Abstract
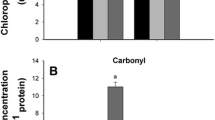
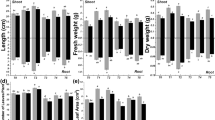
The aim of this research was to study the responses of two lines of Medicago ciliaris: TN11.11 and TN8.7 to iron deficiency under saline conditions. However; the paper showed also the results of a preliminary study which report the contrastive responses of the two lines to salinity. We found that plant growth and chlorophyll content of TN11.11 line were more affected by salinity than TN8.7. The severity of symptoms was linked to the sodium accumulation in shoots as well as a limitation of potassium uptake. Our data allowed us to note that TN8.7 line is less sensitive and can better cope with the salinity. Concerning the effect of salinity on iron deficiency responses, we noted that root PM H+-ATPase and FCR activities were reduced when iron deficiency was associated with salinity. This probably explained the decrease of Fe uptake. On the contrary, PEPC activity was not affected.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BPDS:
-
4,7-diphenyl-1-10-phenanthroline disulfonique acidwissa
- FCR:
-
Fe (III)-chelates reductase
- MDH:
-
Malate dehydrogenase
- PEPC:
-
Phosphoénolpyruvatecarboxylase
- PM H+-ATPase:
-
Plasma membrane H+-ATPase
References
Alpaslan M, Gunes A, Taban S, Erdal I, Tarakcioglu C (1998) Variations in calcium, phosphorus, iron, copper, zinc and manganesecontents of wheat and rice varieties under salt stress. Turk J Agric For 22:227–233
Ashraf M (1994) Breeding for salinity tolerance in plant. Crit Rev Plant Sci 13:17–42
Ashraf M, Harris PJC (2004) Potential biochemical indicators of salinity tolerance in plants. Plant Sci 166:3–16
Azooz MM, Shaddad MA, Abdel-latef AA (2004) The accumulation and compartmentation of praline in relation to salt tolerance of three sorghum cultivars. Ind J plant physiol 9:1–8
Bhivare VN, Nimbalkar JD (1984) Salt stress effects on growth and mineral nutrition of French beans. Plant Soil 80:91–98
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantization of micrograms quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cheruth AJ, Ragupathi G, Muthiah G, Rajaram P (2008) Effects of calcium chloride on metabolism of salt-stressed Dioscorea rotundata. Acta Biol Crac 50:63–67
Crespo D (1987) A survey of the types of legumes suitable for animal production in the Mediterranean regions. In: Proceedings of an international workshop on legume genetic resources for semi-arid temperate environment Smith A and Robertson L (eds) ICARDA, Aleppo, pp 258–280
De Nisi P, Zocchi G (2000) Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in cucumber (cucumis sativus L.) roots under iron deficiency: activity and kinetic characterization. J Exp Bot 352:1903–1909
Dell’Orto M, Brancadoro L, Scienza A, Zocchi G (2000) Use of biochemical parameters to select grapevine genotypes resistant to iron-chlorosis. J Plant Nutr 23:1767–1775
Grusak MA (1995) Whole-root iron (III)-reductase activity the life cycle of iron grown Pisum sativum L. (Fabaceae): relevance to the iron nutrition of developing seeds. Planta 197:111–117
Hassidim M, Braun Y, Lerner MR, Reinhold L (1986) Studies on H+- translocating ATPases in plants of varing resistance to salinity. II. K+ strongly promotes development of membrane potential in vesicles from cotton roots. Plant Physiol 81:1057–1061
Houshmand S, Arzani A, Maibody SAM, Feizi M (2005) Evaluation of salt-tolerant genotypes of durum wheat derived from in vitro and field experiments. Field Crops Res 91:345–354
Khan MA, Ungar IA, Showalter AM (2000) Effects of salinity on growth, water relations and ion accumulation in the subtropical perennial halophyte, Atriplex griffithii var stocksii. Ann Bot 85:225–232
Khosravinejad F, Heydari R, Farboodnia T (2008) Effects of salinity on photosynthetic pigments, respiration and water content in two barley varieties. Pak J Biol Sci 11:2438–2442
Koyro HW, Huchzemeyer B (1999) Salt and drought stress effects on metabolic regulation in maize. In: Pessarakli (ed), Handbook pf plant and crop stress, New York, pp 843–879
Levitt J (1986) Responses of plants to environmental stresses. Academic Press, Nerw York
