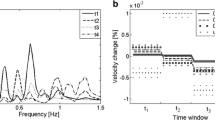
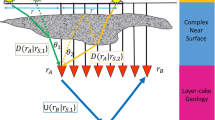
Abstract
The extraction of the response from field fluctuations excited by random sources has received considerable attention in a variety of different fields. We present three methods for the extraction of the systems response that are based on cross-correlation, deconvolution, and the solution of an integral equation, respectively. For systems that are invariant for time-reversal the correlation method requires random sources on a bounding surface only, but when time-reversal invariance is broken, for example by attenuation, a volume distribution of sources is needed. For this reason the correlation method is not useful for diffusive or strongly attenuating systems. We provide examples of the three methods and compare their merits and drawbacks. We show that the extracted field may satisfy different boundary conditions than does the physical field. This can be used, for example, to suppress surface-related multiples in exploration seismology, to study the coupling of buildings to the subsurface, and to remove the airwave in controlled source electromagnetics (CSEM).










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aki K (1957) Space and time spectra of stationary stochastic waves with special reference to microtremors. Bull Earthq Res Inst 35:415–456
Amundsen L (2001) Elimination of free-surface related multiples without the need of the source wavelet. Geophysics 66:327–341
Amundsen L, Løseth L, Mittet R, Ellingsrud S, Ursin B (2006) Decomposition of electromagnetic fields into upgoing and downgoing components. Geophysics 71:G211–G223
Bakulin A, Calvert R (2004) Virtual source: new method for imaging and 4D below complex overburden. Expanded abstracts of the 2004 SEG-meeting, pp 2477–2480
Bakulin A, Calvert R (2006) The virtual source method: theory and case study. Geophysics 71:SI139–SI150
Bakulin A, Mateeva A, Mehta K, Jorgensen P, Ferrandis J, Sinha Herhold I, Lopez J (2007) Virtual source applications to imaging and reservoir monitoring. The Leading Edge 26:732–740
Bensen GD, Ritzwoller MH, Barmin MP, Levshin AL, Lin F, Moschetti MP, Shapiro NM, Yang Y (2007) Processing seismic ambient noise data to obtain reliable broad-band surface wave dispersion measurements. Geophys J Int 169:1239–1260
Brenguier F, Campillo M, Hadziioannou C, Shapiro N, Larose E (2008) Postseismic relaxation along the San Andreas Fault at Parkfield from continuous seismological observations. Science 321:1478–1481
Callen HB, Welton TA (1951) Irreversibility and generalized noise. Phys Rev 83:34–40
Campillo M, Paul A (2003) Long-range correlations in the diffuse seismic coda. Science 299:547–549
Chaput JA, Bostock MG (2007) Seismic interferometry using non-volcanic tremor in Cascadia. Geophys Res Lett 34:L07304. doi:10.1029/2007/GL028987
Chávez-Garcia FJ, Luzón F (2005) On the correlation of seismic microtremors. J Geophys Res 110:B11313. doi:10.1029/2005JB003686
Curtis A, Gerstoft P, Sato H, Snieder R, Wapenaar K (2006) Seismic interferometry—turning noise into signal. The Leading Edge 25:1082–1092
Derode A, Larose E, Tanter M, de Rosny J, Tourin A, Campillo M, Fink M (2003a) Recovering the Green’s function from far-field correlations in an open scattering medium. J Acoust Soc Am 113:2973–2976
Derode A, Larose E, Campillo M, Fink M (2003b) How to estimate the Green’s function for a heterogeneous medium between two passive sensors? Application to acoustic waves. Appl Phys Lett 83:3054–3056
Draganov D, Wapenaar K, Mulder W, Singer J, Verdel A (2007) Retrieval of reflections from seismic background-noise measurements. Geophys Res Lett 34:L04305
Gerstoft P, Fehler MC, Sabra KG (2006) When Katrina hit California. Geophys Res Lett 33:L17308
Griffiths DJ (1999) Introduction to electrodynamics, 3 edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Gutenberg B (1947) Microseisms and weather forecasting. J Meteorol 4:21–28
Hill D, Combee L, Bacon J (2006) Over/under acquisition and data processing: the next quantum leap in seismic technology? First Break 24:81–96
Hornby BE, Yu J (2007) Interferometric imaging of a salt flank using walkaway VSP data. The Leading Edge 26:760–763
Kennett BLN (1979) The suppression of surface multiples on seismic records. Geophys Prosp 27:584–600
