Abstract
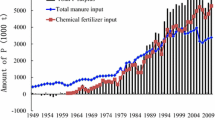
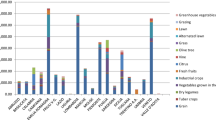
A reduction in chemical phosphate (P) fertilizer application to farmland from 137.6 kg P ha−1 in 1985 to 99.0 kg P ha−1 in 2005 and in manure application from 42.4 kg P ha−1 in 1985 to 32.8 kg P ha−1 in 2005 did not reduce crop P uptake, which averaged 27 kg P ha−1 over the period. Phosphate balance on farmland declined from 153.0 kg P ha−1 in 1985 to 105.4 kg P ha−1 in 2005 while livestock excreta disposal increased from 12.7 kg P ha−1 in 1985 to 23.7 kg P ha−1 in 2005. As a result, residual P associated with agriculture declined from 165.8 kg P ha−1 in 1985 to 129.1 kg P ha−1 in 2005. Phosphate utilization efficiency increased from 15.7% in 1985 to 20.1% in 2005. Median, minimum and maximum values of P flows by region showed similar trends. Phosphate input and withdrawal through crop production by region were not related to regional nitrogen (N) input and withdrawal through crop production. Although non-utilized P associated with agriculture has declined nationally and regionally, it is still higher than that in foreign countries, because of high chemical P fertilizer inputs and low crop yield withdrawal. Because soil P fertility was often sufficiently high previous large P surpluses, reducing P applications did not affect crop yields. Crop P uptake was less than half that of crop N yield. These results indicate that P inputs, especially by chemical fertilizer, for crop production could be reduced, thereby reducing negative environmental effects such as eutrophication of soil and water and conserving limited P resources.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amano H, Ohta K, Kusaba K, Nakai M (1991) Quantification of accumulated phosphate in each kind of soil type and in each kind of form in northern Japan. Development of refreshment and recycle techniques for soil accumulated phosphate Agriculture. Agriculture Forestry and Fisheries Research Council, MAFF, Tokyo, pp 28–36
Antikainen R, Lemola R, Nousiainen JI, Sokka L, Esala M, Huhtanen P, Rekolainen S (2005) Stocks and flows of nitrogen and phosphorus in Finnish food production and consumption system. Agric Ecosyst Environ 107:287–305. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2004.10.025
Bechmann ME, Stalnacke T, Kverno SH (2007) Testing the Norwegian phosphorus index at the field and sub-catchment scale. Agric Ecosyst Environ 120:117–128. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2006.05.009
Buciene A, Svedas A, Antanaitis S (2003) Balances major nutrients N, P and K at the farm and field level and some possibilities to improve comparisons between actual and estimated crop yields. Eur J Agron 20:53–62. doi:10.1016/S1161-0301(03)00073-X
Cordell D, Drangert J-O, White S (2009) The story of phosphorus: Global food security and food for thought. Glob Environ Change (Article in Press). doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2008.10.009
D’Haene K, Magyar M, De Neve S, Palmai O, Nagy J, Nemeth T, Hofman G (2007) Nitrogen and phosphorus balances of Hungarian farms. Eur J Agron 26:224–234. doi:10.1016/j.eja.2006.10.005
Ekholm P, Turtola E, Gronroos J, Seuri P, Ylivainio K (2005) Phosphorus loss from different farming systems estimated from soil surface phosphorus balance. Agric Ecosyst Environ 110:266–278. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2005.04.014
Hechrath G, Brooks PC, Poulton PR, Goulding KWT (1995) Phosphorus leaching from soils containing different phosphorus concentrations in Broadbald experiment. J Environ Qual 24:904–910
Hiradate (2007) What type of soil exotic plants or local plants (In Japanese). Farmland Soil 39–5:30–38
Kyllingsbaek A, Hansen JF (2007) Development in nutrient balances in Danish agriculture 1980–2004. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 79:267–280. doi:10.1007/s10705-007-9114-6
MAFF (1986a) Cost of livestock production (In Japanese). Tokyo
MAFF (1986b) The 61st Statistical Yearbook of Ministry of Agriculture. Forestry and Fisheries, Norin-tokei-kyokai
MAFF (1987) Rice related report (In Japanese). Tokyo
MAFF (1991a) Cost of livestock production (In Japanese). Tokyo
MAFF (1991b) The 66th Statistical Yearbook of Ministry of Agriculture. Forestry and Fisheries, Norin-tokei-kyokai, Tokyo
MAFF (1992) Rice related report (In Japanese). Tokyo
MAFF (1996a) Cost of livestock production (In Japanese). Tokyo
MAFF (1996b) The 71st Statistical Yearbook of Ministry of Agriculture. Forestry and Fisheries, Norin-tokei-kyokai
