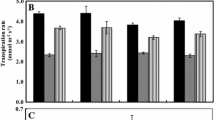
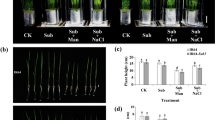
Abstract
Phytohormone play important roles in regulating developmental processes and signaling networks involved in plant responses to submergence stress. We studied the growth, leaf endogenous hormonal levels and related genes of two contrasting rice genotypes (IR64 and IR64-Sub1) pretreated with 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) and paclobutrazol (PB) under submergence conditions. Submergence promoted underwater shoot elongation, chlorophyll degradation and expression of OsCIPK15, altered the leaf endogenous hormone levels, accelerated the yellowing and senescence of leaves, and decreased shoot dry weight and the plant survival rate. IR64 was more sensitive to submergence stress, showing larger increases of leaf GAs, ABA, IAA contents and the expression of OsCPS1, OsGA20ox1 and OsIAA11, which in IR64-Sub1 were significantly decreased with prolonged stress. Furthermore, IR64 showed decreased ZR content, cZOGT1 expression, GA/ABA and ZR/IAA, while IR64-Sub1 showed opposite trends. Shoot elongation, leaf yellowing and senescence, GAs and IAA contents and the expression of OsCPS1, OsGA20ox1 and OsIAA11 in submerged rice leaves were enhanced by ACC application, whereas PB treatment showed opposite effects, and the effects on underwater elongation of PB and Sub1 were clearly superimposable. Compared with GA/ABA, ZR/IAA was not only suitable for non-Sub1 genotypes, but also more accurate in reflecting the submergence characteristics in IR64-Sub1. These findings improve our understanding of the intricate web of connections between plant hormones that regulate physiological responses to stress.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbona V, Gomez-Cadenas A (2008) Hormonal modulation of citrus responses to flooding. J Plant Growth Regul 27(3):241–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-008-9051-x
Bai T, Yin R, Li C, Ma F, Yue Z, Shu H (2011) Comparative analysis of endogenous hormones in leaves and roots of two contrasting malus species in response to hypoxia stress. J Plant Growth Regul 30(2):119–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-010-9173-9
Bailey-Serres J, Voesenek LACJ (2008) Flooding stress: acclimations and genetic diversity. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59(59):313–339. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092752
Barrero JM, Rodríguez PL, Quesada V, Piqueras P, Ponce MR, Micol JL (2006) Both abscisic acid (ABA)-dependent and ABA-independent pathways govern the induction of NCED3, AAO3 and ABA1 in response to salt stress. Plant Cell Environ 29(10):2000–2008
Benschop JJ, Bou J, Peeters AJM, Wagemaker N, Gühl K, Ward D, Hedden P, Moritz T, Voesenek LACJ (2006) Long-term submergence-induced elongation in rumex palustris requires abscisic acid-dependent biosynthesis of gibberellin1. Plant Physiol 141(4):1644–1652
Chang H, Jones ML, Banowetz GM, Clark DG (2003) Overproduction of cytokinins in petunia flowers transformed with PSAG12-IPT delays corolla senescence and decreases sensitivity to ethylene. Plant Physiol 132(4):2174–2183. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.023945
Chen X, Pierik R, Peeters AJM, Poorter H, Visser EJW, Huber H, De Kroon H, Voesenek LACJ (2010) Endogenous abscisic acid as a key switch for natural variation in flooding-induced shoot elongation. Plant Physiol 154(2):969–977. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.162792
Choi D (2007) Ethylene-induced stem growth of deepwater rice is correlated with expression of gibberellin- and abscisic acid-biosynthetic genes. J Plant Biol 50(5):595–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/Bf03030714
Cox MC, Benschop JJ, Vreeburg RA, Wagemaker CA, Moritz T, Peeters AJ, Voesenek LA (2004) The roles of ethylene, auxin, abscisic acid, and gibberellin in the hyponastic growth of submerged Rumex palustris petioles. Plant Physiol 136(2):2948. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.049197
