-
Tyrosine kinase receptors
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- SCLC:
-
Small cell lung cancer
- DRAC:
-
Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines
- bFGF:
-
Basic fibroblast growth factor
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- ENA-78:
-
Epithelial neutrophil-activating peptide 78
- BRAK:
-
Breast and kidney-expressed chemokine
- DCs:
-
Dendritic cells
References
Addison CL, Daniel TO, Burdick MD et al (2000a) The CXC chemokine receptor 2, CXCR2, is the putative receptor for ELR + CXC chemokine-induced angiogenic activity. J Immunol 165(9):5269–5277
Addison CL, Arenberg DA, Morris SB et al (2000b) The CXC chemokine, monokine induced by interferon-gamma, inhibits non-small cell lung carcinoma tumor growth and metastasis. Hum Genet Ther 11(2):247–261
Addison CL, Belperio JA, Burdick MD et al (2004) Overexpression of the duffy antigen receptor for chemokines (DARC) by NSCLC tumor cells results in increased tumor necrosis. BMC Cancer 4:28
Alvarez H, Opalinska J, Zhou L et al (2011) Widespread hypomethylation occurs early and synergizes with gene amplification during esophageal carcinogenesis. PLoS Genet 7(3):e1001356
Angiolillo AL, Sgadari C, Taub DD et al (1995) Human interferon-inducible protein-10 is a potent inhibitor of angiogenesis in vivo. J Exp Med 182(1):155–162
Arenberg DA, Kunkel SL, Polverini PJ et al (1996a) Interferon-γ-inducible protein IP-10 is an angiostatic factor that inhibits human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tumorigenesis and spontaneous metastases. J Exp Med 184(3):981–992
Arenberg DA, Kunkel SL, Polverini PJ et al (1996b) Inhibition of IL-8 reduces tumorigenesis of human non-small cell lung cancer in SCID mice. J Clin Invest 97(12):2792–2802
Arenberg DA, Polverini PJ, Kunkel SL et al (1997) The role of CXC chemokines in the regulation of angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer. J Leukoc Biol 62(5):554–562
Arya M, Patel HR, Williamson M (2003) Chemokines: key players in cancer. Curr Med Res Opin 19(6):557–564
Arya M, Ahmed H, Silhi N et al (2007) Clinical importance and therapeutic implications of the pivotal CXCL12-CXCR4 (chemokine ligand receptor) interaction in cancer cell migration. Tumor Biol 28(3):123–131
Augsten M, Hägglöf C, Olsson E et al (2009) CXCL14 is an autocrine growth factor for fibroblasts and acts as a multi-modal stimulator of prostate tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(9):3414–3419
Auguste P, Javerzat S, Bikfalvi A (2003) Regulation of vascular development by fibroblast growth factors. Cell Tissue Res 314(1):157–166
Bachelder RE, Wendt MA, Mercurio AM (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes breast carcinoma invasion in an autocrine manner by regulating the chemokine receptor CCR4. Cancer Res 62(24):7203–7206
Baird AM, Gray SG, O’Byrne KJ (2011) Epigenetics underpinning the regulation of the CXC (ELR +) chemokines in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One 6(1):e14593
Balkwill F (2004a) Cancer and chemokine network. Nat Rev Cancer 4(7):540–550
Balkwill F (2004b) The significance of cancer cell expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Semin Cancer Biol 14(3):171–179
Belperio JA, Keane MP, Arenberg DA et al (2000) CXC chemokines in angiogenesis. J Leukoc Biol 68(1):1–8
Bertolini F, Dell’Agnola C, Mancuso P et al (2002) CXCR4 neutralization, a novel therapeutic approach for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Cancer Res 62(11):3106–3112
Bikfalvi A (2004) Platelet factor 4: an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Semin Thromb Hemost 30(3):379–385
Bikfalvi A, Gimenez-Gallego G (2004) The control of angiogenesis and tumor invasion by platelet factor-4 and platelet factor-4-derived molecules. Semin Thromb Hemost 30(1):137–144
Bordoni R, Fine R, Murray D et al (1990) Characterization of the role of melanoma growth stimulatory activity (MGSA) in the growth of normal melanocytes, nevocytes, and malignant melanocytes. J Cell Biochem 44(4):207–219
