Abstract
Modified gravity theories include \(f({\mathbf {R}})\)-gravity models that are usually constrained by the cosmological evolutionary scenario. However, it has been recently shown that they can also be constrained by the signatures of accretion disk around constant Ricci curvature Kerr-\(f({\mathbf { R}}_{0})\) stellar sized black holes. Our aim here is to use another experimental fact, viz., the terrestrial Sagnac delay to constrain the parameters of specific \(f({\mathbf {R }})\)-gravity prescriptions. We shall assume that a Kerr-\(f({\mathbf {R}}_{0})\) solution asymptotically describes Earth’s weak gravity near its surface. In this spacetime, we shall study oppositely directed light beams from source/observer moving on non-geodesic and geodesic circular trajectories and calculate the time gap, when the beams re-unite. We obtain the exact time gap called Sagnac delay in both cases and expand it to show how the flat space value is corrected by the Ricci curvature, the mass and the spin of the gravitating source. Under the assumption that the magnitude of corrections are of the order of residual uncertainties in the delay measurement, we derive the allowed intervals for Ricci curvature. We conclude that the terrestrial Sagnac delay can be used to constrain the parameters of specific \(f({\mathbf {R}})\) prescriptions. Despite using the weak field gravity near Earth’s surface, it turns out that the model parameter ranges still remain the same as those obtained from the strong field accretion disk phenomenon.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
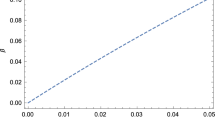
Even if the error residual is a bit higher, it does not significantly alter the limit on \({\mathbf {R}}_{0}\).
We thank an anonymous reviewer for pointing it out to us.
Ruggiero’s notation k is the same as \({\mathbf {R}}_{0}/4\) or \({\varLambda } /2\) in our notation.
References
Capozziello, S., Faraoni, V.: Beyond Einstein Gravity: A Survey of Gravitational Theories for Cosmology and Astrophysics, Fundamental Theories of Physics, vol. 170. Springer, New York (2011)
Pérez, D., Romero, G.E., Perez Bergliaffa, S.E.: Accretion disks around black holes in modified strong gravity. Astron. Astrophys. 551, A4 (2013)
Cembranos, J.A.R., de la Cruz-Dombriz, A., Jimeno Romero, P.: Kerr-Newman black holes in \(f(R)\) theories. Int. J. Geom. Methods Mod. Phys. 11, 1450001 (2014)
Carter, B.: Black hole equilibrium states, part I analytic and geometric properties of the Kerr solutions. In: DeWitt, C., DeWitt, B. (eds.) Black holes—les Astres Occlus, pp. 61–124. Gordon and Breach, New York (1973)
Hafele, J.C., Keating, R.E.: Around-the-world atomic clocks: predicted relativistic time gains. Science 177, 166 (1972)
Hafele, J.C., Keating, R.E.: Around-the-world atomic clocks: observed relativistic time gains. Science 177, 168 (1972)
Schlegel, R.: Phsyical sciences: flying clocks and the Sagnac effect. Nature (London) 242, 180 (1973)
Allan, D.W., Weiss, M.A., Ashby, N.: Around-the-world relativistic Sagnac experiment. Science 228, 69 (1985)
Bhadra, A., Nayak, T.B., Nandi, K.K.: String corrections to the Sagnac effect. Phys. Lett. A 295, 1 (2002)
Nandi, K.K., Alsing, P.M., Evans, J.C., Nayak, T.B.: Brans–Dicke corrections to the gravitational Sagnac effect. Phys. Rev. D 63, 084027 (2001)
Ashtekar, A., Magnon, A.: The Sagnac effect in general relativity. J. Math. Phys. 16, 341 (1975)
Tartaglia, A.: General relativistic corrections to the Sagnac effect. Phys. Rev. D 58, 064009 (1998)
Sultana, J.: The Sagnac effect in conformal Weyl gravity. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 46, 1710 (2014)
Mashhoon, B.: On the gravitational analogue of Larmor’s theorem. Phys. Lett. A 173, 347 (1993)
Aharonov, Y., Bohm, D.: Significance of electromagnetic potentials in the quantum theory. Phys. Rev. 115, 485 (1959)
Semon, M.D.: Experimental verification of an Aharonov–Bohm effect in rotating reference frames. Found. Phys. 12, 49 (1982)
Ruggiero, M.L.: Gravito-electromagnetic Aharonov–Bohm effect: some rotation effects revised. Nuovo Cim. B 119, 893 (2004)
Sakurai, J.J.: Comments on quantum-mechanical interference due to the Earth’s rotation. Phys. Rev. D 21, 2993 (1980)
Nandi, K.K., Zhang, Y.-Z.: General relativistic effects on quantum interference and the principle of equivalence. Phys. Rev. D 66, 063005 (2002)
Alsing, P.M., Evans, J.C., Nandi, K.K.: The phase of a quantum mechanical particle in curved spacetime. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 33, 1459 (2001)
Cohen, J.M., Mashhoon, B.: Standard clocks, interferometry, and gravitomagnetism. Phys. Lett. A 181, 353 (1993)
Lichtenegger, H.I.M., Iorio, L.: The twin paradox and Machs principle. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 126, 129 (2011)
Everitt, C.W.F., et al.: Gravity Probe B: final results of a space experiment to test general relativity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 221101 (2011)
Everitt, C.W.F., et al.: The Gravity Probe B test of general relativity. Class. Quantum Grav. 32, 224001 (2015)
Smith, D.E., Dunn, P.J.: Long term evolution of the Lageos Orbit. Geophys. Res. Lett. 7, 437 (1980)
Ruggiero, M.L.: Gravitomagnetic gyroscope precession in Palatini \(f(R)\) gravity. Phys. Rev. D 79, 084001 (2009)
Hackmann, E., Lämmerzahl, C.: Observables for bound orbital motion in axially symmetric space-times. Phys. Rev. D 85, 044049 (2012). (and references therein)
Hackmann, E., Lämmerzahl, C.: Complete analytic solution of the geodesic equation in Schwarzschild–(anti-)de Sitter spacetimes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 171101 (2008)
Hackmann, E., Kagramanova, V., Kunz, J., Lämmerzahl, C.: Analytical solution of the geodesic equation in Kerr–(anti-) de Sitter space-times. Phys. Rev. D 81, 044020 (2010)
Dolgov, A.D., Kawasaki, M.: Can modified gravity explain accelerated cosmic expansion? Phys. Lett. B 573, 1 (2003)
Kagramanova, V., Kunz, J., Lämmerzahl, C.: Solar system effects in Schwarzschildde Sitter spacetime. Phys. Lett. B 634, 465 (2006)
Sereno, M., Jetzer, P.: Solar and stellar system tests of the cosmological constant. Phys. Rev. D 73, 063004 (2006)
Acknowledgements
Part of the reported study was funded by RFBR according to the research project No. 16-32-00323.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karimov, R.K., Izmailov, R.N., Potapov, A.A. et al. Terrestrial Sagnac delay constraining modified gravity models. Gen Relativ Gravit 50, 44 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10714-018-2365-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10714-018-2365-5