Cox MC, Peeters AJ, Voesenek LA (2006) The stimulating effects of ethylene and auxin on petiole elongation and on hyponastic curvature are independent processes in submerged Rumex palustris. Plant Cell Environ 29(2):282–290. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01420.x
Das KK, Sarkar RK, Ismail AM (2005) Elongation ability and non-structural carbohydrate levels in relation to submergence tolerance in rice. Plant Sci 168(1):131–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.07.023
Das KK, Panda D, Sarkar RK, Reddy JN, Ismail AM (2009) Submergence tolerance in relation to variable floodwater conditions in rice. Environ Exp Bot 66(3):425–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2009.02.015
Dat JF, Capelli N, Folzer H, Bourgeade P, Badot PM (2004) Sensing and signalling during plant flooding. Plant Physiol Biochem 42(4):273–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2004.02.003
Ella ES, Kawano N, Yamauchi Y, Tanaka K, Ismail AM (2003) Blocking ethylene perception enhances flooding tolerance in rice seedlings. Funct Plant Biol 30(30):813–819. https://doi.org/10.1071/Fp03049
Fukao T, Bailey-Serres J (2008) Ethylene—a key regulator of submergence responses in rice. Plant Sci 175(1–2):43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2007.12.002
Fukao T, Bailey-Serres J (2012) The submergence tolerance gene SUB1A delays leaf senescence under prolonged darkness through hormonal regulation in rice. Plant Physiol 160(4):1795–1807. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.207738
Fukao T, Xu K, Ronald PC, Bailey-Serres J (2006) A variable cluster of ethylene response factor–like genes regulates metabolic and developmental acclimation responses to submergence in rice. Plant Cell Online 18(8):2021–2034. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.106.043000
Gautam P, Nayak AK, Lal B, Bhattacharyya P, Tripathi R, Shahid M, Mohanty S, Raja R, Panda BB (2014) Submergence tolerance in relation to application time of nitrogen and phosphorus in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Exp Bot 99(1):159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2013.11.012
Guillaume R, Margret S (2008) Ethylene biosynthesis and signaling in rice. Plant Sci 175(1–2):32–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2008.01.012
Hattori Y, Nagai K, Furukawa S, Song XJ, Kawano R, Sakakibara H, Wu J, Matsumoto T, Yoshimura A, Kitano H (2009) The ethylene response factors SNORKEL1 and SNORKEL2 allow rice to adapt to deep water. Nature 460(7258):1026–1030. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08258
He Z (1993) Guidance to experiment on chemical control in crop plants. Beijing Agricultural University Press, Beijing
Ho VT, Tran AN, Cardarelli F, Perata P, Pucciariello C (2017) A calcineurin B-like protein participates in low oxygen signalling in rice. Funct Plant Biol 44(9):917–928
Hoffmannbenning S, Kende H (1992) On the role of abscisic acid and gibberellin in the regulation of growth in rice. Plant Physiol 99(3):1156–1161. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.99.3.1156
Hou Y, Qiu J, Wang Y, Li Z, Zhao J, Tong X, Lin H, Zhang J (2017) A Quantitative proteomic analysis of brassinosteroid-induced protein phosphorylation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Front Plant Sci 8(1):60
Ismail AM, Singh US, Singh S, Dar MH, Mackill DJ (2013) The contribution of submergence-tolerant (Sub1) rice varieties to food security in flood-prone rainfed lowland areas in Asia. Field Crops Res 152(10):83–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2013.01.007
Jackson MB (2008) Ethylene-promoted elongation: an adaptation to submergence stress. Ann Bot 101(2):229–248. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcm237
Jackson MB, Ram PC (2003) Physiological and molecular basis of susceptibility and tolerance of rice plants to complete submergence. Ann Bot 91(2):227–241. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcf242
Jin Q, Wang Y, Li X, Wu S, Wang Y, Luo J, Mattson N, Xu Y (2017) Interactions between ethylene, gibberellin and abscisic acid in regulating submergence induced petiole elongation in Nelumbo nucifera. Aquat Bot 137:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquabot.2016.11.002