Brand S, Dambacher J, Beigel F et al (2005) CXCR4 and CXCL12 are inversely expressed in colorectal cancer cells and modulate cancer cell migration, invasion, invasion and MMP-9 activation. Exp Cell Res 310(1):117–130
Brysse A, Mestdagt M, Polette M et al (2012) Regulation of CXCL8/IL-8 expression by zonula occludens-1 in human breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 10(1):121–132
Burns JM, Summers BC, Wang Y et al (2006) A novel chemokine receptor for SDF-1 and I-TAC involved in cell survival, cell adhesion, and tumor development. J Exp Med 203(9):2201–2213
Busuttil A, Weigt SS, Keane MP et al (2009) CXCR3 ligands are augmented during the pathogenesis of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Eur Respir J 34(3):676–686
Couty JP, Gershengorn MC (2004) Insights into the viral G protein-coupled receptor encoded by human herpesvirus type-8. Biol Cell 96(5):349–354
Dias S, Choy M, Rafii S (2001) The role of CXC chemokines in the regulation of tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Invest 19(7):732–738
Ehlert JE, Addison CA, Burdick MD et al (2004) Identification and partial characterization of a variant of human CXCR3 generated by posttranscriptional exon skipping. J Immunol 173(10):6234–6240
Ferrer FA, Miller LJ, Andrawis RI et al (1998) Angiogenesis and prostate cancer: in vivo and in vitro expression of angiogenesis factors by prostate cancer cells. Urology 51(1):161–167
Ferretti E, Di Carlo E, Cocco C et al (2010) Direct inhibition of human acute myeloid leukemia cell growth by IL-12. Immunol Lett 133(2):99–105
Frederick MJ, Henderson Y, Xu X et al (2000) In vivo expression of the novel CXC chemokine BRAK in normal and cancerous human tissue. Am J Pathol 156(6):1937–1950
Giuliani N, Bonomini S, Romagnani P et al (2006) CXCR3 and its binding chemokines in myeloma cells: expression of isoforms and potential relationships with myeloma cell proliferation and survival. Haematologica 91(11):1489–1497
Guiducci C, Vicari AP, Sanhaletti S et al (2005) Redirecting in vivo elicited tumor infiltrating macrophages and dendritic cells towards tumor rejection. Cancer Res 65(8):3437–3446
Gupta SK, Singh JP (1994) Inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation by platelet factor-4 involves a unique action on S phase progression. J Cell Biol 127(4):1121–1127
Ha HK, Lee W, Park HJ et al (2011) Clinical significance of CXCL16/CXCR6 expression in patients with prostate cancer. Mol Med Report. 4(3):419–424
Heidemann J, Ogawa H, Dwinell MB et al (2003) Angiogenic effects of interleukin 8(CXCL8) in human intestinal microvascular endothelial cells are mediated by CXCR2. J Biol Chem 278(10):8508–8515
Hillinger S, Yang SC, Zhu L et al (2003) EBV-induced molecule1 ligand chemokine (ELC/CCL19) promotes IFN-γ-dependent antitumor responses in a lung cancer model. J Immunol 171(12):6457–6465
Homey B, Muller A, Zlotnik A (2002) Chemokines: agents for the immunotherapy of cancer? Nat Res Immunol. 2(3):175–184
Inoue K, Slaton JW, Eve BY et al (2000) Interleukin-8 expression regulates tumorigenicity and metastases in androgen-independent prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 6(5):2104–2119
IUIS/WHO (2003) Subcommittee on Chemokine Nomenclature. Chemokine/chemokine receptor nomenclature. Cytokine 21(1):48–49
Kawada K, Sonoshita M, Sakashita H et al (2004) Pivotal role of CXCR3 in melanoma cell metastasis to lymph nodes. Cancer Res 64(11):4010–4017
Keane MP, Belperio JA, Xue YY et al (2004) Depletion of CXCR2 inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis in a murine model of lung cancer. J Immunol 172(5):2853–2860
Keeley EC, Mehrad B, Strieter RM (2008) Chemokines as mediators of neovascularization. Aeterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28(11):1928–1936
Keeley EC, Mehrad B, Strieter RM (2010) CXC chemokines in cancer angiogenesis and metastases. Adv Cancer Res 106:91–111
Keeley EC, Mehrad B, Strieter RM (2011) Chemokines as mediators of tumor angiogenesis and neovascularization. Exp Cell Res 317(5):685–690
Kijowski J, Baj-Krzyworzeka M, Majka M et al (2001) The SDF-1 -CXCR4 axis stimulates VEGF secretion and activates integrins but does not affect proliferation and survival in lymphohematopoietic cells. Stem Cells 19(5):453–466
