Abstract
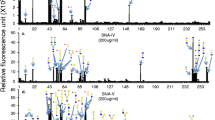
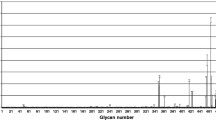
Plant lectins are gaining interest because of their interesting biological properties. Several Adenia species, that are being used in traditional medicine to treat many health ailments have shown presence of lectins or carbohydrate binding proteins. Here, we report the purification, characterization and biological significance of N-Acetyl galactosamine specific lectin from Adenia hondala (AHL) from Passifloraceae family. AHL was purified in a single step by affinity chromatography on asialofetuin Sepharose 4B column, characterized and its fine sugar specificity determined by glycan array analysis. AHL is human blood group non specific and also agglutinates rabbit erythrocytes. AHL is a glycoprotein with 12.5% of the carbohydrate, SDS-PAGE, MALDI-TOF-MS and ESI-MS analysis showed that AHL is a monomer of 31.6 kDa. AHL is devoid of DNase activity unlike other Ribosome inactivating proteins (RIPs). Glycan array analysis of AHL revealed its highest affinity for terminal lactosamine or polylactosamine of N- glycans, known to be over expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and colon cancer. AHL showed strong binding to human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells with MFI of 59.1 expressing these glycans which was effectively blocked by 93.1% by asialofetuin. AHL showed dose and time dependent growth inhibitory effects on HepG2 cells with IC50 of 4.8 μg/ml. AHL can be explored for its clinical potential.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Quattrocchi, U: CRC World Dictionary of Medicinal and Poisonous Plants: Common Names, Scientific Names, Eponyms, Synonyms, and Etymology, 5 Volume Set. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2012)
Polito, L., Bortolotti, M., Maiello, S., Battelli, M.G., Bolognesi, A.: Plants producing ribosome-inactivating proteins in traditional medicine. Molecules. (2016). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111560
Stirpe, F., Battelli, M.G.: Ribosome-inactivating proteins: progress and problems. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63, 1850–1866 (2006)
Shih, N.R., McDonald, K., Jackman, A., Girbes, T., Iglesias, R.: Bifunctional plant defence enzymes with chitinase and ribosome inactivating activities from Trichosanthes kirilowii cell cultures. Plant Sci. 130, 145–150 (1997)
Li, X.D., Chen, W.F., Liu, W.Y., Wang, G.H.: Large-scale preparation of two new ribosome-inactivating proteins-cinnamomin and camphorin from the seeds of Cinnamomum camphora. Protein Expr. Purif. 10, 27–31 (1997)
Roncuzzi, L., Gasperi-Campani, A.: DNA-nuclease activity of the single-chain ribosome-inactivating proteins dianthin 30, saporin 6 and gelonin. FEBS Lett. 392, 16–20 (1996)
Lombard, S., Helmy, M.E., Pieroni, G.: Lipolytic activity of ricin from Ricinus sanguineus and Ricinus communis on neutral lipids. Biochem. J. 358, 773–781 (2001)
Hey, T.D., Hartley, M., Walsh, T.A.: Maize ribosome-inactivating protein (b-32). Homologs in related species, effects on maize ribosomes, and modulation of activity by pro-peptide deletions. Plant Physiol. 107, 1323–1332 (1995)
Reinbothe, S., Reinbothe, C., Lehmann, J., Becker, W., Apel, K., Parthier, B.: JIP60, a methyl jasmonate-induced ribosome-inactivating protein involved in plant stress reactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 91, 7012–7016 (1994)
Stirpe, F., Barbieri, L.: Ribosome-inactivating proteins up to date. FEBS Lett. 195, 1–8 (1986)
Barbieri, L., Ciani, M., Girbes, T., Liu, W.Y., Van Damme, E.J., Peumans, W.J., Stirpe, F.: Enzymatic activity of toxic and non-toxic type 2 ribosome-inactivating proteins. FEBS Lett. 563, 219–222 (2004)
Tomatsu, M., Ohnishi-Kameyama, M., Shibamoto, N.: Aralin, a new cytotoxic protein from Aralia elata, inducing apoptosis in human cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 199, 19–25 (2003)
Pelosi, E., Lubelli, C., Polito, L., Barbieri, L., Bolognesi, A., Stirpe, F.: Ribosome-inactivating proteins and other lectins from Adenia (Passifloraceae). Toxicon. 46, 658–663 (2005)
Nnamani, C.V., Oselebe, H.O., Agbatutu, A.: Assessment of nutritional values of three underutilized indigenous leafy vegetables of Ebonyi State, Nigeria. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 8, 2321–2324 (2009)
Stirpe, F., Bolognesi, A., Bortolotti, M., Farini, V., Lubelli, C., Pelosi, E., Polito, L., Dozza, B., Strocchi, P., Chambery, A., Parente, A., Barbieri, L.: Characterization of highly toxic type 2 ribosome-inactivating proteins from Adenia lanceolata and Adenia stenodactyla (Passifloraceae). Toxicon. 50, 94–105 (2007)
Schrot, J., Weng, A., Melzig, M.F.: Ribosome-inactivating and related proteins. Toxins (Basel). 7, 1556–1615 (2015)
Goldstein, I.J., Hughes, R.C., Monsigny, M., Osawa, T., Sharon, N.: What should be called a lectin? Nature. 285, 66 (1980)
Yuan, Y., Qiu, H., Gao, J., Wang, Z., Liu, C., Liu, Z., Jiang, Z., Li, Y., Wu, S.: Triptolide inhibits MCF-7 and HepG2 cells invasion and migration by inhibiting the synthesis of Polylactosamine chains. J. Anal. Oncol. 5(3), 102–109 (2016)
