Abstract
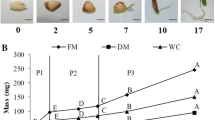
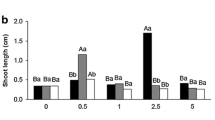
The aim of this work was to study morphological and biochemical aspects during zygotic embryogenesis in O. catharinensis, by measuring changes in the endogenous concentrations of proteins, amino acids, polyamines (PAs), indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) and abscisic acid (ABA). Buffer-soluble and insoluble protein contents were determined by spectrometry, and amino acids, PAs, IAA and ABA concentrations were determined by high performance liquid chromatography. Total amino acid accumulation, predominantly asparagine, occurred when the embryo showed completely developed cotyledons, with posterior reduction in the mature embryo. This decrease in total amino acid concentration in the mature embryo may result from their use in storage␣as well as for LEA protein synthesis. Free putrescine (Put) concentration decreased, while free spermine (Spm) increased during embryo development. This suggest a role for Put in the initial phases of embryogenesis when high rates of cell division occur, while elevated concentration of Spm are essential from the middle to the end of embryo development, when growth is mainly due to cell elongation. An IAA peak in zygotic embryos occurred during initial development, suggesting a link between growth and cellular division as well as with the establishment of bilateral symmetry. ABA concentration declined during initial stages of development then increased at the mature embryo stage, suggesting a possible relationship with dormancy and recalcitrance characteristics. Our results show that changes in the phytohormones (IAA, ABA and PAs) concentrations in combination with amino acids are likely important factors determining the developmental stages of O.␣catharinensis zygotic embryos.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IAA:
-
Indole-3-acetic acid
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- FM:
-
Fresh matter
- Gaba:
-
γ-Aminobutyric acid
- HPLC:
-
High performance liquid chromatography
- PAs:
-
Polyamines
- Put:
-
Putrescine
- Spd:
-
Spermidine
- Spm:
-
Spermine
References
Astarita LV, Floh EIS, Handro W (2003a) Changes in IAA, tryptophan and activity of soluble peroxidase associated with zygotic embryogenesis in Araucaria angustifolia (Brazilian pine). Plant Growth Regul 39:113–118
Astarita LV, Floh EIS, Handro W (2003b) Free amino acids, protein and water content changes associated with seed development in Araucaria angustifolia. Biol Plantarum 47:53–59
Astarita LV, Handro W, Floh EIS (2003c) Changes in polyamines content associated with zygotic embryogenesis in the Brazilian pine, Araucaria angustifolia (Bert.) O. Ktze Rev Bras Bot 26:163–168
Bais HP, Ravishankar GA (2002) Role of polyamines in the ontogeny of plants and their biotechnological applications. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 69:1–34
Berjak P, Pammenter NW (2001) Seed recalcitrance— current perspectives. South Afri J Bot 67:79–89
Bewley JD, Black M (1994) Seeds: physiology of development and germination, 2nd edn. Plenum Publishing, New York, 445 pp
Bouchereau A, Aziz A, Larher F, Martin-Tanguy J (1999) Polyamines and environmental challenges: recent development. Plant Sci 140:103–125
Bradford MB (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the␣quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chatthai M, Misra S (1998) Sequence and expression of embryogenesis-specific cDNAs encoding 2S seed storage proteins in Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirb). Franco Planta 206:138–145
Chiwocha S, von Aderkas P (2002) Endogenous levels of free and conjugated forms of auxin, cytokinins and abscisic acid during seed development in Douglas fir. Plant Growth Regul 36:191–200
Dal Vesco LL, Guerra MP (2001) The effectiveness of nitrogen sources in Feijoa somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 64:19–25
Danin M, Upfold SJ, Levin N, Nadel BL, Altman A, van Staden J (1993) Polyamines and cytokinins in celery embryogenic cell cultures. Plant Growth Regul 12:245–254
Dodeman VL, Ducreux G, Kreis M (1997) Zygotic embryogenesis versus somatic embryogenesis. J Exp Bot 48(313):1493–1509
Faure O, Dewitte W, Nougarède A, Van Ockelen H (1998) Precociously germinating somatic embryos of Vitis vinifera have lower ABA and IAA levels than their germinating zygotic counterparts. Physiol Plantarum 102:591–595
