Abstract
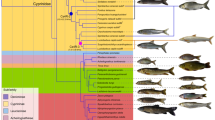
The extent to which genome sizes and other nucleotypic factors influence the phyletic diversification of lineages has long been discussed but remains largely unresolved. In the present work, we present evidence that the genomes of at least 16 species of the neotropical rivulid killifish genus Austrolebias are unusually large, with an average DNA content of about 5.95 ± 0.45 picograms per diploid cell (mean C-value of about 2.98 pg). They are thus larger than the genomes of very nearly all other diploid, i.e. non-(paleo) polyploid species of actinopterygian fishes so far reported. Austrolebias species appear to be conventional diploids in all other respects and there is no reason to believe that they arise from polyploid ancestors. The genome sizes reported for other rivulid killifishes, including a putative sister group, are considerably smaller and fall within the range typical of most other cyprinodontoid species. Therefore, it appears that the ancestor(s) of contemporary Austrolebias have undergone one or more episodes of genome expansion encompassing sudden speciation process during the Pleistocene. In addition, these findings are consistent with the hypothesis of a positive correlation between species richness and genome size.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike H (1974) A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Autom Control AC-19:716–723
Arezo MJ, Pereiro L, Berois N (2005) Early development in the annual fish Cynolebias viarius. J Fish Biol 66:1357–1370. doi:10.1111/j.0022-1112.2005.00688.x
Arim M, Abades SR, Laufer G, Loureiro M, Marquet PA (2010) Food web structure and body size: trophic position and resource acquisition. Oikos 119:147–153. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0706.2009.17768.x
Avise JC (1994) Molecular markers, natural history and evolution. Chapman & Hall, New York
Belote DF, Costa WJEM (2002) Reproductive behavior patterns in the neotropical annual fish genus Simpsonichthys Carvalho, 1959 (Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae): description and phylogenetic implications. Bol Mus Nac (Rio de J.) 489:1–10
Belote DF, Costa WJEM (2003) Reproductive behavior of the Brazilian annual fish Cynolebias albipunctatus Costa & Brasil, 1991 (Teleostei, Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae): a new report of sound production in fishes. Arq Mus Nac (Rio de J.) 61:241–244
Belote DF, Costa WJEM (2004) Reproductive behavior patterns in three species of the South American annual fish genus Austrolebias Costa, 1998 (Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae). Bol Mus Nac (Rio de J.) 514:1–7
Berois N, Arezo MJ, Papa NG, Clivio GA (2012) Annual fish: development adaptations for an extreme environment. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol 1:595–602. doi:10.1002/wdev.39
Brown WM, George M Jr, Wilson AC (1979) Rapid evolution of animal mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:1967–1971. doi:10.1073/pnas.76.4
Cardozo V (1999) Tasa Metabólica y excreción del nitrógeno en peces anuales Cynolebias viarius (Cyprinodontiformes). MSc. Dissertation. Thesis. PEDECIBA, Facultad de Ciencias, UDELAR, Uruguay
Carvalho ML, Oliveira C, Foresti F (1998) Nuclear DNA content of thirty species of Neotropical fishes. Genet Mol Biol 21:47–54
Ciudad J, Cid E, Velasco A, Lara JM, Aijón J, Orfao A (2002) Flow cytometry measurement of the DNA contents of G0/G1 diploid cells from three different teleost fish species. Cytometry 48:20–25. doi:10.1002/cyto.10100
Costa WJEM (1998) Phylogeny and classification of Rivulidae revisited: origin and evolution of annualism and miniaturization in rivulid fishes (Cyprinodontiformes: Aplocheiloidei). J Comp Biol 3:33–94
Costa WJEM (2006) The South American annual killifish genus Austrolebias (Teleostei: Cyprinodontiformes: Rivulidae): phylogenetic relationships, descriptive morphology and taxonomic revision. Zootaxa 1213:1–162
Denton TE (1973) Fish chromosome methodology. CE Thomas Springfield, Illinois
Drummond AJ, Rambaut A (2007) Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees BEAST. BMC Evol Biol 7:214. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-7-214
Elder JF, Turner BJ, Thomerson JE, Taphorn DC (1993) Karyotypes of nine Venezuelan annual killifishes (Cyprinodontidae), with comments on karyotype differentiation in annual killifishes. Ichthyol Explor Freshw 4:261–268
Errea A, Danulat E (2001) Growth of the annual fish Cynolebias viarius (Cyprinodontiformes), in the natural habitat compared to laboratory conditions. Environ Biol Fishes 61:261–268
Fernández AS, Rosillo JC, Casanova G, Olivera-Bravo S (2011) Proliferation zones in the brain of adult fish Austrolebias (Cyprinodontiformes: Rivulidae): a comparative study. Neuroscience 189:12–24
Ferrer J, Malabarba LR, Costa WJEM (2008) Austrolebias paucisquama (Cyprinodontiformes: Rivulidae), a new species of annual killifish from southern Brazil. Neotrop Ichthyol 6:175–180
García G (2006) Multiple simultaneous speciation in killifishes of the Cynolebias adloffi species complex (Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae) from phylogeography and chromosome data. J Zool Syst Evol Res 44:75–87. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0469.2005.00346.x