Kittang AO, Hatfield K, Sand K et al (2010) The chemokine network in acute myelogenous leukemia: molecular mechanisms involved in leukemogenesis and therapeutic implications. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 341:149–172
Kulbe H, Levinson NR, Balkwill F et al (2004) The chemokine network in cancer–much more than directing cell movement. Int J Dev Biol 48(5–6):489–496
Lasagni L, Francalanci M, Annunziato F et al (2003) An alternatively spliced variant of CXCR3 mediates the inhibition of endothelial cell growth induced by IP-10, Mig, and I-TAC, and acts as functional receptor for platelet factor 4. J Exp Med 197(11):1537–1549
Liu Y, Huang H, Saxena A et al (2002) Intratumoral coinjection of two adenoviral vectors expressing functional interleukin-18 and inducible protein-10, respectively, synergizes to facilitate regression of established tumors. Cancer Gene Ther 9(6):533–542
Loetscher M, Loetscher P, Brass N et al (1998) Lymphocyte-specific chemokine receptor CXCR3: regulation, chemokine binding and gene localization. Eur J Immunol 28(11):3696–3705
Luan J, Shattuck BR, Haghnegahdar H et al (1997) Mechanism and biological significance of constitutive expression of MGSA/GRO chemokines in malignant melanoma tumor progression. J Leukoc Biol 62(5):588–597
Luster AD (1998) Chemokines-chemotactic cytokines that mediate inflammation. N Eng J Med 338(7):436–445
Ma X, Norsworthy K, Kundu N et al (2009) CXCR3 expression is associated with poor survival in breast cancer and promotes metastasis in a murine model. Mol Cancer Ther 8(3):490–498
Maione TE, Gray GS, Petro J et al (1990) Inhibition of angiogenesis by recombinant human platelet factor-4 and related peptides. Science 247(4938):77–79
Manna SK, Ramesh GT (2005) Interleukin-8 induces nuclear transcription factor-kappaB through a TRAF6-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 280(8):7010–7021
Mc Donnell S, Chaudhry V, Mansilla-soto J et al (1999) Metastatic and non- metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC) cells induce host metalloproteinase production in vivo. Clin Exp Metastasis 17(4):341–349
Mehrad B, Keane MP, Strieter RM (2007) Chemokines as mediators of angiogenesis. Thromb Haemost 97(5):755–762
Mendelsohn J, Baselga J (2006) Epidermal growth factor receptor targeting in cancer. Semin Oncol 33(4):369–385
Moore BB, Arenberg DA, Addison CL et al (1998) CXC chemokines mechanism of action in regulating tumor angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 2(2):123–134
Moore BB, Arenberg DA, Stoy K et al (1999) Distinct CXC chemokines mediate tumorigenicity of prostate cancer cells. Am J Pathol 154(5):1503–1512
Muller A, Homey B, Soto H et al (2001) Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature 410(6824):50–56
Muller M, Carter S, Hofer MJ et al (2010) The chemokine receptor CXCR3 and its ligands CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11 in neuroimmunity-a tale of conflict and conundrum. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 36(5):368–387
Narvaiza I, Mazzolini G, Barajas M et al (2000) Introtumoral coinjection of two adenovirus, one encoding the chemokine IFN-γ-inducible protein-10 and another encoding IL-12, results in marked antitumoral synergy. J Immunol 164(6):3112–3122
Nor JE, Christensen J, Liu J et al (2001) Up-regulation of Bcl-2 in microvascular endothelial cells enhances intratumoral angiogenesis and accelerates tumor growth. Cancer Res 61(5):2183–2188
Norgauer J, Metzner B, Schraufstatter I (1996) Expression and growth-promoting function of IL-8 receptor βin human melanoma cells. J Immunol 156(3):1132–1137
Olbina G, Cieslak D, Ruzdijic S et al (1996) Reversible inhibition of IL-8 receptor βmRNA expression and proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer by antisense oligonucleotides. Anticancer Res 16(6):3525–3530
Palmer K, Hitt M, Emtage PC et al (2001) Combined CXC chemokine and interleukin-12 gene transfer enhances antitumor immunity. Gene Ther 8(4):282–290