Kohler MD, Heaton TH, Bradford SC (2007) Propagating waves in the steel, moment-frame Factor building recorded during earthquakes. Bull Seismol Soc Am 97:1334–1345
Kubo R (1966) The fluctuation–dissipation theorem. Rep Prog Phys 29:255–284
Larose E, Derode A, Campillo M, Fink M (2004) Imaging from one-bit correlations of wideband diffuse wave fields. J Appl Phys 95:8393–8399
Larose E, Montaldo G, Derode A, Campillo M (2006a) Passive imaging of localized reflectors and interfaces in open media. Appl Phys Lett 88:104103
Larose E, Margerin L, Derode A, van Tiggelen B, Campillo M, Shapiro N, Paul A, Stehly L, Tanter M (2006b) Correlation of random wavefields: an interdisciplinary review. Geophysics 71:SI11–SI21
Le Bellac M, Mortessagne F, Batrouni GG (2004) Equilibrium and non-equilibrium statistical thermodynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lobkis OI, Weaver RL (2001) On the emergence of the Green’s function in the correlations of a diffuse field. J Acoust Soc Am 110:3011–3017
Longuet-Higgins MS (1950) A theory for the generation of microseisms. Phil Trans R Soc Lond A 243:1–35
Louie JN (2001) Faster, better: shear-wave velocity to 100 meters depth from refraction microtremor analysis. Bull Seismol Soc Am 91:347–364
Malcolm A, Scales J, van Tiggelen BA (2004) Extracting the Green’s function from diffuse, equipartitioned waves. Phys Rev E 70:015601
Mehta K, Snieder R, Graizer V (2007a) Downhole receiver function: a case study. Bull Seismol Soc Am 97:1396–1403
Mehta K, Bakulin A, Sheiman J, Calvert R, Snieder R (2007b) Improving the virtual source method by wavefield separation. Geophysics 72:V79–V86
Mehta K, Snieder R, Calvert R, Sheiman J (2008a) Acquisition geometry requirements for generating virtual-source data. The Leading Edge 27:620–629
Mehta K, Sheiman JL, Snieder R, Calvert R (2008b) Strengthening the virtual-source method for time-lapse monitoring. Geophysics 73:S73–S80
Miyazawa M, Snieder R, Venkataraman A (2008) Application of seismic interferometry to extract P and S wave propagation and observation of shear wave splitting from noise data at Cold Lake, Canada. Geophysics 73:D35–D40
Moldoveanu N, Combee L, Egan M, Hamson G, Sydora L, Abriel W (2007) Over/under towed-streamer acquisition: a method to extend seismic bandwidth to both higher and lower frequencies. The Leading Edge 26:41–58
Morse PM, Ingard KU (1968) Theorerical acoustics. McGraw-Hill, New York
Paul A, Campillo M, Margerin L, Larose E, Derode A (2005) Empirical synthesis of time-asymmetrical Green functions from the correlation of coda waves. J Geophys Res 110:B08302. doi:10.1029/2004JB003521
Pharez S, Hendrick N, Tenghemn R (2008) First look at seismic data from a towed dual-sensor streamer. The Leading Edge 27:904–913
Poletto F, Miranda F (2004) Seismic while drilling, fundamentals fo drill-bit seismic for exploration. In: Helbig K, Treitel S (eds) Handbook of geophysical exploration, vol 35. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Poletto F, Malusa M, Miranda F, Tinivella U (2004) Seismic-while-drilling by using dual sensors in drill strings. Geophysics 69:1261–1271
Prieto G, Lawrence JF, Beroza GC (2009) Anelastic earth structure from the coherency of the ambient seismic field. J Geophys Res (submitted)
Rector JW, Marion BP (1991) The use of drill-bit energy as a downhole seismic source. Geophysics 56:628–634
Rickett JE, Claerbout JF (1999) Acoustic daylight imaging via spectral factorization: helioseismology and reservoir monitoring. The Leading Edge 18:957–960
Rickett JE, Claerbout JF (2000) Calculation of the sun’s acoustic impulse response by multidimensional spectral factorization. Sol Phys 192:203–210
Riley DC, Claerbout JF (1976) 2-D multiple reflections. Geophysics 41:592–620
Ritzwoller MH (2009) Ambient noise seismic imaging. In: McGraw Hill yearbook of science and technology 2009. McGraw-Hill, New York
Robinson EA (1999) Seismic inversion and deconvolution. In: Helbig K, Treitel S (eds) Handbook of geophysical exploration, vol 4B. Pergamon, Amsterdam
Roux P, Fink M (2003) Green’s function estimation using secondary sources in a shallow water environment. J Acoust Soc Am 113:1406–1416