García G, Scvortzoff E, Máspoli MC, Vaz-ferreira R (1993) Analysis of karyotypic evolution in natural populations of Cynolebias (Pisces, Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae) using banding techniques. Cytologia 58:85–94
García G, Scvortzoff E, Hernández A (1995) Karyotypic heterogeneity in South American annual killifishes of the genus Cynolebias (Pisces, Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae). Cytologia 60:103–110
García G, Wlasiuk G, Lessa EP (2000) High levels of mitochondrial cytochrome b divergence in the annual killifishes of the genus Cynolebias (Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae). Zool J Linn Soc 129:93–110
García G, Lalanne AI, Aguirre G, Cappetta M (2001) Chromosome evolution in annual killifish genus Cynolebias and mitochondrial phylogenetic analysis. Chromosome Res 9:93–100
García G, Alvarez-Valin F, Gómez N (2002) Mitochondrial genes: signals and noise in phylogenetic reconstruction within killifish genus Cynolebias (Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae). Biol J Linn Soc Lond 76:49–59
García D, Loureiro M, Tassino B (2008) Reproductive behavior in the fish Austrolebias reicherti Loureiro & García 2004 (Cyprinodontiformes: Rivulidae). Neotrop Ichthyol 6:243–248
García G, Loureiro M, Berois N, Arezo MJ, Casanova G, Olivera A (2009) Pattern of differentiation in the annual killifish genus Austrolebias (Cyprinodontiformes: Rivulidae) from a biosphere reserve site in South America: a multidisciplinary approach. Biol J Linn Soc Lond 98:620–635
García G, Gutiérrez V, Vergara J, Calviño P, Duarte A, Loureiro M (2012) Patterns of population differentiation in annual killifishes from the Paraná–Uruguay–La Plata Basin: the role of vicariance and dispersal. J Biogeogr 39:1707–1719. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2699.2012.02722.x
Guindon S, Dufayard JF, Lefort V, Anisimova M, Hordijk W, Gascuel O (2010) New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst Biol 59:307–321. doi:10.1093/sysbio/syq010
Gutiérrez V, Arezo MJ, García G (2007) Characterization of partial Hox genes sequences in annual fishes of the Cynolebiatinae subfamily (Cyprinodontiformes: Rivulidae). Gen Mol Biol 30:494–503
Hillis DM, Bull JJ (1993) An empirical test of bootstrapping as a method for assessing confidence in phylogenetic analysis. Syst Biol 42:182–192. doi:10.2307/2992540
Hinegardner R, Rosen DE (1972) Cellular DNA content and evolution of teleostean fishes. Am Nat 106:621–644
Kimura MA (1980) Simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Kligerman AD, Bloom SE (1977) Rapid chromosome preparations from solid tissues of fishes. J Fish Res Board Can 34:266–269
Kornfield IL (1984) Descriptive genetics of cichlid fishes. In: Turner BJ (ed) Evolutionary genetics of fishes. Plenum Press, New York, pp 591–616
Kraaijeveld K (2010) Genome size and species diversification. Evol Biol 37:227–233. doi:10.1007/s11692-010-9093-4
Lamatsch DK, Steinlein C, Schmid M, Schartl M (2000) Non-invasive determination of genome size and ploidy level in fishes by flow cytometry: detection of triploid Poecillia Formosa. Cytometry 39:91–95
Loureiro M, de Sá RO (1996) External morphology of the chorion of the annual fishes Cynolebias (Cyprinodontiformes: Rivulidae). Copeia 1996:1016–1022
Loureiro M, de Sá RO (1998) Osteological analysis of the killifish genus Cynolebias (Cyprinodontiformes: Rivulidae). J Morphol 238:109–262
Loureiro M, García G (2004) Cynolebias reicherti a new annual fish (Rivulidae: Cynolebiatinae) from southern Laguna Merim basin. Acta Zool Lilloana 48:13–25
Loureiro M, Duarte A, Zarucki M (2011) A new species of Austrolebias Costa (Cyprinodontiformes: Rivulidae) from northeastern Uruguay, with comments on distribution patterns. Neotrop Ichthyol 9:335–342
Mabble BK, Alexandrou MA, Taylor MI (2011) Genome duplication in amphibians and fish: an extended synthesis. J Zool 284:151–182. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.2011.00829.x
Mank JE, Avise JC (2006) Cladogenetic correlates of genomic expansions in the recent evolution of actinopterygiian fishes. Proc R Soc B 273:33–38. doi:10.1098/rspb 2005.3295
Máspoli MC, García G (1988) Estudio comparativo del cariotipo de especies del género Cynolebias Steindachner, 1876 (Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae). Bol Soc Zool Uruguay 4:27–33
Medrano JF, Aasen E, Sharrow L (1990) DNA extraction from nucleated red blood cells. Biotechniques 8:43
Moshgani M, Van Dooren TJM (2011) Maternal and paternal contributions to egg size and egg number variation in the blackfin pearl killifish Austrolebias nigripinnis. Evol Ecol 25:1179–1195
Ojima Y, Yamamoto K (1990) Cellular DNA contents of fishes determined by flow cytometry. La Kromosomo II 57:1871–1888
Palumbi S, Martin A, Romano S, McMillan WO, Stice L, Grabowski G (1991) The simple fool’s guide to PCR. Department of Zoology and Kewalo Marine Laboratory, Univ. Hawaii, Honolulu
Passos C, Tassino B, Loureiro M, Rosenthal GG (2013) Intra- and intersexual selection on male body size in the annual killifish Austrolebias charrua. Behav Process 96:20–26.