Parsonage G, Machado LR, Hui JW et al (2012) CXCR6 and CCR5 localize T lymphocyte subsets in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Am J Pathol 180(3):1215–1222
Pawson T, Scott JD (1997) Signaling through scaffold, anchoring, and adaptor proteins. Science 278(5346):2075–2080
Perollet C, Han ZC, Savona C et al (1998) Platelet factor-4 modulates fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF-2) activity and inhibits FGF-2 dimerization. Blood 91(9):3289–3299
Phillips RJ, Burdick MD, Lutz M et al (2003) The stromal derived factor-1/CXCL12-CXC chemokine receptor 4 biological axis in non-small cell lung cancer metastases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167(12):1676–1686
Richards BL, Eisma RJ, Spiro JD et al (1997) Coexpression of interleukin-8 receptors in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Surg 174(5):507–512
Richmond A, Thomas HG (1986) Purification of melanoma growth stimulatory activity. J Cell Physiol 129(3):375–384
Richmond A, Fan GH, Dhawan P et al (2004) How do chemokine/chemokine receptor activations affect tumorigenesis? Novartis Found Symp 256:74–89
Rollins Barrett J (2006) Inflammatory chemokines in cancer growth and progression. Euro J Cancer. 42(6):760–767
Romagnani P, Annunziato F, Lasagni L et al (2001) Cell cycle-dependent expression of CXC chemokine receptor3 by endothelial cells mediates angiostatic activity. J Clin I nvest. 107(1):53–63
Rossi D, Zlotnik A (2000) The biology of chemokines and their receptors. Annu Rev Immunol 18:217–242
Rubin JB, Kung AL, Klein RS et al (2003) A small-molecule antagonist of CXCR4 inhibits intracranial growth of primary brain tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(23):13513–13518
Ruehlmann JM, Xiang R, Niethammer AG et al (2001) MIG (CXCL9) chemokine gene therapy combines with antibody-cytokine fusion protein to suppress growth and dissemination of murine colon carcinoma. Cancer Res 61(23):8498–8503
Salcedo R, Oppenheim JJ (2003) Role of the chemokines in angiogenesis: CXCL12/SDF-1 and CXCR4 interaction, a key regulator of endothelial cell responses. Microcirculation 10(3–4):359–370
Salcedo R, Wasserman K, Young HA et al (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibrolast growth factor induce expression of CXCR4 on human endothelial cells: in vivo neovasculaeization induced by stromal-derived factor-l alpha. Am J Pathol 154(4):1125–1135
Salcedo R, Resau JH, Halverson D et al (2000) Differential expression and responsiveness of chemokine receptors (CXCR1-3) by human microvascular endothelial cells and umbilical vein endothelial cells. FASEB J 14(14):2055–2064
Sambandam Y, Sundaram K, Liu A et al (2012) CXCL13 activation of c-Myc induces RANK ligand expression in stromal/preosteoblast cells in the oral squamous cell carcinoma tumor-bone microenvironment. Oncogene. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.24
Schruefer R, Lutze N, Schymeinsky J et al (2005) Human neutrophils promote angiogenesis by a paracrine feedforward mechanism involving endothelial interleukin-8. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288(3):H1186–H1192
Schwarze SR, Luo J, Isaacs WB et al (2005) Modulation of CXCL14 (BRAK) expression in prostate cancer. Prostate 64(1):67–74
Sgadari C, Farber JM, Angiolillo AL et al (1997) Mig, the monokine induced by interferon-gamma, promotes tumor necrosis in vivo. Blood 89(8):2635–2643
Sharma S, Yang SC, Hillinger S et al (2003) SLC/CCL21-mediated anti-tumor responses require IFN-γ, MIG/CXCL9 and IP-10/CXCL10. Mol Cancer 2(1):22
Shellenberger TD, Wang M, Gujrati M et al (2004) BRAK/CXCL14 is a potent inhibitor of angiogenesis and is a chemotactic factor for immature dendritic cells. Cancer Res 64(22):8262–8270
Shyamala V, Khoja H (1998) Interleukin-8 receptors R1and R2 activate mitogen-activated protein kinases and induce c-fos, independent of Ras and Raf-1 in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochemistry 37(45):15918–15924
Singh RK, Gutman M, Radinsky R et al (1994) Expression of interleukin 8 correlates with the metastatic potential of human melanoma cells in nude mice. Cancer Res 54(12):3242–3247