Roux P, Kuperman WA, NPAL Group (2004) Extracting coherent wave fronts from acoustic ambient noise in the ocean. J Acoust Soc Am 116:1995–2003
Roux P, Sabra KG, Gerstoft P, Kuperman WA (2005) P-waves from cross correlation of seismic noise. Geophys Res Lett 32:L19303. doi:10.1029/2005GL023803
Rytov SM, Kravtsov YuA, Tatarskii VI (1989) Principles of statistical radiophysics, vol 3, elements of random fields. Springer, Berlin
Sabra KG, Roux P, Thode AM, D’Spain GL, Hodgkiss WS (2005a) Using ocean ambient noise for array self-localization and self-synchronization. IEEE J Ocean Eng 30:338–347
Sabra KG, Gerstoft P, Roux P, Kuperman WA, Fehler MC (2005b) Surface wave tomography from microseisms in Southern California. Geophys Res Lett 32:L14311. doi:10.1029/2005GL023155
Sabra KG, Roux P, Gerstoft P, Kuperman WA, Fehler MC (2006) Extracting coherent coda arrivals from cross-correlations of long period seismic waves during the Mount St. Helens 2004 eruption. J Geophys Res 33:L06313. doi:1029.2005GL025563
Sabra KG, Conti S, Roux P, Kuperman WA (2007) Passive in-vivo elastography from skeletal muscle noise. Appl Phys Lett 90:194101
Sabra KG, Srivastava A, di Scalea FL, Bartoli I, Rizzo P, Conti S (2008) Structural health monitoring by extraction of coherent guided waves from diffuse fields. J Acoust Soc Am 123:EL8
Sawazaki K, Sato H, Nakahara H, Nishimura T (2009) Time-lapse changes of seismic velocity in the shallow ground caused by strong ground motion shock of the 2000 Western-Tottori earthquake, Japan, as revealed from coda deconvolution analysis. Bull Seismol Soc Am 99:352–366
Schuster GT, Yu J, Sheng J, Rickett J (2004) Interferometric/daylight seismic imaging. Geophys J Int 157:838–852
Sens-Schönfelder C, Wegler U (2006) Passive image interferometry and seasonal variations at Merapi volcano, Indonesia. Geophys Res Lett 33:L21302. doi:10.1029/2006GL027797
Shapiro NM, Campillo M (2004) Emergence of broadband Rayleigh waves from correlations of the ambient seismic noise. Geophys Res Lett 31:L07614. doi:10.1029/2004GL019491
Shapiro NM, Campillo M, Stehly L, Ritzwoller MH (2005) High-resolution surface-wave tomography from ambient seismic noise. Science 307:1615–1618
Slob E, Draganov D, Wapenaar K (2007) Interferometric electromagnetic Green’s functions representations using propagation invariants. Geophys J Int 169:60–80
Snieder R (2004) Extracting the Green’s function from the correlation of coda waves: a derivation based on stationary phase. Phys Rev E 69:046610
Snieder R (2006) Retrieving the Green’s function of the diffusion equation from the response to a random forcing. Phys Rev E 74:046620
Snieder R (2007) Extracting the Green’s function of attenuating heterogeneous acoustic media from uncorrelated waves. J Acoust Soc Am 121:2637–2643
Snieder R, Şafak E (2006) Extracting the building response using seismic interferometry: theory and application to the Millikan library in Pasadena, California. Bull Seismol Soc Am 96:586–598
Snieder R, Sheiman J, Calvert R (2006a) Equivalence of the virtual source method and wavefield deconvolution in seismic interferometry. Phys Rev E 73:066620
Snieder R, Wapenaar K, Larner K (2006b) Spurious multiples in seismic interferometry of primaries. Geophysics 71:SI111–SI124
Snieder R, Wapenaar K, Wegler U (2007a) Unified Green’s function retrieval by cross-correlation: connection with energy principles. Phys Rev E 75:036103
Snieder R, Hubbard S, Haney M, Bawden G, Hatchell P, Revil A, Calvert R, Curtis A, Fehler M, Gerstoft P, Hornby B, Landrø M, Lesmes D, Mehta K, Mooney M, Pacheco C, Prejean S, Sato H, Schuster J, Wapenaar K, Wilt M (2007b) Advanced non-invasive geophysical monitoring techniques. Ann Rev Earth Planet Sci 35:653–683
Snieder R, van Wijk K, Haney M, and Calvert R (2008) The cancellation of spurious arrivals in Green’s function extraction and the generalized optical theorem. Phys Rev E 78:036606
Stehly L, Campillo M, Shapiro NM (2006) A study of seismic noise from long-range correlation properties. J Geophys Res 111. doi:10.1029/2005JB004237
Stehly L, Campillo M, Froment B, Weaver RL (2008) Reconstructing Green’s function by correlation of the coda of the correlation (C3) of ambient seismic noise. J Geophys Res 113:B11306
