Abstract
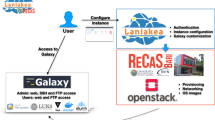
Driven by advances in data generation technologies and fuelled by radical reduction in costs, genomics has become a data science. Nonetheless the field of genomics has been restrained by the ability to analyse data. Science gateways, such as Galaxy, have the potential to enable bench biologists to analyse their own data without needing be familiar with the command line. Implementing a production scale Galaxy service, sufficiently well-featured and resourced to meet the needs of the end-users, is a significant undertaking and requires the consideration and combination of a number of factors to be successfully adopted by the community. In this paper, we describe the process that we undertook to implement a Galaxy service and describe what we consider to be the essential components of such a service. Our experience and insights will be of interest to those who are planning on implementing a science gateway service in a research organisation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, J., Pacitti, E., Valduriez, P., Mattoso, M.: A Survey of Data-Intensive Scientific Workflow Management. J. Grid Comput. 13, 457 (2015). doi:10.1007/s10723-015-9329-8
Emeakaroha, V. C., Maurer, M., Stern, P., ŁAbaj, P.P., Brandic, I., Kreil, D.P.: Managing and optimizing bioinformatics workflows for data analysis in clouds. J. Grid Comput. 11, 407 (2013). doi:10.1007/s10723-013-9260-9
Le Blanc, A., Brooke, J., Fellows, D., Soldati, M., Pérez-Suárez, D., Marassi, A., Santin, A.: Workflows for heliophysics. J. Grid Comput. 11, 481 (2013). doi:10.1007/s10723-013-9256-5
Gugnani, S., Blanco, C., Kiss, T., Terstyanszky, G.: Extending Science Gateway Frameworks to Support Big Data Applications in the Cloud J Grid Computing (2016). doi:10.1007/s10723-016-9369-8
Goecks, J., Nekrutenko, A., Taylor, J.: and The Galaxy Team. Galaxy: a comprehensive approach for supporting accessible, reproducible, and transparent computational research in the life sciences. Genome Biol. 11(8), R86 (2010)
Blankenberg, D., Von Kuster, G., Coraor, N., Ananda, G., Lazarus, R., Mangan, M., Nekrutenko, A., Taylor, J.: Galaxy: a web-based genome analysis tool for experimentalists, vol. 19. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology (2010)
Giardine, B., Riemer, C., Hardison, R. C., Burhans, R., Elnitski, L., Shah, P., Zhang, Y., Blankenberg, D., Albert, I., Taylor, J., Miller, W., Kent, W. J., Nekrutenko, A.: Galaxy: a platform for interactive large-scale genome analysis. Genome Res. 15(10), 1451–5 (2005)
Oakley, T. H., Alexandrou, M. A., Ngo, R., Pankey, M. S., Churchill, C. K., Chen, W., Lopker, K. B.: Osiris: accessible and reproducible phylogenetic and phylogenomic analyses within the Galaxy workflow management system. BMC Bioinform. 15, 230 (2014). doi:10.1186/1471-2105-15-230
Bedoya-Reina, O. C., Ratan, A., Burhans, R., Kim, H. L., Giardine, B., Riemer, C., Li, Q., Olson, T. L., Loughran, T. P. Jr., Vonholdt, B. M., Perry, G. H., Schuster, S. C., Miller, W.: Galaxy tools to study genome diversity. Gigascience 2(1), 17 (2013). doi:10.1186/2047-217X-2-17
Blankenberg, D., Johnson, J.: The Galaxy Team, Taylor, J. Nekrutenko, A. Wrangling Galaxy’s reference data. Bioinformatics 30(13), 1917–1919 (2014)
Blankenberg, D., Von Kuster, G., Bouvier, E., Baker, D., Afgan, E., Stoler, N.: the Galaxy Team, Taylor, J., Nekrutenko, A. Dissemination of scientific software with Galaxy ToolShed. Genome Biol. 15, 403 (2014). doi:10.1186/gb4161
Hook, S.E., Johnston, E.L., Nair, S., Roach, A.C., Moncuquet, P., Twine, N.A., Raftos, D.A.: Next generation sequence analysis of the transcriptome of Sydney rock oysters (Saccostrea glomerata) exposed to a range of environmental stressors. Mar. Genomics 18, B:109–11 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.margen.2014.08.003
Hook, S. E., Twine, N. A., Simpson, S. L., Spadaro, D. A., Moncuquet, P., Wilkins, M.R.: 454 pyrosequencing-based analysis of gene expression profiles in the amphipod Melita plumulosa: transcriptome assembly and toxicant induced changes. Aquat. Toxicol. 153, 73–88 (2014 Aug). doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.11.022
Hook, S.E., Osborn, H.L., Gissi, F., Moncuquet, P., Twine, N.A., Wilkins, M.R., Adams, M.S.: RNA-Seq analysis of the toxicant-induced transcriptome of the marine diatom, Ceratoneis closterium. Mar. Genomics 16, 45–53 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.margen.2013.12.004
Bragg, L., Stone, G., Imelfort, M., Hugenholtz, P., Tyson, G. W.: Fast, accurate error-correction of amplicon pyrosequences using Acacia. Nat. Methods 9(5), 425–6 (2012). doi:10.1038/nmeth.1990
Greenfield, P., Duesing, K., Papanicolaou, A., Bauer, D. C.: Blue: correcting sequencing errors using consensus and context. Bioinformatics 30(19), 2723–32 (2014). doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu368
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McGrath, A., McMahon, S., Li, S. et al. The Essential Components of a Successful Galaxy Service. J Grid Computing 14, 533–543 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-016-9379-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-016-9379-6