M’sehli W, Youssfi S, Donnini S, Dell’Orto M, De Nisi P, Abdelly C, Gharsalli M (2008) Root exudation and rhizosphere acidification by two lines of Medicago ciliaris in response to lime-induced iron deficiency. Plant Soil 312:151–162
M’sehli W, Dell’Orto M, De Nisi P, Donnini S, Abdelly C, Zocchi G, Gharsalli M (2009a) a) Responses of two ecotypes of Medicago ciliaris to direct and bicarbonate-induced iron deficiency conditions. Acta Physiol. Plantarum 31:667–673
M’sehli W, Dell’Orto M, Donnini S, De Nisi P, Zocchi G, Abdelly C, Gharsalli M (2009b) b) Variability of metabolic responses and antioxidant defence in two lines of Medicago ciliaris to Fe defeciency. Plant Soil 320:219–230
Maas EV, Ogata G, Garber MJ (1972) Influence of salinity on Fe, Mn and Zn uptake by plants. Agron 64:793–795
Munns R, Jannes RA, Lauchli A (2006) Approaches to increasing the salt tolerance of wheat and other cereals. J Exp Bot 57:1025–1043
Nakamura Y, Kasamo K, Shimosato N, Sakata M, Ohta E (1992) Stimulation of the extrusion of protons and H + -ATPase activities with the decline in pyrophosphate activity of the tonoplast in intact mung bean roots under high salt stress and its relation to external levels of Ca2+ ions. Plant Cell Physiol 33:139–149
Olmos E, Pigueras A, Hellin E (1993) Changes in plasma membrane ATPase activity related with salt tolerance in cells of Pisum sativum. Plant Physiol 24:174–183
Papastylianou I (1990) The role of Legumes in the farming systems of Cyprus. In: Osman AE, Ibrahim MH, Jones Kluwer MA (eds) The role of Legumes in the farming systems of the Mediterranean areas. Academic Publishers, London, pp 39–48
Qureshi RH, Rashid A, Ahmed N (1990) A procedure for quick screening of wheat cultivars for salt tolerance. In: Bassam NEI, Damborth M, Laughman BC (eds) Genetic aspects of plant mineral nutrition. Kluwer Academic Publisher, The Netherlands, pp 315–324
Rabhi M, Barhoumi Z, Ksouri R, Abdelly C, Gharsalli M (2007) Interactive effects of salinity and iron deficiency in Medicago ciliaris. C R Biol 330:779–788
Römheld V, Marschner H (1986) Mobilization of iron in the rhizosphere of different plant species. Adv Plant Nutr 2:155–204
Schachtman DP, Munns R (1992) Sodium accumulation in leaves of Triticum species that differ in salt tolerance. Aust J Plant Physiol 9:331–340
Serrano R, Mulet JM, Rios G, Marquez JA, De Larriona IF et al (1999) Glimpse of the mechanisms of ion homeostasis during salt stress. J Exp Bot 50:1023–1036
Shiyab S, Shibli R, Mohammad M (2003) Influence of sodium chloride salt stress on growth and nutrient acquisition of sour orange in vitro. J Plant Nutr 26:985–996
Shrivastava N, Sharma V (1998) Effect of salinity on growth, Na+, Cl- ion content and membrane ATPases in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 25:83–88
Torrecillas A, Léon A, Del Amor F, Martinez-Mompean MC (1984) Rapid determination of chlorophyll. Fruits 39:617–622
Turan MA, Elkarim AHA, Taban N, Taban S (2010) Effect of salt on growth and ion distribution and accumulation in shoot and root of maize plant. Afr J Agric Res 23:584–588
Yousfi S, M’sehli W, Mahmoudi H, Abdelly C, Gharsalli M (2007) Effect of salt on physiological responses of barley to iron deficiency. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:309–314
Yu BJ, Gong HM, Liu YL (1999) Effects of exogenous fatty acids on H+-ATPase activity and lipid composition of plasma membrane vesicles isolated from roots of barley seedlings under salt stress. J Plant Physiol 155:646–651
Zocchi G (1988) Separation of membrane vesicles from maize roots having different calcium transport activities. Plant Sc. Letters 54:103–107
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education, Scientific Research and Technology (LR02CB02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
M’sehli, W., Jellali, N., Dell’Orto, M. et al. Responses of two lines of Medicago ciliaris to Fe deficiency under saline conditions. Plant Growth Regul 64, 221–230 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-010-9561-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-010-9561-y