Tatarskii VP (1987) Example of the description of dissipative processes in terms of reversible dynamic equations and some comments on the fluctuation dissipation theorem. Sov Phys Usp 30:134–152
Thompson D, Snieder R (2006) Seismic anisotropy of a building. The Leading Edge 25:1093
Trampert J, Cara M, Frogneux M (1993) \(SH\) propagator matrix and \({Q}_s\) estimates from borehole- and surface-recorded earthquake data. Geophys J Int 112:290–299
Um ES, Alumbaugh DL (2007) On the physics of the marine controlled-source electromagnetic method. Geophysics 72:WA13–WA26
Vasconcelos I, Snieder R (2008a) Interferometry by deconvolution, Part 1—theory for acoustic waves and numerical examples. Geophysics 73:S115–S128
Vasconcelos I, Snieder R (2008b) Interferometry by deconvolution: Part 2—theory for elastic waves and application to drill-bit seismic imaging. Geophysics 73:S129–S141
Vasconcelos I, Snieder R, Hornby B (2008a) Imaging internal multiples from subsalt VSP data—examples of target-oriented interferometry. Geophysics 73:S157–S168
Vasconcelos I, Snieder R, Sava P, Taylor T, Malin P, Chavarria A (2008b) Drill bit noise illuminates the san andreas fault. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 89(38):349
Verschuur DJ, Berkhout AJ, Wapenaar CPA (1992) Adaptive surface-related multiple elimination. Geophysics 57:1166–1177
Wapenaar K (2004) Retrieving the elastodynamic Green’s function of an arbitrary inhomogeneous medium by cross correlation. Phys Rev Lett 93:254301
Wapenaar K, Fokkema J (2006) Green’s function representations for seismic interferometry. Geophysics 71(4):SI33–SI46
Wapenaar K, Fokkema J, Dillen M, Scherpenhuijsen P (2000) One-way acoustic reciprocity and its applications in multiple elimination and time-lapse seismics. In: 70th annual SEG meeting, Calgray, expanded abstracts, pp 2377–2380
Wapenaar K, Fokkema J, Snieder R (2005) Retrieving the Green’s function by cross-correlation: a comparison of approaches. J Acoust Soc Am 118:2783–2786
Wapenaar K, Slob E, Snieder R (2006) Unified Green’s function retrieval by cross-correlation. Phys Rev Lett 97:234301
Wapenaar K, Slob E, Snieder R (2008) Seismic and electromagnetic controlled-source interferometry in dissipative media. Geophys Prosp 56:419–434
Weaver RL (2008) Ward identities and the retrieval of Green’s functions in the correlations of a diffuse field. Wave Motion 45:596–604
Weaver RL, Lobkis OI (2001) Ultrasonics without a source: thermal fluctuation correlations at MHz frequencies. Phys Rev Lett 87:134301
Weaver R, Lobkis O (2003) On the emergence of the Green’s function in the correlations of a diffuse field: pulse-echo using thermal phonons. Ultrasonics 40:435–439
Weaver RL, Lobkis OI (2005) Fluctuations in diffuse field-field correlations and the emergence of the Green’s function in open systems. J Acoust Soc Am 117:3432–3439
Webb SC (1998) Broadband seismology and noise under the ocean. Rev Geophys 36:105–142
Weber J (1956) Fluctuation–dissipation theorem. Phys Rev 101:1620–1626
Webster GM (ed.) (1978) Deconvolution, vol 1 of geophysics reprint series. SEG, Tulsa
Weglein AB, Gasparotto FA, Carvalho PM, Stolt RH (1998) An inverse scattering series method for attenuating multiples in seismic reflection data. Geophysics 62:1975–1989
Wegler U, Sens-Schönfelder C (2007) Fault zone monitoring with passive image interferometry. Geophys J Int 168:1029–1033
van Borselen RG, Fokkema JT, van den Berg PM (1996) Removal of surface-related wave phenomena—the marine case. Geophysics 61:202–210
van Wijk K (2006) On estimating the impulse response between receivers in a controlled ultrasonic experiment. Geophysics 71:SI79–SI84
Yang Y, Ritzwoller MH (2008) Teleseismic surface wave tomography in the western US using the transportable array component of USArray. Geophys Res Lett 5:L04308
Acknowledgments
We thank two anonymous reviewers for their useful corrections and suggestions. This work was supported by the NSF (Grant EAS-0609595), by ExxonMobil Upstream Research Co., and by the GameChanger program of Shell.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Snieder, R., Miyazawa, M., Slob, E. et al. A Comparison of Strategies for Seismic Interferometry. Surv Geophys 30, 503–523 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-009-9069-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-009-9069-z