Abstract
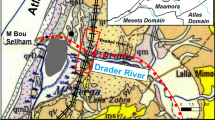
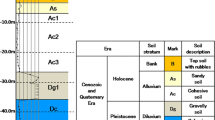
This paper describes the performance of the Moroccan high-speed railway embankment over alluvial soft ground treated with prefabricated vertical drains. For analyzing soil behavior, numerical analyses were performed under 2D finite element Plaxis code. The authors undertook Class-B prediction at first, using two different constitutive models, soft soil and soft soil creep (SSC) models. Class-C prediction was then performed using only SSC. By comparing the predictions with field measurement, it was concluded that the time-dependent model (SSC) produced acceptable results . However, reasonable modification for the SSC model input parameters in Class-C prediction led to obtain accurate matches with field measurements.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberkan M (1989) Etude des formations quaternaires des marges du bassin du Rharb (Maroc nord-occidental). Thèse de doctorat d’état. Université Bordeaux I
Abuel Naga HM, Bergado DT, Gniel J (2015) Design chart for prefabricated vertical drains improved ground. Geotext Geomemb 43:537–546
Al Mazini I, Mridekh A, Kili M, El Mansouri B, El Bouhaddioui M, Magrane B (2018) Plio-quaternary deposits in the eastern rharb (nw morocco): Electro-sequential characterization. J Afr Earth Sc 138:32–41
Amavasai A, Sivasithamparam N, Dijkstra J, Karstunen M (2018) Consistent class A & C predictions of the Ballina test embankment. Comput Geotech 93:75–86
Chai JC, Shen SL, Miura N, Bergado DT (2001) Simple method of modeling PVD-improved subsoil. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 127(11):965–972
Chai JC, Horpibulsuk S, Shen SL, Carter JP (2014) Consolidation analysis of clayey deposits under vacuum pressure with horizontal drains. Geotext Geomembr 42:437–444
Chen JF, Tolooiyam A, Xue JF, Shi ZM (2016) Performance of a geogrid reinforced soil wall on PVD drained multilayer soft soils. Geotext Geomemb 44(3):219–229
Cirac P (1985) Le bassin sud-rifain occidental au Néogène supérieur. Evolution de ladynamique sédimentaire et de la paléogéographie au cours d’une phase decomblement. Thèse de doctorat d’état. Université Bordeaux I
Combe M (1975) Bassin du Gharb-Maâmora In ressources en eau du Maroc Tome 2. Notes et 501 mémoire du Service Géologique (Maroc) 231:93–128
Da Silva EM, Juste JL, Durant P, Justo E, Vazquez Boza M (2017) The effect of geotextile reinforcement and prefabricated vertical drains on the stability and settlement of embankment. Geotext Geomemb 45:441–447
Di Filippo G, Bandini V, Cascone E, Biondi G (2017) Measurements and prediction of settlements induced by preloading and vertical drains on a heterogeneous soil deposit. Measurement 104:302–315
El Bouhaddioui M, Mridekh A, Kili M, El Mansouri B, EL Gasmi ElH, Magrane B (2014) Le Bassin du Rharb, Répartition des lithofaciés plio-quaternaires, contexte paléogéographique et géodynamique, contribution des diagraphies. Notes et Mém Serv Geol Maroc 577:125–137
El Bouhaddioui M, Mridekh A, Kili M, El Mansouri B, El Gasmi EIH, Magrane B (2016) Electrical and well log study of the Plio-Quaternary deposits of the southern part of the Rharb Basin northern Morocco. J Afr Earth Sci 123:110–122
Flinch JF (1993) Tectonic Evolution of the Gibraltar Arc. Ph.D. thesis Rice University. Houston Texas USA
Flinch JF, Vail PR (1998) Plio-pleistocene sequence and tectonics of the gibrator arc mesozoic and cenozoic sequence stratigraphiy of European Basin. SEMP Special Publ 60:119–208
Hashemi H, Naeimifar I, Uromeihy A et al (2015) Evaluation of rock nail wall performance in jointed rock using numerical method. Geotech Geol Eng 33(3):593–607
Hosseinpour I, Almeida MSS, Riccio M, Baroni M (2017) Strength and compressibility characteristics of a soft clay subjected to ground treatment. Geotech Geol Eng 35(3):1051–1066
Indraratna B, Baral P, Rujikiatkamjorn C, Perera D (2018) Class A and predictions for Ballina trial embankment with vertical drains using standard test data from industry and large diameter test specimens. Comput Geotech 93:232–246
Jaaidi EB (1993) La couverture sédimentaire post-glacial de la plate forme continentale atlantique ouest-rifaine (Maroc Nord-Occidental). Exemple d’une séquence transgressive (Dsc thesis). Univ Mohammed V Faculté des sciences de Rabat
Jang WY, Chung SG (2014) Long term settlement analysis of partially improved thick clay deposit. Geotext Geomembr 42(6):620–628
Jiang QH, Qi ZF, Wei W, Zhou CB (2015) Stability assessment of a high rock slope by strength reduction finite element method. Bull Eng Geol Environ 74(4):1153–1162
Jostad HP, Palmeiri F, Andresen L et al (2018) Numerical prediction and back-calculation of time-dependent behavior of Ballina test embankment. Comput Geotech 93:123–132
Karunaratne GP (2011) Prefabricated and electrical vertical drains for consolidation of soft clay. Geotext Geomembr 29:391–401