Jung KH, Seo YS, Walia H, Cao P, Fukao T, Canlas PE, Amonpant F, Baileyserres J, Ronald PC (2010) The submergence tolerance regulator Sub1A mediates stress-responsive expression of AP2/ERF transcription factors. Plant Physiol 152(3):1674–1692. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.152157
Kawano N, Ella E, Ito O, Yamauchi Y, Tanaka K (2002) Metabolic changes in rice seedlings with different submergence tolerance after desubmergence. Environ Exp Bot 47(3):195–203
Kawano N, Ito O, Sakagami J (2009) Morphological and physiological responses of rice seedlings to complete submergence (flash flooding). Ann Bot 103(2):161–169. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcn171
Kazan K, Manners JM (2009) Linking development to defense: auxin in plant-pathogen interactions. Trends Plant Sci 14(7):373–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2009.04.005
Kende H, Van der Knaap E, Cho HT (1998) Deepwater rice: a model plant to study stem elongation. Plant Physiol 118(4):1105–1110. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.118.4.1105
Klok EJ, Wilson IW, Wilson D, Chapman SC, Ewing RM, Somerville SC, Peacock WJ, Dolferus R, Dennis ES (2002) Expression profile analysis of the low-oxygen response in Arabidopsis root cultures. Plant Cell 14(10):2481–2494
Kudahettige NP, Pucciariello C, Parlanti S, Alpi A, Perata P (2011) Regulatory interplay of the Sub1A and CIPK15 pathways in the regulation of α-amylase production in flooded rice plants. Plant Biol 13(4):611–619
Kudo T, Makita N, Kojima M, Tokunaga H, Sakakibara H (2012) Cytokinin activity of cis-zeatin and phenotypic alterations induced by overexpression of putative cis-Zeatin-O-glucosyltransferase in Rice. Plant Physiol 160(1):319–331
Lal B, Gautam P, Rath L, Haldar D, Panda BB, Raja R, Shahid M, Tripathi R, Bhattacharyya P, Mohanty S (2015) Effect of nutrient application on growth, metabolic and enzymatic activities of rice seedlings during flooding stress and subsequent re-aeration. J Agron Crop Sci 201(2):138–151. https://doi.org/10.1111/jac.12094
Le NH, Vantoai T, Streeter J, Banowetz G (2005) Regulation of flooding tolerance of SAG12:ipt Arabidopsis plants by cytokinin. J Exp Bot 56(415):1397. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eri141
Lee SC, Mustroph A, Sasidharan R, Vashisht D, Pedersen O, Oosumi T, Voesenek LACJ, Bailey-Serres J (2011) Molecular characterization of the submergence response of the Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype Columbia. New Phytol 190(2):457. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03590.x
Lin KH, Tsou CC, Hwang SY, Chen LFO, Lo HF (2008) Paclobutrazol leads to enhanced antioxidative protection of sweetpotato under flooding stress. Bot Stud 49(1):9–18. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004
Lomin SN, Yonekurasakakibara K, Romanov GA, Sakakibara H (2011) Ligand-binding properties and subcellular localization of maize cytokinin receptors. J Exp Bot 62(14):5149–5159
Moubayidin L, Mambro RD, Sabatini S (2009) Cytokinin-auxin crosstalk. Trends Plant Sci 14(10):557–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2009.06.010
Muraro D, Byrne H, King J, Voss U, Kieber J, Bennett M (2011) The influence of cytokinin-auxin cross-regulation on cell-fate determination in Arabidopsis thaliana root development. J Theor Biol 283(1):152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtbi.2011.05.011
Nambara E, Marionpoll A (2005) Abscisic acid biosynthesis and catabolism. Annu Rev Plant Biol 56(56):165. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.56.032604.144046
Nishiuchi S, Yamauchi T, Takahashi H, Kotula L, Nakazono M (2012) Mechanisms for coping with submergence and waterlogging in rice. Rice 5(1):2314–2322. https://doi.org/10.1186/1939-8433-5-2
Olivella C, Biel C, Savé R, Vendrell M (2000) Hormonal and physiological responses of Gerbera jamesonii to flooding stress. Hortscience 35(2):222–225
