Abstract
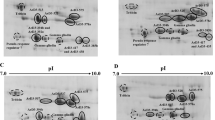
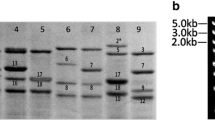
The low molecular weight glutenin subunits (LMW-GS) are the major components of glutenins and are important for the end-use quality of wheat. Five novel LMW-GS genes (designated as LMW-Jiachazharen, LMW-Bangdadongmai-3, LMW-Jiachaaigan, LMW-Maoyintumai and LMW-Rikezehongmai) were isolated from Tibetan wheat landraces. The coding regions of LMW-Jiachazharen, LMW-Bangdadongmai-3, LMW-Jiachaaigan, LMW-Maoyintumai and LMW-Rikezehongmai were 912, 897, 915, 927 and 906 bp in length, which encoded 302, 297, 303, 307 and 300 amino acid residues, respectively. Analysis of the deduced amino acid sequences showed that the five novel genes were classified as LMW-m type, with the predicted molecular weights of 32,013.97, 31,622.89, 32,107.07, 32,939.41 and 31,731.64 Da, respectively. The LMW-Jiachazharen, LMW-Jiachaaigan, LMW-Maoyintumai possessed seven cysteine residues, which resulted from a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of the G–A transition. However, except for eight conserved cysteine residues, LMW-Bangdadongmai-3 contained an extra one, as the result of a SNP of the T–C transition. In addition, the corresponding five LMW-GS were identified and confirmed by sodium SDS-PAGE and MALDI-TOF-MS, respectively. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that the five novel genes were glutenin-like proteins and designated as LMW-m type genes. The five novel genes may be new candidate LMW-GS genes with potential value for wheat quality improvement.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
An X, Zhang Q, Yan Y, Li Q, Zhang Y, Wang A, Pei Y, Tian J, Wang H, Hsam SLK, Zeller FJ (2006) Cloning and molecular characterization of three novel LMW-i glutenin subunit genes from cultivated einkorn (Triticum monococcum L.). Theor Appl Genet 113:383–395
Bietz JA, Shepherd KW, Wall JS (1975) Single kernel analysis of glutenin: use in wheat genetics and breeding. Cereal Chem 52:513–532
Cassidy BG, Dvorak J, Anderson OD (1998) The wheat low-molecular-weight glutenin genes: characterization of six new genes and progress in understanding gene family structure. Theor Appl Genet 96:743–750
Chen F, Liu S, Zhao F, Xu C, Xia G (2010) Molecular characterisation of the low-molecular weight glutenin subunit genes of tall wheatgrass and functional properties of one clone Ee34. Amino Acids 38:991–999
D’Ovidio R, Masci S (2004) The low-molecular-weight glutenin subunits of wheat gluten. J Cereal Sci 39:321–339
Feng B, An X, Xu Z, Liu D, Zhang A, Wu N, Wang T (2011) Molecular cloning of a novel chimeric HMW glutenin subunit gene 1Dx5′ from a common wheat line W958. Mol Breed 28:163–170
Gupta RB, Shepherd KW (1990) Two-step one-dimensional SDS-PAGE analysis of LMW subunits of glutenin. Theor Appl Genet 80:65–74
Ikeda TM, Nagamine T, Fukupka H, Yano H (2002) Identification of new low-molecular-weight glutenin subunit genes in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 104:680–687
Ikeda TM, Araki E, Fujita Y, Yano H (2006) Characterization of low-molecular-weight glutenin subunit genes and their protein products in common wheats. Theor Appl Genet 112:327–334
Jackson EA, Holt LM, Payne PI (1983) Characterization of high-molecular-weight gliadin and low-molecular-weight subunits of wheat endosperm by two-dimensional electrophoresis and the chromosomal location of their controlling genes. Theor Appl Genet 66:29–37
Jiang C, Pei Y, Zhang Y, Li X, Yao D, Yan Y, Ma W, Hsam SL, Zeller FJ (2008) Molecular cloning and characterization of four novel LMW glutenin subunit genes from Aegilops longissima, Triticum dicoccoides and T. zhukovskyi. Hereditas 145:92–98
Lauriere M, Bouchez I, Doyen C, Eynard L (1996) Identification of glycosylated forms of wheat storage proteins using two-dimensional electrophoresis and blotting. Electrophoresis 17:497–501
Lew EJL, Kuzmicky DD, Kasarda DD (1992) Characterization of low- molecular-weight glutenin subunits by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography, sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and N-terminal amino-acid sequencing. Cereal Chem 69:508–515
Masci S, D’Ovidio R, Lafiandra D, Kasarda DD (1998) Characterization of a low-molecular-weight glutenin subunit gene from bread wheat and the corresponding protein that represents a major subunit of the glutenin polymer. Plant Physiol 118:1147–1158
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8(19):4321–4325
Payne PI, Law CN, Mudd EE (1980) Control by homoeologous group 1 chromosome of the highmolecular-weight subunits of glutenin, a major protein of wheat endosperm. Theor Appl Genet 58:113–120
Payne PI, Holt LM, Reader SM, Miller TE (1987) Chromosomal location of genes coding for endosperm proteins of Hordeum chilense, determined by two-dimensional electrophoresis of wheat-H. chilense chromosome addition lines. Biochem Genet 25:53–85
Pei YH, Wang AL, An XL, Li XH, Zhang YZ, Huang XQ, Yan YM (2006) Characterization and comparative analysis of three low molecular weight glutenin C-subunit genes isolated from Aegilops tauschii. Can J Plant Sci 87:273–280
Shewry PR, Halford NG, Tatham AS (1992) High molecular weight subunits of wheat glutenin. J Cereal Sci 15:105–120
Yan ZH, Dai SF, Liu DC, Wei YM, Zheng YL (2007) Allelic variation of high molecular weight glutenin subunits in the hexaploid wheat landraces of Tibet, China. Int J Agric Res 2(9):838–843
Zeng XQ, Wang YJ, Li WY, Wang CY, Liu XL, Ji WQ (2010) Comparison of the genetic diversity between Triticum aestivum ssp. tibetanum Shao and Tibetan wheat landraces (Triticum aestivum L.) by using intron-splice junction primers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 57:1141–1150
Zhao HX, Wang RJ, Guo AG (2004) Development of primers specific for LMW-GS genes located on chromosome 1D and molecular characterization of a gene from Glu-D3 complex locus in bread wheat. Hereditas 141:193–198
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Key Project of Transgenic Biologic Varieties Breeding of China (Grant No. 2011ZX08009-003) and the Knowledge Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. KSCX3-EW-N-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, Q., Feng, B., Xu, Z. et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of five novel low molecular weight glutenin subunit genes from Tibetan wheat landraces (Triticum aestivum L.). Genet Resour Crop Evol 60, 799–806 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-012-9877-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-012-9877-8