Faure O, Mengoli M, Nougarede A, Bagni N (1991) Polyamine pattern and biosynthesis in zygotic and somatic embryo stages of Vitis vinifera. J. Plant Physiol 138:545–549
Feirer RP (1995) The biochemistry of conifer embryo development: amino acids, polyamines, and storage proteins. In: Jain SM, Gupta PK, Newton RJ (eds) Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants, vol. 1. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 317–336
Finch-Savage WE, Clay HA (1994) Evidence that ethylene, light and abscisic acid interact to inhibit germination in the recalcitrant seeds of Quercus robur L.␣J␣Exp Bot 45:1295–1299
Fischer C, Neuhaus G (1996) Influence of auxin on the establishment of bilateral symmetry in monocots. Plant J 9:659–669
Garin E, Demarch GG, Grenier E, Martintanguy J (1995) Polyamine changes during the development of zygotic embryos in Prunus avium: effects of a 2,4-D and kinetin treatment on growth and polyamine levels in cotyledons cultivated in vitro. Plant Growth Regul 16:279–286
Jürgens G (1996) Cell division and morphogenesis in angiosperm embryogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol 7:867–872
Kakkar RK, Nagar PK, Ahuja PS, Rai VK (2000) Polyamines and plant morphogenesis. Physiol Plantarum 43:1–11
Kamada H, Harada H (1984) Changes in endogenous amino acids compositions during somatic embryogenesis in Daucus carota L. Plant Cell Physiol 25:27–38
Kong L, Attree SM, Fowke LC (1997) Changes of endogenous hormone levels in developing seeds, zygotic embryos and megagametophytes in Picea glauca. Physiol Plantarum 101:23–30
Kong L, Attree SM, Fowke LC (1998) Effects of polyethylene glycol and methylglyoxal bis(guanylhydrazone) on endogenous polyamine levels and somatic embryo maturation in white spruce (Picea glauca). Plant Sci 133:211–220
Lam H-M, Coschigano K, Schultz C, Melo-Oliveira R, Tjaden G, Oliveira I, Ngai N, Hsieh M-H, Coruzzi G (1995) Use of Arabidopsis mutants and genes to study amide amino acid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 7:887–898
Lea PJ (1993) Nitrogen metabolism. In: Lea PJ, Leegood RC (eds) Plant biochemistry and molecular biology. Wiley & Sons, New York, pp 155–180
Lea PJ, Robinson SA, Stewart GR (1989) The use of mutants lacking glutamine synthetase and glutamate synthetase to study their role in plant nitrogen metabolism. In: Poulton JE, Romeo JT, Conn EE (eds) Recent advances in phytochemistriy. Plenum Press, New York, pp 569–607
Lin T-P, Chen M-H (1995) Biochemical characteristics associated with the development of the desiccation-sensitive seeds of Machilus thunbergii. Sieb Zucc Ann Bot 76:381–387
Liu Z-H, Wang W-C, Chua N-H (1993) Auxin polar transport is essential for the establishment of bilateral symmetry during early plant embryogenesis. Plant Cell 5:621–630
Macnicol PK (1983) Developmental changes in the free amino acid pool and total protein amino acids of pea␣cotyledons (Pisum sativum L.). Plant Physiol 72:492–497
Marion-Poll A (1997) ABA and seed development. Trends Plant Sci 2:447–448
Merkle SA, Parrot WA, Flinn BS (1995) Morphogenic aspects of somatic embryogenesis. In: Thope TA (eds) In vitro embryogenesis in plants. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 155–203
Michalczuck L, Cooke TD, Cohen JD (1992) Auxin levels at different stages of carrot somatic embryogenesis. Phytochemistry 4:1097–1103
Minocha R, Smith DR, Reeves C, Steele KD, Minocha SC (1999) Polyamine levels during the development of zygotic and somatic embryos of Pinus radiata. Physiol Plantarum 105:155–164
Mordhorst AP, Toonen MAJ, De Vries SC (1997) Plant embryogenesis. Crit Rev Plant Sci 16:535–576
Moura-Costa PH, Viana AM, Mantell SH (1993) In vitro plantlet regeneration of Ocotea catharinensis, an endangered Brasilian hardwood forest tree of S.␣Brazil. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 35:279–286
Prewein C, Endemann M, Reinöhl V, Salaj J, Sunderlikova V, Wihelm E (2006) Physiological and morphological characteristics during development of pedunculate oak (Quercus robur L.) zygotic embryos Trees 20:53–60
Puga-Hermida MI, Gallardo M, Matilla AJ (2003) The zygotic embryogenesis and ripening Brassica rapa sedes provokes important alterations in the levels of free and conjugated abscisic acid and polyamines. Physiol Plantarum 117:279–288