Panda D, Sarkar RK (2014) Mechanism associated with nonstructural carbohydrate accumulation in submergence tolerant rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. J Plant Interact 9(1):62–68. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2012.763000
Ram PC, Singh BB, Singh AK, Ram P, Singh PN, Singh HP, Boamfa I, Harren F, Santosa E, Jackson MB, Setter TL, Reuss J, Wade LJ, Singh VP, Singh RK (2002) Submergence tolerance in rainfed lowland rice: physiological basis and prospects for cultivar improvement through marker-aided breeding. Field Crops Res 76(2–3):131–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4290(02)00035-7
Razem FA, Baron K, Hill RD (2006) Turning on gibberellin and abscisic acid signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9(5):454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2006.07.007
Robert-Seilaniantz A, Navarro L, Bari R, Jones JD (2007) Pathological hormone imbalances. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10(4):372–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2007.06.003
Saika H, Okamoto M, Miyoshi K, Kushiro T, Shinoda S, Jikumaru Y, Fujimoto M, Arikawa T, Takahashi H, Ando M (2007) Ethylene promotes submergence-induced expression of OsABA8ox1, a gene that encodes ABA 8′-hydroxylase in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 48(2):287–298. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcm003
Sarkar RK, Das S, Ravi I (2001) Changes in certain antioxidative enzymes and growth parameters as a result of complete submergence and subsequent re-aeration of rice cultivars differing in submergence tolerance. J Agron Crop Sci 187(2):69–74. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1439-037X.2001.00510.x
Sauter M (2000) Rice in deep water: “How to take heed against a sea of troubles”. Naturwissenschaften 87(7):289–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001140050725
Sheikh Mohammadi MH, Etemadi N, Arab MM, Aalifar M, Arab M, Pessarakli M (2017) Molecular and physiological responses of Iranian perennial ryegrass as affected by trinexapac ethyl, paclobutrazol and abscisic acid under drought stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 111:129–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.11.014
Singh S, Mackill DJ, Ismail AM (2009) Responses of SUB1 rice introgression lines to submergence in the field: yield and grain quality. Field Crops Res 113(1):12–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2009.04.003
Singh S, Mackill DJ, Ismail AM (2014) Physiological basis of tolerance to complete submergence in rice involves genetic factors in addition to the SUB1 gene. AoB Plants 6:plu060. https://doi.org/10.1093/aobpla/plu060
Stamm P, Kumar PP (2010) The phytohormone signal network regulating elongation growth during shade avoidance. J Exp Bot 61(11):2889. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq147
Steffens B, Sauter M (2014) Role of ethylene and other plant hormones in orchestrating the responses to low oxygen conditions. In: van Dongen JT, Licausi F (eds) Low-oxygen stress in plants: oxygen sensing and adaptive responses to hypoxia. Springer, Vienna, pp 117–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-1254-0_7
Tognetti VB, Bielach A, Hrtyan M (2017) Redox regulation at the site of primary growth: auxin, cytokinin and ROS crosstalk. Plant Cell Environ 40(11):2586–2605. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13021
Van ZM, Voesenek LA, Peeters AJ, Millenaar FF (2009) Hormone- and light-mediated regulation of heat-induced differential petiole growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 151(3):1446–1458. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.144386
van Veen H, Vashisht D, Voesenek LACJ, Sasidharan R (2014) Different survival strategies amongst plants to cope with underwater conditions. In: van Dongen JT, Licausi F (eds) Low-oxygen stress in plants: oxygen sensing and adaptive responses to hypoxia. Springer, Vienna, pp 329–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-1254-0_17
Vashisht D, Hesselink A, Pierik R, Ammerlaan JMH, Bailey-Serres J, Visser EJW, Pedersen O, Zanten MV, Vreugdenhil D, Jamar DCL (2011) Natural variation of submergence tolerance among Arabidopsis thaliana accessions. New Phytol 190(2):299–310. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03552.x