MAFF (1997) Rice related report (In Japanese). Tokyo
MAFF (1998) Agricultural production environment report (in Japanese). Tokyo
MAFF (2001a) Cost of livestock production (in Japanese). Tokyo
MAFF (2001b) The 75th Statistical Yearbook of Ministry of Agriculture. Forestry and Fisheries, Norin-tokei-kyokai
MAFF (2002) Rice related report (in Japanese). Tokyo
MAFF (2006a) Cost of livestock production (in Japanese). Tokyo
MAFF (2006b) The 80th Statistical Yearbook of Ministry of Agriculture. Forestry and Fisheries, Norin-tokei-kyokai
MAFF (2007a) Production cost of rice and wheat (in Japanese). Tokyo
MAFF (2007b) The 81st Statistical Yearbook of Ministry of Agriculture. Forestry and Fisheries, Norin-tokei-kyokai, Tokyo
Masujima H (2001) Environmental aspects of material cycles in arable land (in Japanese). Jour JSIDRE 69:1237–1240
Ministry of Education Culture and Sports (2000) The food content standard, Ver. 5. Publisher of Ministry of Found, Tokyo
Mishima S (2001) Quantitative evaluation of environmental risk associated with nitrogen flow in agricultural production and mitigation plan for 2 typical prefecture in Japan. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 47(3):511–518
Mishima S (2003) Trends of phosphate fertilizer demand and phosphate balance in farmland soils in Japan. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 49:39–45
Mishima S, Endo A, Kohyama K (2009) Recent trend of residual nitrogen on the national and regional scale in Japan and its relation with groundwater quality. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 83:1–11
Nishio M (2002) Trend of chemical fertilizer consumption. Jpn J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 73:219–225
Nishio M (2003) Analysis of the actual state of phosphate application in arable farming in Japan. Jpn J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 74:435–443
Obara H (2000) Outline of the soil monitoring and soil quality changes of the arable land in Japan. Pedologist 44:134–142 in Japanese with English summary
Obara H, Nakai M (2004) Available phosphate of arable lands in Japan Changes of characteristics in Japanese arable lands (II). Jpn J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 75:59–67
OECD (2000) Environmental indicators for agriculture issue and design vol 2. Paris
OECD (2001) Environmental indicators for agriculture methods and results, vol 3. Paris
OECD (2008) Environmental performance of agriculture in OECD Countries Since 1990. http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/44/26/40678331.pdf
Ondersteijn DJM, Beldman ACG, Daatselaar CHG, Giesen GWJ, Huirne RBM (2002) The Dutch mineral accounting system and European nitrate directive: implications for N and P management and farm performance. Agric Ecosyst Environ 92:283–296. doi:10.1016/S0167-8809(01)00288-2
Owa N (1996) Nutrient balance on crop production. In: Kanto-Tokai N (ed) New movement on effective use of fertilizer. National Agricultural Research Center, Tsukuba, pp 1–15
Prasad R, Power JF (1997) Soil fertility management for sustainable agriculture. RC Publisher, New York, p 171
Sharpley AN, Weld JL, Beegle DB, kleinman PJA, Gburek WJ, Moore PA, Mullins G (2003) Development of phosphorus indices for nutrient management planning strategies in the United States. J Soil Water Conserv 58:137–152
Takeuchi M (1997) Nitrate and phosphate outflow from arable land. Jpn J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 68:708–715
Tochigi prefecture (2004) Soil fertilization standard (in Japanese). Utsunomiya
Tsuiki K, Harada Y (1997) Livestock excretion and future theme in Japan. In: Nishio M (ed) Environmental conservation and new animal industry (in Japanese). Nourinsuisan-gijutukyokai, Tokyo, pp 15–29
Watanabe K, Uehara Y, Toyota K, Shinohara M, Kunoh H, Goto I, Murakami K, Maekawa K (2004) Relationship between mineral nutrition and plant disease (in Japanese). Jpn J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 75:399–404
Yasuda T (2003) Sustainable food production and phosphorus resources (in Japanese). Agric Hortic 78:1253–1257
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishima, S., Endo, A. & Kohyama, K. Recent trends in phosphate balance nationally and by region in Japan. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 86, 69–77 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-009-9274-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-009-9274-7