Kelly RB, Sloan SW, Pineda JA, Kouretzis G, Huang J (2018) Outcomes of the newcastle symposium for the prediction of embankment behavior on soft soil. Comput Geotech 93:9–41
Khabbazian M, Kaliakin VN, Meehan CL (2015) Column supported embankments with geosynthetic encased columns: validity of the unit cell concept. Geotech Geol Eng 33(3):425–442
Kili M (2007) Les Aquifères profonds du bassin du Rharb (Maroc) Géométrie, Bilan et Modélisation. These d’état Es-Sciences. Université Ibn Tofail Kenitra
Krishnamoorthy A, Kamal S (2016) Stability of an embankment on soft consolidating soil with vertical drains. Geotech Geol Eng 34(2):657–669
Lam LG, Bergado DT, Hino T (2015) PVD improvement of soft Bangkok clay with and without vacuum preleading using analytical and numerical analyses. Geotext Geomembr 43:547–557
Lambe TW (1973) Predictions in soil engineering. Geotechnique 23:149–202
Larsson R (1990) Behaviour of organic clay and gyttja. Swedish Getechnical Institute. Linköping report no 38
Larsson R, Sällfors G (1986) Automatic continuous consolidation testing in Sweden. In: Young RN, Townsend FC (eds) Consolidation of soils: testing and evaluation, ASTM STP 892. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, pp 299–328
Le Coz J (1964) Le Rharb. Fellahs et colons. Etude de géographie régionale. Inframar 1. Rabat p 481
Le Roy P, Sahabi M, Maad N, Rabineau M, Gutsher MA, Babonneau N, Van Vliet Lanoe B, Brahim LA, M’hammdi N, Trentesaux A, Dakki M, Hssain M (2014) 3D architecture of quaternary sediment along the NW Atlantic Moroccan Rharb continental shelf: a stratal pattern under the dual control of tectonics and climatic variations. Mar Pet Geol 49:129–142
Litto W, Jaaidi E, Medina F (2001) Etude sismo-structurale de la marge nord du bassin du Gharb (avant-pays rifain, Maroc): mise en évidence d’une distension d’âge miocène tardif. Eclogae Geol Helv 94:63–73
Mesri G, Godlewski PM (1977) Time and stress-compressibility inter-relationship. J Geotech Eng 103(5):417–430
Morel JL (1988) Evolution récente de l’orogène rifaine et de son avant-pays depuis la fin de la mise en place des nappes. Thèse d’Etat Paris. Mémoire Géo diffusion, p 584
Neher HP, Wehnert M, Bonnier PG (2001) An evaluation of soft soil models based on trail embankment. In: Proceedings of 10th international conference on computer methods and advances in geomechanics. Tucson, pp 373–378
Rezania M, Bagheri M, Nezhad MM, Sivasithamparam N (2017) Creep analysis of an earth embankment on soft soil deposit with and without PVD improvement. Geotext Geomemb 45:537–547
Shams Maleki Y, Khazaei J (2017) A numerical comparison of the behavior of a braced excavation using two and three-dimensional creep plastic analyses. Geotech Geol Eng 35(5):2017–2035
Šuklje L (1957) The analysis of the consolidation process by the isotaches method. In: Proceedings of the 4th international conference on soil mechanics and foundation engineering (London), pp 200–206
Taechakumthorn C, Rowe RK (2012) Performance of a reinforced embankment on a sensitive Champlain clay deposit. Can Geotech J 49:917–927
Tavenas F, Leblond P, Jean P, Leroueil S (1983) The permeability of natural soft clays, part II: permeability characteristics. Can Gertech J 20(4):645–660
Toto EA, Miloudi AE, Basri ME, Hafid M, Zouhri L, Mouraouah SE, Benammi M, Mouraouah AE, Brahim AI, Birouk A, Kasmi M (2012) New geophysical and geological evidence for the present day southernmost active deformational from of the Rif thrust-and-fold belt and the oceanic accretionary prism of cadiz: the Dhar Doum-Lalla Zahra fault, Northwestern Atlantic Coastal Morocco. Environ Earth Sci 67:2411–2422
Tschuchnigg F, Schweiger HF (2018) Embankment prediction and back analysis by means of 2D and 3D finite element analyses. Comput Geotech 93:104–114
Vermeer PA, Neher HP (1999) A soft soil model that accounts for creep. Beyound 2000 in computational geotechnics. Ten years of Plaxis International Balkema. Amsterdam, pp 249–261
Zhang Z, Ye GB, Xu Y (2018) Comparative analysis on performance of vertical drain improved clay deposit under vacuum or surcharge loading. Geotext Geomemb 46(2):146–154
Zouhri L, Lamoureux C, Vachard D, Pique A (2002) Evidence of flexural extension of the Rif foreland: the Rharb-Maâmora basin (northern Morocco). Bulletin de la Société Géologique de France 6:509–514
Acknowledgements
The work presented was supported by the LPEE (Laboratoire Public d’Essais et d’Etudes). The author would like to thank all personnel in the LPEE for providing all data necessary for the completion of this work. We also thank anonymous reviewers for their comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mridakh, A.H., Lahlou, F., Ejjaaouani, H. et al. Soil Improvement of Alluvial Deposits Under High-Speed Railway Embankment: Field Case Study. Geotech Geol Eng 37, 3589–3603 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-019-00855-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-019-00855-8