Voesenek LACJ, Rijnders JHGM, Peeters AJM, Van de Steeg HMV, De Kroon H (2004) Plant hormones regulate fast shoot elongation under water: from genes to communities. Ecology 85(1):16–27. https://doi.org/10.1890/02-740
Vreeburg RAM, Benschop JJ, Peeters AJM, Colmer TD, Ammerlaan AHM, Staal M, Elzenga TM, Staals RHJ, Darley CP, Mcqueen-Mason SJ (2005) Ethylene regulates fast apoplastic acidification and expansin A transcription during submergence-induced petiole elongation in Rumex palustris. Plant J Cell Mol Biol 43(4):597–610. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02477.x
Vriezen WH, Zhou Z, Van Der Straeten D (2003) Regulation of submergence-induced enhanced shoot elongation in Oryza sativa L. Ann Bot 91(2):263–270. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcf121
Weiler EW, Jourdan PS, Conrad W (1981) Levels of indole-3-acetic acid in intact and decapitated coleoptiles as determined by a specific and highly sensitive solid-phase enzyme immunoassay. Planta 153(6):561–571. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00385542
Wu H, Xiang J, Chen HZ, Zhang YP, Zhang YK, Zhu DF (2018) Effects of exogenous growth regulators on plant elongation and carbohydrate consumption of rice seedlings under submergence. Chin J Appl Ecol 29(1):149–157
Xiang J, Chen H, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Zhu D (2016) Morphological and physiological responses of rice seedlings to water temperature under complete submergence. Chin J Rice Sci 30(5):525–531. https://doi.org/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2016.5183
Xiang J, Wu H, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Li Z, Lin H, Chen H, Zhang J, Zhu D (2017) Transcriptomic analysis of gibberellin- and paclobutrazol-treated rice seedlings under submergence. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102225
Xu K, Xu X, Fukao T, Canlas P, Maghirang-Rodriguez R, Heuer S, Ismail AM, Bailey-Serres J, Ronald PC, Mackill DJ (2006) Sub1A is an ethylene-response-factor-like gene that confers submergence tolerance to rice. Nature 442(7103):705–708. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04920
Yang J, Zhang J, Wang Z, Zhu Q, Wang W (2001) Hormonal changes in the grains of rice subjected to water stress during grain filling. Plant Physiol 127(1):315–323. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.127.1.315
Zhang J, Toai TV, Huynh L, Preiszner J (2000) Development of flooding-tolerant Arabidopsis thaliana by autoregulated cytokinin production. Mol Breed 6(2):135–144. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009694029297
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31501272), Agricultural Sciences and Technologies Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) to Rice High Efficiency cultivation technology Group, and Special Fund for Agroscientific Research in the Public Interest (Grant No. 2101203032). We thank Robbie Lewis, MSc, from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Group China (http://www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.Wu, J.Xiang. and D.H.Zhu. conceived the project, designed and coordinated the experiments, H.Wu, J.Xiang. H.Z.Chen, Y.P.Zhang, and Y.K.Zhang performed the physiological experiments and analysed the data, H.Wu and J.Xiang wrote the manuscript. J.Xiang and Y.P.Zhang completed qRT-PCR tests, data analysis and paper revision. All author read the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of competing financial and non-financial interests, or other interests that might be perceived to influence the results and/or discussion reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, H., Chen, H., Zhang, Y. et al. Effects of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate and paclobutrazol on the endogenous hormones of two contrasting rice varieties under submergence stress. Plant Growth Regul 87, 109–121 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-018-0457-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-018-0457-6