Radwanski ER, Last RL (1995) Tryptophan biosynthesis and metabolism: biochemical and molecular genetics. Plant Cell 7:921–934
Rock CD, Quatrano RS (1995) The role of hormones during seed development. In: Davies PJ (eds) Plant hormones: physiology, biochemistry and molecular biology, 2nd edn. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 671–697
Sallandrouze A, Faurobert M, Maâtaoui ME (2002) Characterization of the development tages of cypress zygotic embryos by two-dimensional electrophoresis and by cytochemistry. Physiol Plantarum 114:608–618
Santa-Catarina C, Meyer G de A, Macedo J, de Amorim W, Viana AM (2004) Repetitive somatic embryogenesis of Ocotea catharinensis Mez. (Lauraceae): effect of embryoid development stage, activated charcoal and dehydration. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 78:55–62
Santa-Catarina C, Randi ÁM, Viana AM (2003) Growth and accumulation of storage reserves by somatic embryos of Ocotea catharinensis Mez. (Lauraceae). Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 74:67–71
Santa-Catarina C, Moser JR, Bouson ZL, Floh EIS, Maraschin M, Viana AM (2005) Protocol of somatic embryogenesis: Ocotea catharinensis Mez (Lauraceae). In: Jain SM, Gupta PK (eds) Protocol for somatic embryogenesis in woody plants. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 427–443
Satya-Naraian V, Nair PM (1990) Metabolism, enzymology and possible roles of 4-aminobutyrate in higher plants. Phytochemistry 29:367–375
Shoeb F, Yadav JS, Bajaj S, Rajam MV (2001) Polyamines as biomarkers for plant regeneration capacity: improvement of regeneration by modulation of polyamine metabolism in different genotypes of indica rice. Plant Sci 160:1229–1235
Silveira V, Balbuena TS, Santa-Catarina C, Floh EIS, Guerra MP, Handro W (2004a) Biochemical changes during zygotic embryogenesis in Pinus taeda L. Plant Growth Regul 44:147–156
Silveira V, Floh EIS, Handro W, Guerra MP (2004b) Effect of plant growth regulators on the cellular growth and levels of intracellular protein, starch and polyamines in embryogenic suspension cultures of Pinus taeda. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 76:53–60
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1995) Biometry, 3rd edn. Freeman and Co, New York, 957 pp
Stone SL, Gifford DJ (1997) Structural and biochemical changes in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) seeds during germination and early-seedling growth. I. Storage protein reserves. Int J Plant Sci 158:727–737
Suhasini K, Sagare AP, Sainkar SR, Krishnamurthy KV (1997) Comparative study of the development of zygotic and somatic embryos of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Plant Sci 128:207–216
Viana AM (1998) Somatic embryogenesis in Ocotea catharinensis Mez (Lauraceae). In: Mantell SH, Bruns S, Tragardh C, Viana AM (eds) Recent advances in biotechnology for conservation and management. International Foundation for Science, Stockholm, pp␣244–253
Viana AM, Mantell H (1999) Somatic embryogenesis of Ocotea catharinensis: an endangered tree of the Mata Atlântica (S. Brazil). In: Jain S, Gupta P, Newton R (eds) Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants, vol. 5. Kluwer Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 3–30
von Wettstein D, Gough S, Kannangara CG (1995) Chlorophyll biosynthesis. Plant Cell 7:1039–1057
Walden R, Cordeiro A, Tiburcio AF (1997) Polyamines: small molecules triggering pathways in plant growth and development. Plant Physiol 113:1009–1013
Weber H, Borisjuk L, Wobus W (1997) Sugar import and metabolism during seed development. Trends Plant Sci 2:169–174
Wise JM, Tunnacliffe A (2004) POPP the question: what do LEA proteins do? Trends Plant Sci 9:13–17
Acknowledgements
This research was carried out with financial support from the State of São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) and the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq). The authors thank M.Sc. Antônio da Silva and Instituto Florestal of São Paulo for providing O. catharinensis fruits.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santa-Catarina, C., Silveira, V., Balbuena, T.S. et al. IAA, ABA, polyamines and free amino acids associated with zygotic embryo development of Ocotea catharinensis . Plant Growth Regul 49, 237–247 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-006-9129-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-006-9129-z