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817–818. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/14.9.817
Rambaut A, Drummond AJ (2009) Tracer v.1.5. http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer
Rebollo R, Horard B, Hubert B, Vieira C (2010) Jumping genes and epigenetics: towards new species. Gene 454:1–7. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2010.01.003
Reichwald K, Lauber C, Nanda I, Kirschner J, Hartmann N, Schories S, Gausmann U, Taudien S, Schilhabel MB, Szafranski K et al (2009) High tandem repeat content in the genome of the short-lived annual fish Nothobranchius furzeri: a new vertebrate model for aging research. Genome Biol 10:R16.1–R16.17. doi:10.1186/gb-2009-10-2-r16
Rodríguez F, Oliver JL, Marín A, Medina JR (1990) The general stochastic model of nucleotide substitution. J Theor Biol 142:482–501
Scheel JJ (1972) Rivuline karyotypes and their evolution (Rivulinae, Cyprinodontidae, Pisces). Z Zool Syst Evol Forsch 10:180–209
Simpson BRC (1979) The phenology of annual killifishes. Symp Zool Soc Lond 44:243–261
Smith EM, Gregory TR (2009) Patterns of genome size diversity in the ray-finned fishes. Hydriobiologia 625:1–25
Swofford DL (2002) PAUP* Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods) ver. 4.0b5. Sinauer Associates, MA
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr121
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak FM, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876
Vaz-Ferreira R, Sierra B, Scaglia S (1964) Eco-etología de la reproducción en los peces del género Cynolebias Steindachner, 1876. Apar Arch Soc Biol Montev 26:44–49
Vinogradov AE (1998) Genome size and GC-percent in vertebrates as determined by flow cytometry: the triangular relationship. Cytometry 31:100–109
Walford RL, Liu BH (1965) Husbandry, life span, and growth rate of the annual fish, Cynolebias adloffi. Exp Gerontol 1:161–171
Wourms JP (1972) The developmental biology of annual fishes. II. Naturally occurring dispersion and reaggregation of blastomeres during the development of annual fish eggs. J Exp Zool 182:169–200
Acknowledgments
We thank the following colleagues for kindly providing the following fish specimens: L. Malabarba (A. adloffi) and W.J.E.M. Costa (C. melanotaenia) from RS Brazil (1991 and 1997, respectively); V. Etzel and G. Hessfeld (A. vandenbergi, A. patriciae) from Paraguay (2004); P. Calviño (A. bellottii, A. nigripinnis, A. monstrosus, A. elongatus, A. nonoiuliensis, A. robustus, A. juanlangi, A. periodicus) from Chaco, Salta and Buenos Aires Provinces as well as from aquarium strains; M. Loureiro, S. Serra and A. Duarte (A. quirogay, A. elongatus, A. reicherti, A. vazferreirai, A. nigripinnis, A. cinereus) from different ponds of Uruguay and D. Rodriguez-Ithurralde and N. Papa for zebrafish (Danio rerio) donation. The authors are also grateful to the Japanese government for the donation of equipment. G.G., V.G., and G.F. acknowledge the support of SNI (ANII, Uruguay).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García, G., Gutiérrez, V., Ríos, N. et al. Burst speciation processes and genomic expansion in the neotropical annual killifish genus Austrolebias (Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae). Genetica 142, 87–98 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-014-9756-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-014-9756-7