Srinivasan, N., Bane, S.M., Ahire, S.D., Ingle, A.D., Kalraiya, R.D.: Poly N-acetyllactosamine substitutions on N-and not O-oligosaccharides or Thomsen–Friedenreich antigen facilitate lung specific metastasis of melanoma cells via galectin-3. Glycoconj. J. 26(4), 445–456 (2009)
Miyake, M., Kohno, N., Nudelman, E.D., Hakomori, S.-I.: Human IgG3.Monoclonal Antibody Directed to an Unbranched Repeating Type 2 Chain (Galβ1→4GlcNAcβ1→3Galβ1→4GlcNAcβ1→3Galβ1→R) Which Is Highly Expressed in Colonic and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 49, 5689–5695 (1989)
Spiro, R.G., Bhoyroo, V.D.: Structure of the O-glycosidically linked carbohydrate units of fetuin. J. Biol. Chem. 249, 5704–5717 (1974)
March, S.C., Parikh, I., Cuatrecasas, P.: A simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 60, 149–152 (1974)
Liener, I.E., Hill, E.G.: The effect of heat treatment on the nutritive value and hemagglutinating activity of soybean oil meal. J. Nutr. 49, 609–620 (1953)
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
DuBois, M., Gilles, K.A., Hamilton, J.K., Rebers, P.A., Smith, F.: Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. (1965). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60111a017
Goldman, M.: Fluorescent Antibody Methods. Academic Press, New York (1968)
Duk, M., Lisowska, E., Wu, J.H., Wu, A.M.: The biotin/avidin-mediated microtiter plate lectin assay with the use of chemically modified glycoprotein ligand. Anal. Biochem. 221, 266–272 (1994)
Laemmli, U.K.: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. nature. 227, 680–685 (1970)
Chevallet, M., Luche, S., Rabilloud, T.: Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Nat. Protoc. 1, 1852–1858 (2006)
Zacharius, R.M., Zell, T.E., Morrison, J.H., Woodlock, J.J.: Glycoprotein staining following electrophoresis on acrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 30, 148–152 (1969)
Blixt, O., Head, S., Mondala, T., Scanlan, C., Huflejt, M.E., Alvarez, R., Bryan, M.C., Fazio, F., Calarese, D., Stevens, J.: Printed covalent glycan array for ligand profiling of diverse glycan binding proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101, 17033–17038 (2004)
Shang, C., Van Damme, E.J.: Comparative analysis of carbohydrate binding properties of Sambucus nigra lectins and ribosome-inactivating proteins. Glycoconj. J. 31, 345–354 (2014)
Wu, A.M., Wu, J.H., Singh, T., Lai, L.J., Yang, Z., Herp, A.: Recognition factors of Ricinus communis agglutinin 1 (RCA (1)). Mol. Immunol. 43, 1700–1715 (2006)
Carrillo, C., Cordoba-Diaz, D., Cordoba-Diaz, M., Girbes, T., Jimenez, P.: Effects of temperature, pH and sugar binding on the structures of lectins ebulin f and SELfd. Food Chem. 220, 324–330 (2017)
singh, A.p., Saxena, K.D.: Effect of temperature, pH and denaturing agents on biological activity of MCJ lectin. Chem. Sci. Trans. 2(4), 1508–1512 (2013)
Lyimo, B., Funakuma, N., Minami, Y., Yagi, F.: Characterization of a new alpha-galactosyl-binding lectin from the mushroom Clavaria purpurea. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 76, 336–342 (2012)
Green, E.D., Adelt, G., Baenziger, J.U., Wilson, S., Van Halbeek, H.: The asparagine-linked oligosaccharides on bovine fetuin. Structural analysis of N-glycanase-released oligosaccharides by 500-megahertz 1H NMR spectroscopy. J. Biol. Chem. 263(34), 18253–18268 (1988)
Battelli, M.G., Scicchitano, V., Polito, L., Farini, V., Barbieri, L., Bolognesi, A.: Binding and intracellular routing of the plant-toxic lectins, lanceolin and stenodactylin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1800, 1276–1282 (2010)
Sharma, A., Ng, T.B., Wong, J.H., Lin, P.: Purification and characterization of a lectin from Phaseolus vulgaris cv. (Anasazi beans). J Biomed Biotechnol. 2009, 929568 (2009)
Funding
SRI would like to thank Protein-Glycan Interaction Resource of the CFG (supporting grant R24 GM098791) and the National Center for Functional Glycomics (NCFG) at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School (supporting grant P41 GM103694) for the glycan array analysis of AHL. The work was supported by the funding from University Grant Commission under UPE (F.NO.14 3/2012 (NS/PE) project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: SRI, AHL purification and characterization: MS, cell culture and Flow cytometry: PH and MS, glycan array and analyzed the data: SRI and VRH, DNase activity: KH, ESI/MS: KAS Contributed reagents/ materials/analysis tools: SRI, and BMS. Wrote the paper: SRI, BMS and MS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors don’t have any conflict of interest to declare concerning to the present work.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 295 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, M., Hegde, P., Hiremath, K. et al. Purification, characterization and fine sugar specificity of a N-Acetylgalactosamine specific lectin from Adenia hondala. Glycoconj J 35, 511–523 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-018-9843-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-018-9843-6