Singh S, Wu S, Varney M et al (2011) CXCR1 and CXCR2 silencing modulates CXCL8-dependent endothelial cell proliferation, migration and capillary-like structure formation. Microvasc Res 82(3):318–325
Soto H, Wang W, Strieter RM et al (1998) The CC chemokine 6ckine binds the CXC chemokine receptor CXCR3. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95(14):8205–8210
Stamatovic SM, Keep RF, Mostarica-Stojkovic M et al (2006) CCL2 regulates angiogenesis via activation of Ets-1 transcription factor. J Immunol 177(4):2651–2661
Stewart YJ, Smyth MJ (2009) Chemokine-chemokine receptors in cancer immunotherapy. Immunotherapy 1(1):109–127
Strieter RM, Polverini PJ, Kunkel SL et al (1995) The functional role of the ELR motif in CXC chemokine-mediated angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 270(45):27348–27357
Strieter RM, Belperio JA, Burdick MD et al (2004) CXC chemokines: angiogenesis, immunoangiostasis, and metastases in lung cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1028:351–360
Strieter RM, Burdick MD, Mestas J et al (2006) Cancer CXC chemokine networks and tumor angiogenesis. Euro J Cancer. 42(6):768–778
Struyf S, Burdick MD, Peeters E et al (2007) Platelet factor-4 variant chemokine CXCL4L1 inhibits melanoma and lung carcinoma growth and metastasis by preventing angiogenesis. Cancer Res 67(12):5940–5948
Stuyf S, Burdick MD, Proost P et al (2004) Platelets release CXCL14L1, a nonallelic variant of the chemokine platelet factor-4/CXCL4 and potent inhibitor of angiogenesis. Circ Res 95(9):855–857
Sugden PH, Clerk A (1997) Regulation of the ERK subgroup of MAP kinase cascades through G protein-coupled receptors. Cell Signal 9(5):337–351
Takamori H, Oades ZG, Hoch OC et al (2000) Autocrine growth effect of IL-8 and GRO-α on a human pancreatic cancer cell line, Capan-1. Pancreas 21(1):52–56
Tanaka Toshiyuki, Bai Zhongbin, Srinoulprasert Yuttana et al (2005) Chemokines in tumor progression and metastasis. Cancer Sci 96(6):317–322
Vandercappellen J, Van Damme J, Struyf S (2008) The role of CXC chemokines and their receptors in cancer. Cancer Lett 267(2):226–244
Vicari Alain P, Caux Christophe (2002) Chemokines in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 13(2):143–154
Vicari AP, Treilleux I, Lebecque S (2004) Regulation of the trafficking of tumor-infiltrating dendritic cells by chemokines. Semin Cancer Biol 14(3):161–169
Wang J, Loberg R, Taichman RS (2006) The pivotal role of CXCL12 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 axis in bone metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25(4):573–587
Yang J, Richmond A (2004) The angiostatic activity of interferon-inducible protein-10/CXCL10 in human melanoma depends on binding to CXCR3 but not to glycosaminoglycan. Mol Ther 9(6):846–855
Yoneda J, Kuniyasu H, Crispens MA et al (1998) Expression of angiogenesis-related genes and progression of human ovarian carcinomas in nude mice. J Natl Cancer Inst 90(6):447–454
Youngs SJ, Ali SA, Taub DD et al (1997) Chemokines induce migrational responses in human breast carcinoma cell lines. Int J Cancer 71(2):257–266
Zhou Y, Larsen PH, Hao C et al (2002) CXCR4 is a major chemokine receptor on glioma cells and mediates their survival. J Biol Chem 277(51):49481–49487
Zipin-Roitman A, Meshel T, Sagi-Assif O et al (2007) CXCL10 promotes invasion-related properties in human colorectal carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 67(7):3396–3405
Zlotnik A (2004) Chemokines in neoplastic progression. Semin Cancer Biol 14(3):181–185
Zlotnik A, Yoshie O (2000) Chemokines: a new classification system and their role in immunity. Immunity 12(2):121–127
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Yu Wang for his critical reading of the manuscript.
Conflicts of interest
The authors indicated no potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Q., Han, X., Peng, J. et al. The role of CXC chemokines and their receptors in the progression and treatment of tumors. J Mol Hist 43, 699–713 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-012-9435-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-012-9435-x